weekly progress report
... mg (corresponding to −150 mV) in the X-axis, 500 mg (or 150 mV) on the Y-axis, and −200 mg (or −60 mV) on the Z-axis. This ST pin may be left open circuit or connected to common (COM) in normal use. Never expose the ST pin to volatges greater than VS + 0.3 V. If this cannot be guaranteed due to the ...
... mg (corresponding to −150 mV) in the X-axis, 500 mg (or 150 mV) on the Y-axis, and −200 mg (or −60 mV) on the Z-axis. This ST pin may be left open circuit or connected to common (COM) in normal use. Never expose the ST pin to volatges greater than VS + 0.3 V. If this cannot be guaranteed due to the ...
ONEAC CDR Series Power Conditioners: The CDR series for mid
... • Convenience outlets: allows other equipment to take advantage of ONEAC’s clean power output and single ground. • ISO 9001 design & manufacturing, with 5 year warranty: highest assurance of consistent product quality and reliability in the industry. • International approvals: GS, UL, c-UL, and CE p ...
... • Convenience outlets: allows other equipment to take advantage of ONEAC’s clean power output and single ground. • ISO 9001 design & manufacturing, with 5 year warranty: highest assurance of consistent product quality and reliability in the industry. • International approvals: GS, UL, c-UL, and CE p ...
Vatten & Avlopp-arkiv
... transmitter circuit from the processing circuit and prevents linked measurement circuits from influencing each other. The Protective Separation with high isolation level provides protection for personnel and downstream devices against impermissibly high voltage. The transmitter repeater is short cir ...
... transmitter circuit from the processing circuit and prevents linked measurement circuits from influencing each other. The Protective Separation with high isolation level provides protection for personnel and downstream devices against impermissibly high voltage. The transmitter repeater is short cir ...
Harmonic Analysis of 6-Pulse and 12-Pulse Converter Models
... century, but it was inefficient due to the power loss in conductors. Alternating current (AC) offered much better efficiency, since it could easily be transformed to higher voltages, with far less loss of power. AC technology was soon accepted as the only feasible technology for generation, transmis ...
... century, but it was inefficient due to the power loss in conductors. Alternating current (AC) offered much better efficiency, since it could easily be transformed to higher voltages, with far less loss of power. AC technology was soon accepted as the only feasible technology for generation, transmis ...
A 24 Vin, 40 Watt, Low Cost, DC-to-DC Converter
... amp output version. Other output voltages from 3.3 up to 28 Vdc are easy to implement by modifying the values (or ratings) of R8, R11, R12, C9, D5 and T1’s secondary turns. ...
... amp output version. Other output voltages from 3.3 up to 28 Vdc are easy to implement by modifying the values (or ratings) of R8, R11, R12, C9, D5 and T1’s secondary turns. ...
2A. Two similar inductive coils with negligible resistance are wound
... 3A. Analytically derive the phasor relationship between voltage and current in a pure inductor. Hence show that average power consumed by the inductor is zero. Draw the waveform showing voltage, current and power. ...
... 3A. Analytically derive the phasor relationship between voltage and current in a pure inductor. Hence show that average power consumed by the inductor is zero. Draw the waveform showing voltage, current and power. ...
TRANSIENT RESPONSE OF A WIND ENERGY CONVERSION
... simultaneously as an active filter and power generator. This study is intended to address the system response to two types of transient phenomena: voltage dips (fast transients) and wind speed variations (slow transients). The system response to voltage dips is governed by the electrical system dyna ...
... simultaneously as an active filter and power generator. This study is intended to address the system response to two types of transient phenomena: voltage dips (fast transients) and wind speed variations (slow transients). The system response to voltage dips is governed by the electrical system dyna ...
DESIGN, FABRICATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF A PIEZOELECTRIC
... load capacitor as well as the maximum instantaneous power versus input acceleration value. The output voltage does not increase linearly with the input acceleration and reaches almost 2V for 2g excitation. The maximum instantaneous power of charging of the capacitor was calculated from temporal vari ...
... load capacitor as well as the maximum instantaneous power versus input acceleration value. The output voltage does not increase linearly with the input acceleration and reaches almost 2V for 2g excitation. The maximum instantaneous power of charging of the capacitor was calculated from temporal vari ...
