Answers to Biological Inquiry Questions – Brooker et al ARIS site
... ANSWER: Retroelements. A single element can be transcribed into multiple copies of RNA, which can be converted to DNA by reverse transcriptase, and inserted into multiple sites in the genome. Figure 21.8 BIOLOGICAL INQUIRY QUESTION: What is the advantage of a gene family? ANSWER: The overall advanta ...
... ANSWER: Retroelements. A single element can be transcribed into multiple copies of RNA, which can be converted to DNA by reverse transcriptase, and inserted into multiple sites in the genome. Figure 21.8 BIOLOGICAL INQUIRY QUESTION: What is the advantage of a gene family? ANSWER: The overall advanta ...
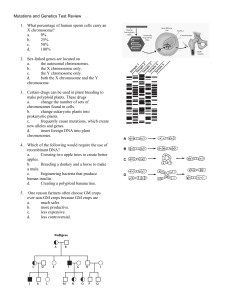
Mutations and Genetics Test Review 1. What percentage of human
... Mutations and Genetics Test Review 1. What percentage of human sperm cells carry an X chromosome? a. ...
... Mutations and Genetics Test Review 1. What percentage of human sperm cells carry an X chromosome? a. ...
Chapter 5
... Gene conversion between multiple copies allows the active genes to be maintained during evolution. ...
... Gene conversion between multiple copies allows the active genes to be maintained during evolution. ...
Genetic Test Study Guide
... 19. State and describe the 3 methods for developing organisms with desirable traits. a. Selective Breeding-selecting organisms with desired traits to be parents of the next genereation b. Cloning-producing organisms that have exactly the same genes as another organism c. Genetic Engineering-genetic ...
... 19. State and describe the 3 methods for developing organisms with desirable traits. a. Selective Breeding-selecting organisms with desired traits to be parents of the next genereation b. Cloning-producing organisms that have exactly the same genes as another organism c. Genetic Engineering-genetic ...
EGL Exome Coverage Tool
... EGL Exome Coverage Tool This tool can be used to view typical depth of sequence coverage obtained by exome sequencing performed by our laboratory. These data were calculated based on approximately 30 samples processed using our exome pipeline. An individual base is considered to have high coverage i ...
... EGL Exome Coverage Tool This tool can be used to view typical depth of sequence coverage obtained by exome sequencing performed by our laboratory. These data were calculated based on approximately 30 samples processed using our exome pipeline. An individual base is considered to have high coverage i ...
Human Genome Project
... completion of a “working draft” DNA sequence (90%) of the human genome By 2003 ...
... completion of a “working draft” DNA sequence (90%) of the human genome By 2003 ...
Genetics of Sex - University of San Francisco
... Y significantly smaller than X, few genes shared between the two In the Y chromosome, the shutting down of X–Y crossing over during evolution triggered a monotonic decline in gene function PAR1 homology maintained by recombination in male meiosis, genes in this region not subject to dosage compensat ...
... Y significantly smaller than X, few genes shared between the two In the Y chromosome, the shutting down of X–Y crossing over during evolution triggered a monotonic decline in gene function PAR1 homology maintained by recombination in male meiosis, genes in this region not subject to dosage compensat ...
Gene linkage and Gene maps
... Offspring _ b+bvg+vg bbvgvg b+bvgvg bbvg+vg since Morgan’s results show that both of the nonparental pheonotypes were also produced, Morgan suggested that body color and wing size genes are only partially linked genetically Genetic Recombination When the offspring’s pheonotypes do not match the pare ...
... Offspring _ b+bvg+vg bbvgvg b+bvgvg bbvg+vg since Morgan’s results show that both of the nonparental pheonotypes were also produced, Morgan suggested that body color and wing size genes are only partially linked genetically Genetic Recombination When the offspring’s pheonotypes do not match the pare ...
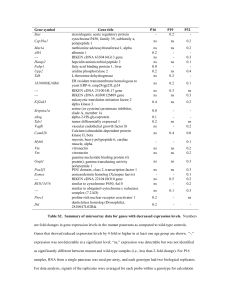
Table S2. Summary of microarray data for genes with decreased
... “Present” in at least one array out of a total of 4 arrays were selected for further analyses, and those with ratios ≤ 0.5 or ≥ 2.0 were considered as differentially expressed genes at a significant level. For P19 and P32 experiments, cDNA sample was similarly generated from total pancreatic RNA (10 ...
... “Present” in at least one array out of a total of 4 arrays were selected for further analyses, and those with ratios ≤ 0.5 or ≥ 2.0 were considered as differentially expressed genes at a significant level. For P19 and P32 experiments, cDNA sample was similarly generated from total pancreatic RNA (10 ...
Unit 3.4 Inheritance
... 4. The specific position on a homologous chromosome of a gene ___________________________ 5. Having two different alleles at a locus ______________________________ 6. A heritable factor that controls a specific characteristic. ________________________________ 7. The characteristic on an organism. __ ...
... 4. The specific position on a homologous chromosome of a gene ___________________________ 5. Having two different alleles at a locus ______________________________ 6. A heritable factor that controls a specific characteristic. ________________________________ 7. The characteristic on an organism. __ ...
