CHAPTER 2 - ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN DEVELOPMENT
... 2.18. What is the biochemical makeup of an individual called? a. genotype c. gene locus b. heredity d. phenotype a, factual, easy, p. 49 2.19. A mother and a father have four children (biological not adopted). All four children have blue eyes. Which of the following statements must be true? a. Each ...
... 2.18. What is the biochemical makeup of an individual called? a. genotype c. gene locus b. heredity d. phenotype a, factual, easy, p. 49 2.19. A mother and a father have four children (biological not adopted). All four children have blue eyes. Which of the following statements must be true? a. Each ...
2006a Tests of parallel molecular evolution in a long
... mutations of unknown effect in one population (34), with the pattern observed in many other genes that were chosen completely at random (35). Here, we use the idea of ‘‘candidate gene’’ to mean only that a mutational substitution was previously found in that gene in one population, not that the gene ...
... mutations of unknown effect in one population (34), with the pattern observed in many other genes that were chosen completely at random (35). Here, we use the idea of ‘‘candidate gene’’ to mean only that a mutational substitution was previously found in that gene in one population, not that the gene ...
Recombinases
... integrase-bound attL and attR sites. Because these phages can also excise from their integrated state, the recombinases must be able to catalyze attL°øattR recombination. φRv1 encodes an Xis protein (and the other phages are expected to do so too), and Xis not only enables the φRv1 integrase to prom ...
... integrase-bound attL and attR sites. Because these phages can also excise from their integrated state, the recombinases must be able to catalyze attL°øattR recombination. φRv1 encodes an Xis protein (and the other phages are expected to do so too), and Xis not only enables the φRv1 integrase to prom ...
xxZx*x
... Nondisjunction refers to an error in cell division. In some cases, homologous chromosomes do not separate from each other during cell division. In other cases, the problem occurs when slsfer chromatids do not separate from each other. Nondisjunction can occur in mitosis or meiosis. If nondisjunction ...
... Nondisjunction refers to an error in cell division. In some cases, homologous chromosomes do not separate from each other during cell division. In other cases, the problem occurs when slsfer chromatids do not separate from each other. Nondisjunction can occur in mitosis or meiosis. If nondisjunction ...
Chapter 1 - Online Open Genetics
... A mutation is a change in nucleotide sequence. including regulating the expression of other genes. This Chapter 11 goes into more detail of what this means. expression of genes leads to how an organism looks – its What’s important now is that you understand that the phenotype. amino acids of a prote ...
... A mutation is a change in nucleotide sequence. including regulating the expression of other genes. This Chapter 11 goes into more detail of what this means. expression of genes leads to how an organism looks – its What’s important now is that you understand that the phenotype. amino acids of a prote ...
Unequal Crossing Over Locus by KIR Cutting Edge: Expansion of the
... sequencing, and segregation analysis of KIR genes in the family indicated that two known alleles of both KIR2DL4 (X97229, AF034773) and KIR3DL1/S1 (AF262969, AF022044) segregated on the c haplotype, whereas a single distinct allele of each of these loci segregated on each of the a, b, and d haplotyp ...
... sequencing, and segregation analysis of KIR genes in the family indicated that two known alleles of both KIR2DL4 (X97229, AF034773) and KIR3DL1/S1 (AF262969, AF022044) segregated on the c haplotype, whereas a single distinct allele of each of these loci segregated on each of the a, b, and d haplotyp ...
The Classical Genetic Switch in Lambda Phage- Lysis and
... In order to understand how switching happens between the lysis and lysogeny states in the lambda phage, we focus on two regulatory genes CI and cro and a regulatory region OR called the right operator as shown in Fig 3. During the lysogeny phase CI is switched ON and cro is OFF. The operator OR is c ...
... In order to understand how switching happens between the lysis and lysogeny states in the lambda phage, we focus on two regulatory genes CI and cro and a regulatory region OR called the right operator as shown in Fig 3. During the lysogeny phase CI is switched ON and cro is OFF. The operator OR is c ...
(a) (b)
... chromosomes in each cell is randomly inactivated during embryonic development • The inactive X condenses into a Barr body • If a female is heterozygous for a particular gene located on the X chromosome, she will be a mosaic for that character ...
... chromosomes in each cell is randomly inactivated during embryonic development • The inactive X condenses into a Barr body • If a female is heterozygous for a particular gene located on the X chromosome, she will be a mosaic for that character ...
Human-Genetics-Concepts-and-Applications-9E
... to which a gene is transcribed and translated, producing protein. D. gene expression refers to changes in the DNA sequence, whereas mutation refers to the processes of DNA replication, RNA transcription, and protein synthesis. E. mutations occur in RNA and gene expression affects DNA. ...
... to which a gene is transcribed and translated, producing protein. D. gene expression refers to changes in the DNA sequence, whereas mutation refers to the processes of DNA replication, RNA transcription, and protein synthesis. E. mutations occur in RNA and gene expression affects DNA. ...
03 Mode of Iheritance-20-10
... – The hybrid F1 plants, each of which has one gene for tallness and one for shortness, would be referred to as heterozygous. – The genes responsible for these contrasting characteristics are referred to as allelomorphs, or alleles for short. ...
