Lecture 9 - PIV, Filters and Multiple Diodes
... Calculate the transformer turns ratio and the PIV voltages for each type of the full wave rectifier a) center-tapped b) bridge Assume the input voltage of the transformer is 220 V (rms), 50 Hz from AC main line source. The desired peak output voltage is 9 volt; also assume diodes cut-in voltage = 0. ...
... Calculate the transformer turns ratio and the PIV voltages for each type of the full wave rectifier a) center-tapped b) bridge Assume the input voltage of the transformer is 220 V (rms), 50 Hz from AC main line source. The desired peak output voltage is 9 volt; also assume diodes cut-in voltage = 0. ...
335-project2 - UTK-EECS
... kHz (midband) with an output signal level of 5 V peak-peak. Follow the schematic shown in figure 1. (b) The power supply voltage is to be +15 V DC and maximum quiescent power supply current is 5 mA. The output signal as observed on the oscilloscope must show no evidence of severe distortion (clippin ...
... kHz (midband) with an output signal level of 5 V peak-peak. Follow the schematic shown in figure 1. (b) The power supply voltage is to be +15 V DC and maximum quiescent power supply current is 5 mA. The output signal as observed on the oscilloscope must show no evidence of severe distortion (clippin ...
Document
... able to operate with extremely low dc capacitance values. The theoretical limit is calculated for the maximum capacitor voltage ripple, and hence minimum dc capacitance values that can be used in the converter. The proposed low-capacitance StatCom (LC-StatCom) is able to operate with large capacitor ...
... able to operate with extremely low dc capacitance values. The theoretical limit is calculated for the maximum capacitor voltage ripple, and hence minimum dc capacitance values that can be used in the converter. The proposed low-capacitance StatCom (LC-StatCom) is able to operate with large capacitor ...
Chapter 36 Summary – Magnetism
... (electrons, branches) which move more easily on a (conductor, insulator) than they do on a (conductor, insulator). A negatively charged object has (fewer, more) electrons than a neutral object. Current, which is the flow of (voltage, charge), flows from (high, low) voltage to (high, low) voltage. Th ...
... (electrons, branches) which move more easily on a (conductor, insulator) than they do on a (conductor, insulator). A negatively charged object has (fewer, more) electrons than a neutral object. Current, which is the flow of (voltage, charge), flows from (high, low) voltage to (high, low) voltage. Th ...
ROHM Stepper Motor Drivers
... a 12 to 76V input, 3A variable output voltage, DC/DC Buck converter with integrated 76V MOSFET optimized for high power (high voltage x large current) applications such as motors, factory automation equipment, communications infrastructure, and industrial machinery. In recent years, with the increas ...
... a 12 to 76V input, 3A variable output voltage, DC/DC Buck converter with integrated 76V MOSFET optimized for high power (high voltage x large current) applications such as motors, factory automation equipment, communications infrastructure, and industrial machinery. In recent years, with the increas ...
ppt - MakeItOrTakeIt
... connected to ground. • The output of this comparator will be logic high (i.e., supply voltage) if the noninverting terminal input is greater than the inverting terminal input of the comparator. • If the inverting terminal input is greater than the non-inverting terminal input then the output of the ...
... connected to ground. • The output of this comparator will be logic high (i.e., supply voltage) if the noninverting terminal input is greater than the inverting terminal input of the comparator. • If the inverting terminal input is greater than the non-inverting terminal input then the output of the ...
latch_up - WordPress.com
... in a bulk CMOS technology. When a chip is in a state of latch – up it draws a large current from the power supply but does not function in response to input stimuli. A chip may be operating normally and then enter a state of latch-up; in this case , removing and reconnecting the power supply may res ...
... in a bulk CMOS technology. When a chip is in a state of latch – up it draws a large current from the power supply but does not function in response to input stimuli. A chip may be operating normally and then enter a state of latch-up; in this case , removing and reconnecting the power supply may res ...
SOT-723 Plastic-Encapsulate Diodes 5V0AT7 CESDLC
... ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (Ta= 25°C unless otherwise noted, VF = 0.9 V Max. @ IF = 10mA for all types) ...
... ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (Ta= 25°C unless otherwise noted, VF = 0.9 V Max. @ IF = 10mA for all types) ...
Diodes and Bridge Rectifiers - Electrical and Computer Engineering
... Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Experiment No. 3 - Diodes and Bridge Rectifiers Overview: The purpose of this experiment is to introduce diode rectifier circuits used in DC power supplies. Almost all electronic systems require at least one DC power supply that converts AC line volt ...
... Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Experiment No. 3 - Diodes and Bridge Rectifiers Overview: The purpose of this experiment is to introduce diode rectifier circuits used in DC power supplies. Almost all electronic systems require at least one DC power supply that converts AC line volt ...
