Supplementary Text - Austin Publishing Group
... directly or indirectly slowing down the aggregation processes. Thus these genes could suppress formation of mutant HTT aggregates and are considered to be “suppressor” of aggregates formed by mutant HTT. On the basis of functional categorization, these proteins belong to broad functional classes lik ...
... directly or indirectly slowing down the aggregation processes. Thus these genes could suppress formation of mutant HTT aggregates and are considered to be “suppressor” of aggregates formed by mutant HTT. On the basis of functional categorization, these proteins belong to broad functional classes lik ...
Power Point 3 - G. Holmes Braddock
... an individual has two copies of the mutant allele. When just one copy of the mutant allele is present, an individual is a carrier of the mutation, but does not develop the condition. Females and males are affected equally by traits transmitted by autosomal recessive inheritance. When two carriers ma ...
... an individual has two copies of the mutant allele. When just one copy of the mutant allele is present, an individual is a carrier of the mutation, but does not develop the condition. Females and males are affected equally by traits transmitted by autosomal recessive inheritance. When two carriers ma ...
Collect, analyze and synthesize
... compare location of BLASTX result to locate exact first and last base of the exon such that the conserved amino acids are linked together in a single long open reading frame l ...
... compare location of BLASTX result to locate exact first and last base of the exon such that the conserved amino acids are linked together in a single long open reading frame l ...
MCB 421-2006: Homologous Recombination
... stage when two entire genome complements are brought together in a single nucleus of a zygote in preparation for meiosis. So, every chromosome in zygote has its homolog, — an essentially identical chromosome, with a few differences (our “markers”, for example). Zygote can multiply mitotically for so ...
... stage when two entire genome complements are brought together in a single nucleus of a zygote in preparation for meiosis. So, every chromosome in zygote has its homolog, — an essentially identical chromosome, with a few differences (our “markers”, for example). Zygote can multiply mitotically for so ...
Implications of the Human Genome for Understanding Human
... now live in a world in which the 2.9 billion nucleotide codes of the human genome are available as a resource for scientific discovery. Some of the findings from the sequencing of the human genome were expected, confirming knowledge presaged by many decades of research in both human and comparative ...
... now live in a world in which the 2.9 billion nucleotide codes of the human genome are available as a resource for scientific discovery. Some of the findings from the sequencing of the human genome were expected, confirming knowledge presaged by many decades of research in both human and comparative ...
Comprehensive Cardiomyopathy Panel
... Next Generation Sequencing: All coding exons and the flanking 15 bases (splice sites or untranslated regions of the genes listed in the panel, as well as 22 reported non-coding region mutations in DMD, are enriched from the patient’s genomic DNA and sequenced using a solid-state sequencing-by-synthe ...
... Next Generation Sequencing: All coding exons and the flanking 15 bases (splice sites or untranslated regions of the genes listed in the panel, as well as 22 reported non-coding region mutations in DMD, are enriched from the patient’s genomic DNA and sequenced using a solid-state sequencing-by-synthe ...
in trans
... Estimates vary: - Brem et al papers: ~25% traits explained by local polymorphs - other studies say close to 100% - Many MORE individual genes explained by distant polymorphs * but because many link to same loci, there are fewer distantly acting loci ...
... Estimates vary: - Brem et al papers: ~25% traits explained by local polymorphs - other studies say close to 100% - Many MORE individual genes explained by distant polymorphs * but because many link to same loci, there are fewer distantly acting loci ...
View - Max-Planck
... (HH3-21; Hamburger and Hamilton 1951) probing with the 1784-bp BamHI cDNA fragment. In situ hybridization and histology of whole embryos was performed as described, except that specimens from all stages were treated with proteinase K (Pera and Kessel 1997; Stein and Kessel 1995; Lemaire et al. 1997) ...
... (HH3-21; Hamburger and Hamilton 1951) probing with the 1784-bp BamHI cDNA fragment. In situ hybridization and histology of whole embryos was performed as described, except that specimens from all stages were treated with proteinase K (Pera and Kessel 1997; Stein and Kessel 1995; Lemaire et al. 1997) ...
Extending Mendelian Genetics
... In mammals, the expression of sex-linked genes in females is also different from the way in which genes on other chromosomes are expressed. In each cell of female mammals, one of the two X chromosomes is randomly “turned off ” by a process called X chromosome inactivation. Because of X chromosome ...
... In mammals, the expression of sex-linked genes in females is also different from the way in which genes on other chromosomes are expressed. In each cell of female mammals, one of the two X chromosomes is randomly “turned off ” by a process called X chromosome inactivation. Because of X chromosome ...
MGA 8/e Chapter 12
... 19. There are no restriction fragments on the autoradiogram. The fragments are on the filter (nitrocellulose, nylon) used to blot the gel. The radioactivity of the probes is captured by the X-ray film as it decays, producing an exposed region of film. 20. YACs B, D, and E hybridize to one fragment, ...
... 19. There are no restriction fragments on the autoradiogram. The fragments are on the filter (nitrocellulose, nylon) used to blot the gel. The radioactivity of the probes is captured by the X-ray film as it decays, producing an exposed region of film. 20. YACs B, D, and E hybridize to one fragment, ...
Human Cytomegalovirus UL34 Early and late Proteins Are Essential
... 2.1. Both UL34 Proteins Are Essential for Viral Replication Yu et al. [4] and Dunn et al. [3] identified UL34 as essential for viral replication in their global analyses of the HCMV genome. We extended their results by constructing and studying recombinant viruses using the bacterial artificial chro ...