LA5744TP - ON Semiconductor
... 1. C3 is for the soft start function. Delete C3 and keep the SS pin open when the soft start function is not necessary. 2. In some cases, the output may not turn on if power is applied when a load is connected. If this is a problem, increase the value of the inductor. ...
... 1. C3 is for the soft start function. Delete C3 and keep the SS pin open when the soft start function is not necessary. 2. In some cases, the output may not turn on if power is applied when a load is connected. If this is a problem, increase the value of the inductor. ...
uninterruptible power supplies
... Classification according to EN/IEC 62040-3: VFI SS-111 The individual components are matched to each other and controlled by different microprocessors. The rectifier converts the mains voltage into a DC voltage, from which the subsequent connected inverter forms a regulated, sinusoidal alternating v ...
... Classification according to EN/IEC 62040-3: VFI SS-111 The individual components are matched to each other and controlled by different microprocessors. The rectifier converts the mains voltage into a DC voltage, from which the subsequent connected inverter forms a regulated, sinusoidal alternating v ...
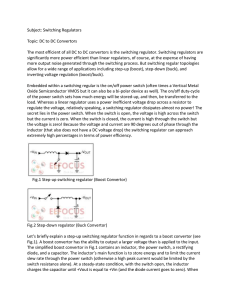
Subject: Switching Regulators Topic: DC to DC Convertors The most
... This switching regulator uses a MOSFET transistor as the power switching device. It has an on board oscillator which sets the switching frequency with a single external capacitor for 350 kHz (typical operation). The output can switch up to 2A with current limit and thermal shutdown capability. Overa ...
... This switching regulator uses a MOSFET transistor as the power switching device. It has an on board oscillator which sets the switching frequency with a single external capacitor for 350 kHz (typical operation). The output can switch up to 2A with current limit and thermal shutdown capability. Overa ...
CDR - UCF EECS
... Measure and report power consumed by each device plugged into an outlet Give users the ability to set goals that can be met during a month or longer period Forecast power consumption and turn off offending devices (with permission) that will prevent the user from reaching previously set goals Accura ...
... Measure and report power consumed by each device plugged into an outlet Give users the ability to set goals that can be met during a month or longer period Forecast power consumption and turn off offending devices (with permission) that will prevent the user from reaching previously set goals Accura ...
CN-0027 利用AD5547/AD5557 DAC实现精密、单极性、同相配置
... (Continued from first page) "Circuits from the Lab" are intended only for use with Analog Devices products and are the intellectual property of Analog Devices or its licensors. While you may use the "Circuits from the Lab" in the design of your product, no other license is granted by implication or ...
... (Continued from first page) "Circuits from the Lab" are intended only for use with Analog Devices products and are the intellectual property of Analog Devices or its licensors. While you may use the "Circuits from the Lab" in the design of your product, no other license is granted by implication or ...
Rectifier

A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current (AC), which periodically reverses direction, to direct current (DC), which flows in only one direction. The process is known as rectification. Physically, rectifiers take a number of forms, including vacuum tube diodes, mercury-arc valves, copper and selenium oxide rectifiers, semiconductor diodes, silicon-controlled rectifiers and other silicon-based semiconductor switches. Historically, even synchronous electromechanical switches and motors have been used. Early radio receivers, called crystal radios, used a ""cat's whisker"" of fine wire pressing on a crystal of galena (lead sulfide) to serve as a point-contact rectifier or ""crystal detector"".Rectifiers have many uses, but are often found serving as components of DC power supplies and high-voltage direct current power transmission systems. Rectification may serve in roles other than to generate direct current for use as a source of power. As noted, detectors of radio signals serve as rectifiers. In gas heating systems flame rectification is used to detect presence of a flame.Because of the alternating nature of the input AC sine wave, the process of rectification alone produces a DC current that, though unidirectional, consists of pulses of current. Many applications of rectifiers, such as power supplies for radio, television and computer equipment, require a steady constant DC current (as would be produced by a battery). In these applications the output of the rectifier is smoothed by an electronic filter (usually a capacitor) to produce a steady current.More complex circuitry that performs the opposite function, converting DC to AC, is called an inverter.