Ferroresonant Single Phase Charger – Micro ARE-M
... For 24 and 48-volt models, the filtering provided produces a ripple level of less than 30 millivolts rms with electrical noise less than 22 dBrnc measured on a battery with an eight-hour capacity rating of four times the rectifier current rating. For 130-volt models, the filtering provided produces ...
... For 24 and 48-volt models, the filtering provided produces a ripple level of less than 30 millivolts rms with electrical noise less than 22 dBrnc measured on a battery with an eight-hour capacity rating of four times the rectifier current rating. For 130-volt models, the filtering provided produces ...
BSMJ series self-healing LV Shunt capacitors
... a. Novel in structure,light in weight It is produced with Zinc-and-aluminum metallized polypropylene film as the medium so the dimension and the weight is respectively only the 1/4 and 1/5 of the old. b. Low loss Because the actual value is less then 0.12%,energy loss of the capacitor itself is few, ...
... a. Novel in structure,light in weight It is produced with Zinc-and-aluminum metallized polypropylene film as the medium so the dimension and the weight is respectively only the 1/4 and 1/5 of the old. b. Low loss Because the actual value is less then 0.12%,energy loss of the capacitor itself is few, ...
1) Complete each sentence using an appropriate phrase from this
... The transformer steps dow n the AC mains voltage ...
... The transformer steps dow n the AC mains voltage ...
DN130 - Power Supplies for Subscriber Line Interface Circuits
... regulation, lowers the voltage rating required on the output capacitors and lowers the RMS currents, allowing the use of cheaper output capacitors. Either the – 23.8V output or the – 71.5V output can be at full load without effecting the other corresponding output. The circuit’s step response is ver ...
... regulation, lowers the voltage rating required on the output capacitors and lowers the RMS currents, allowing the use of cheaper output capacitors. Either the – 23.8V output or the – 71.5V output can be at full load without effecting the other corresponding output. The circuit’s step response is ver ...
Transistor Switch and Emitter Follower Phys 3610/6610 Lab 18 Student: TA:
... from 1 above? What happens to the output voltage under these load conditions? Would AC coupling between the switch output and the load help to increase the voltage drop across the load? Check experimentally what voltage drop can be obtained. What capacitor value would be needed to keep the voltage w ...
... from 1 above? What happens to the output voltage under these load conditions? Would AC coupling between the switch output and the load help to increase the voltage drop across the load? Check experimentally what voltage drop can be obtained. What capacitor value would be needed to keep the voltage w ...
CN-0009 利用AD5662 DAC实现4 mA至20 mA过程控制环路
... range (3.49 mA to 20.9 mA) allows the user to calibrate the 4 mA to 20 mA range by using software and the 16-bit resolution of the AD5662. The Schottky diode is required in this circuit to prevent loop supply power-on transients from pulling the noninverting input of the AD8627 more than 300 mV belo ...
... range (3.49 mA to 20.9 mA) allows the user to calibrate the 4 mA to 20 mA range by using software and the 16-bit resolution of the AD5662. The Schottky diode is required in this circuit to prevent loop supply power-on transients from pulling the noninverting input of the AD8627 more than 300 mV belo ...
Rectifier

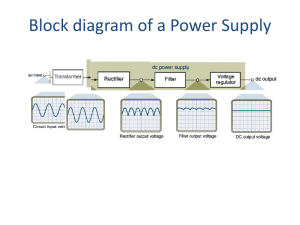
A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current (AC), which periodically reverses direction, to direct current (DC), which flows in only one direction. The process is known as rectification. Physically, rectifiers take a number of forms, including vacuum tube diodes, mercury-arc valves, copper and selenium oxide rectifiers, semiconductor diodes, silicon-controlled rectifiers and other silicon-based semiconductor switches. Historically, even synchronous electromechanical switches and motors have been used. Early radio receivers, called crystal radios, used a ""cat's whisker"" of fine wire pressing on a crystal of galena (lead sulfide) to serve as a point-contact rectifier or ""crystal detector"".Rectifiers have many uses, but are often found serving as components of DC power supplies and high-voltage direct current power transmission systems. Rectification may serve in roles other than to generate direct current for use as a source of power. As noted, detectors of radio signals serve as rectifiers. In gas heating systems flame rectification is used to detect presence of a flame.Because of the alternating nature of the input AC sine wave, the process of rectification alone produces a DC current that, though unidirectional, consists of pulses of current. Many applications of rectifiers, such as power supplies for radio, television and computer equipment, require a steady constant DC current (as would be produced by a battery). In these applications the output of the rectifier is smoothed by an electronic filter (usually a capacitor) to produce a steady current.More complex circuitry that performs the opposite function, converting DC to AC, is called an inverter.