... 2.1. Both UL34 Proteins Are Essential for Viral Replication Yu et al. [4] and Dunn et al. [3] identified UL34 as essential for viral replication in their global analyses of the HCMV genome. We extended their results by constructing and studying recombinant viruses using the bacterial artificial chro ...
Foundations of Biology
... Men have only one X chromosome and they are normal (at least they think so) Women have two X chromosomes and they are normal Mary Lyon proposed that the extra dosage of X chromosome that women have is compensated for by turning off one of the X chromosomes. This turned off chromosome can be ...
... Men have only one X chromosome and they are normal (at least they think so) Women have two X chromosomes and they are normal Mary Lyon proposed that the extra dosage of X chromosome that women have is compensated for by turning off one of the X chromosomes. This turned off chromosome can be ...
SMN1 - IS MU
... (b) In patients with FSHD, the chromatin structure of D4Z4 adopts a more open configuration (open springs and open circles) leading to inefficient transcriptional repression (black arrows) of the D4Z4 repeat. (c) The DUX4 gene is located within each D4Z4 unit. On permissive chromosomes, the last cop ...
... (b) In patients with FSHD, the chromatin structure of D4Z4 adopts a more open configuration (open springs and open circles) leading to inefficient transcriptional repression (black arrows) of the D4Z4 repeat. (c) The DUX4 gene is located within each D4Z4 unit. On permissive chromosomes, the last cop ...
File
... 1. Concept: How did Mendel solve the problem of offspring ending up with double sets of alleles – two from each parent? ...
... 1. Concept: How did Mendel solve the problem of offspring ending up with double sets of alleles – two from each parent? ...
Life-Span-Development-1st-edition
... “reptilian phase” was ultimately rejected, but Darwin’s central concept that change is the result of interaction with the environment remains a powerful contemporary developmental principle. Stem cells are primitive, undifferentiated “pre-cells” found in large numbers in an embryo and appear to illu ...
... “reptilian phase” was ultimately rejected, but Darwin’s central concept that change is the result of interaction with the environment remains a powerful contemporary developmental principle. Stem cells are primitive, undifferentiated “pre-cells” found in large numbers in an embryo and appear to illu ...
3-08-10geneticdisordersmeiosis
... represent a cell undergoing meiosis. On the last set of four circles. Refer to page 500 2. Use modeling clay to form 2 pairs of chromosomes about as thick as a pencil. Make one pair longer than the other. ...
... represent a cell undergoing meiosis. On the last set of four circles. Refer to page 500 2. Use modeling clay to form 2 pairs of chromosomes about as thick as a pencil. Make one pair longer than the other. ...
genetic disorders and hereditary disorders
... forms of the disease, the red blood cells change shape, usually looking much like that of a banana, upon deoxygenation because of polymerization of the abnormal sickle haemoglobin (haemoglobin precipitates into long crystals inside the cell making it sickle shaped rather than the normal biconcave ...
... forms of the disease, the red blood cells change shape, usually looking much like that of a banana, upon deoxygenation because of polymerization of the abnormal sickle haemoglobin (haemoglobin precipitates into long crystals inside the cell making it sickle shaped rather than the normal biconcave ...
Relationship of Gene Expression and Chromosomal Abnormalities in Colorectal Cancer
... chromosomal locations and coordinated alterations in DNA copy number and transcription levels were revealed at specific positions. We show that across many large regions of the genome, changes in expression level are correlated with alterations in DNA content. Often, large chromosomal segments, cont ...
... chromosomal locations and coordinated alterations in DNA copy number and transcription levels were revealed at specific positions. We show that across many large regions of the genome, changes in expression level are correlated with alterations in DNA content. Often, large chromosomal segments, cont ...
See Fig. 13.1c
... mobilize large pieces of DNA and integrate large pieces of foreign DNA behind a promoter so that they are easily transcribed… ...
... mobilize large pieces of DNA and integrate large pieces of foreign DNA behind a promoter so that they are easily transcribed… ...
Problem Set 2
... chromosomes, one long and one short. Simple genetic analysis indicates that the gene (R) that specifies the red spots is located on the long chromosome, and a gene (L) that specifies body length resides on the short chromosome. A. Show the products at the beginning of G1 phase of a single mitosis of ...
... chromosomes, one long and one short. Simple genetic analysis indicates that the gene (R) that specifies the red spots is located on the long chromosome, and a gene (L) that specifies body length resides on the short chromosome. A. Show the products at the beginning of G1 phase of a single mitosis of ...
PowerPoint
... amyliod proteins in their brains • These proteins are associated with Alzheimers • The chance of a person with Trisomy 21 developing Alzheimer’s disease is 25% compared to 6% in the general population ...
... amyliod proteins in their brains • These proteins are associated with Alzheimers • The chance of a person with Trisomy 21 developing Alzheimer’s disease is 25% compared to 6% in the general population ...
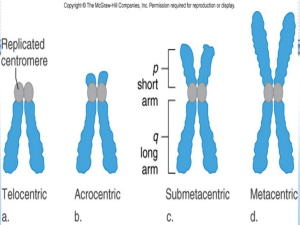
Section D - Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Chromosome Structure
... These sequences often contain self-complementary regions which can form stem-loop or hairpin structure, some need rho protein as accessory factor. ...
... These sequences often contain self-complementary regions which can form stem-loop or hairpin structure, some need rho protein as accessory factor. ...