... – The hybrid F1 plants, each of which has one gene for tallness and one for shortness, would be referred to as heterozygous. – The genes responsible for these contrasting characteristics are referred to as allelomorphs, or alleles for short. ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... they understood right away how DNA could be copied. All a cell had to do was to separate the two strands and then use base pairing to make a new complementary strand for each. But the structure of DNA by itself did not explain how a gene actually works. That question required a great deal more resea ...
... they understood right away how DNA could be copied. All a cell had to do was to separate the two strands and then use base pairing to make a new complementary strand for each. But the structure of DNA by itself did not explain how a gene actually works. That question required a great deal more resea ...
J Biol Chem, v 275, pp 12237-12242
... libraries (13–15). The 175-kDa protein product is post-translationally cleaved to form disulfide-linked ␣2 and ␦ peptides, both of which are heavily glycosylated. Biochemical and mutation analysis supports a single transmembrane domain in the ␦ subunit that anchors the ␣2␦ protein to the membrane (1 ...
... libraries (13–15). The 175-kDa protein product is post-translationally cleaved to form disulfide-linked ␣2 and ␦ peptides, both of which are heavily glycosylated. Biochemical and mutation analysis supports a single transmembrane domain in the ␦ subunit that anchors the ␣2␦ protein to the membrane (1 ...
Genome-wide DNA replication profile for
... genes, however, reside in β-heterochromatin, which, unlike the centromeric α-heterochromatin, does not possess highly repetitive DNA and has a euchromatin-like gene density13. Thus, the various forms of D. melanogaster heterochromatin differ in several respects, including replication timing. Regions ...
... genes, however, reside in β-heterochromatin, which, unlike the centromeric α-heterochromatin, does not possess highly repetitive DNA and has a euchromatin-like gene density13. Thus, the various forms of D. melanogaster heterochromatin differ in several respects, including replication timing. Regions ...
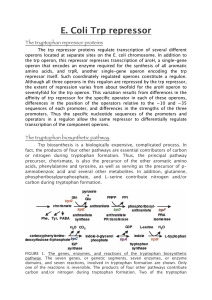
The tryptophan biosynthetic pathway
... biologically essential compounds, i.e., niacin in most eukaryotes, indoleacetic acid in most plants, and indole in many bacteria. Thus the regulatory strategies designed for the genes of tryptophan biosynthesis of each organism have had to be compatible with other metabolic objectives. ...
... biologically essential compounds, i.e., niacin in most eukaryotes, indoleacetic acid in most plants, and indole in many bacteria. Thus the regulatory strategies designed for the genes of tryptophan biosynthesis of each organism have had to be compatible with other metabolic objectives. ...
BI321F12 Review Lecture 01 Model organisms etc
... • Genetic material is usually DNA, a double helix of complementary polynucleotides. • Genes are segments of DNA encoding the amino acid sequence of proteins. • The DNA of a (eukaryotic) cell is broken up into a series of (usually) linear pieces complexed with proteins – these are the chromosomes. • ...
... • Genetic material is usually DNA, a double helix of complementary polynucleotides. • Genes are segments of DNA encoding the amino acid sequence of proteins. • The DNA of a (eukaryotic) cell is broken up into a series of (usually) linear pieces complexed with proteins – these are the chromosomes. • ...
Supporting information for “Dynamics of cell
... auxin treatment. Correspondingly, treated plants show reduced levels of Z type cytokinins, whereas the levels of iPtype cytokinins are less affected. ...
... auxin treatment. Correspondingly, treated plants show reduced levels of Z type cytokinins, whereas the levels of iPtype cytokinins are less affected. ...
... certain amino acids known as “opines”. The infected plant’s cells are forced to synthesize opines, which are not catabolized by the plant, as a source of energy for Agrobacterium. Auxins and cytokinins cause the infected plant’s cells to divide. TDNA is transferred into the plant’s cells and finally ...
Cytogenetics Cytogenetics
... sequentially within each. Sub-bands are catered for by using a decimal system ...
... sequentially within each. Sub-bands are catered for by using a decimal system ...
SF 106 year 1 report 2010
... instance, the database has been searched for candidate genes related to fruit softening to be used in objective 3.1. ...
... instance, the database has been searched for candidate genes related to fruit softening to be used in objective 3.1. ...
Tobacco TTG2 regulates vegetative growth and seed production via
... which harbors the gene encoding red-fluorescent protein (RFP), resembles the WT in terms of vegetative growth, seed production, and related physiological responses such as floral anthocyanin synthesis and flower colorization [19]. In contrast, growth and development are greatly enhanced in NtTTG2-ov ...
... which harbors the gene encoding red-fluorescent protein (RFP), resembles the WT in terms of vegetative growth, seed production, and related physiological responses such as floral anthocyanin synthesis and flower colorization [19]. In contrast, growth and development are greatly enhanced in NtTTG2-ov ...
Modified `one amino acid-one codon` engineering of high GC
... obtain adequate expression levels, which is especially important for industrial enzyme production processes. Natural REase-coding genes found in wild-type (wt) organisms are often not highly expressed, due to the ‘toxicity’ of their protein product to their hosts, if not fully protected by cognate M ...
... obtain adequate expression levels, which is especially important for industrial enzyme production processes. Natural REase-coding genes found in wild-type (wt) organisms are often not highly expressed, due to the ‘toxicity’ of their protein product to their hosts, if not fully protected by cognate M ...