Congenital And Genetic Disorders
... DNA is copied from generation to generation by a process called semiconservative replication This is a highly accurate process Even so, occasionally, a copy error occurs resulting in a mutation Mutations can arise by other processes DNA “code” is transcribed to RNA and then translated into protein s ...
... DNA is copied from generation to generation by a process called semiconservative replication This is a highly accurate process Even so, occasionally, a copy error occurs resulting in a mutation Mutations can arise by other processes DNA “code” is transcribed to RNA and then translated into protein s ...
1) Give a brief explanation and examples of: Incomplete dominance
... and Human Genetic Disorders on pgs. 125 – 132 Write and Answer: ...
... and Human Genetic Disorders on pgs. 125 – 132 Write and Answer: ...
Epigenet-web
... 2. an observed to expected CpG dinucleotide ratio of 0.60 or greater 3. and both occurring within a sequence window of 200 bp or greater. CpGs are vastly underrepresented genome-wide compared to what would be expected by chance (0.23 in the human genome and 0.19 in the mouse genome, respectively) Th ...
... 2. an observed to expected CpG dinucleotide ratio of 0.60 or greater 3. and both occurring within a sequence window of 200 bp or greater. CpGs are vastly underrepresented genome-wide compared to what would be expected by chance (0.23 in the human genome and 0.19 in the mouse genome, respectively) Th ...
Name_______________________ Period
... What is a Barr body? Why do human females show a Barr body in their cells? ...
... What is a Barr body? Why do human females show a Barr body in their cells? ...
Slide 1
... -2 alleles contribute to the phenotype -Result: Having 2 dominant alleles will result in a phenotype expressing both alleles (not blending) Multiple alleles -More than 2 alleles for a gene Result: More combinations of genotypes and phenotypes ...
... -2 alleles contribute to the phenotype -Result: Having 2 dominant alleles will result in a phenotype expressing both alleles (not blending) Multiple alleles -More than 2 alleles for a gene Result: More combinations of genotypes and phenotypes ...
Lecture 7 – PDF
... Multiple sex chromosomes (generally sex chromosome-autosome translocations) C. Sex linkage and sex-linked genes: 1. Genes on X but not on Y -- leads to a “criss-cross” pattern of inheritance where sons receive their X chromosome from the maternal parent and daughters receive an X from both ...
... Multiple sex chromosomes (generally sex chromosome-autosome translocations) C. Sex linkage and sex-linked genes: 1. Genes on X but not on Y -- leads to a “criss-cross” pattern of inheritance where sons receive their X chromosome from the maternal parent and daughters receive an X from both ...
Binary Switches in Gene Expression: The Histone Code
... human genome exists within every cell, only a small percentage of genes are activated in any given cell type. These different gene expression profiles are formulated during early development in a multicellular organism, when cell division, cell differentiation, tissue and organ formation rapidly occ ...
... human genome exists within every cell, only a small percentage of genes are activated in any given cell type. These different gene expression profiles are formulated during early development in a multicellular organism, when cell division, cell differentiation, tissue and organ formation rapidly occ ...
Genetics Challenge Name 1. The abbreviation for deoxyribonucleic
... 8. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ are rod-shaped structures found in the nucleus of every cell in an organism. ...
... 8. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ are rod-shaped structures found in the nucleus of every cell in an organism. ...
Concept Check Questions with answers
... •All three genes have very similar sequences in the control elements of their enhancers •That way, the same specific transcription factors can bind to all three ...
... •All three genes have very similar sequences in the control elements of their enhancers •That way, the same specific transcription factors can bind to all three ...
No Slide Title
... • Only 94 of the 1262 InterPro types (7%) are vertebrate-specific - so most domains are older than common ancestor of all animals - new ones are not “invented” very often • Many of these are concerned with defence/immunity and the nervous system • Most novelty is generated by new protein “architectu ...
... • Only 94 of the 1262 InterPro types (7%) are vertebrate-specific - so most domains are older than common ancestor of all animals - new ones are not “invented” very often • Many of these are concerned with defence/immunity and the nervous system • Most novelty is generated by new protein “architectu ...
• father of Genetics • Austrian monk who studied ______ and
... • __________________________ - The failure of a chromosome pair to separate during meiosis. • Body (somatic) cells may have more or less than normal amount of chromosomes, usually lethal. • __________________________________________: An extra chromosome (trisomy) on the 21st chromosome. • Have va ...
... • __________________________ - The failure of a chromosome pair to separate during meiosis. • Body (somatic) cells may have more or less than normal amount of chromosomes, usually lethal. • __________________________________________: An extra chromosome (trisomy) on the 21st chromosome. • Have va ...
The effects of Fndc5 overexpression on characteristics of mouse
... Fndc5 formerly known as peroxisomal protein, is suggested to be a PGC1-alpha-dependent myokine and is secreted as Irisin , responsible for browning of white fat tissues. In adult mouse, mRNA expression level of Fndc5 is high in heart, skeletal muscle and brain. Our previous studies have revealed a s ...
... Fndc5 formerly known as peroxisomal protein, is suggested to be a PGC1-alpha-dependent myokine and is secreted as Irisin , responsible for browning of white fat tissues. In adult mouse, mRNA expression level of Fndc5 is high in heart, skeletal muscle and brain. Our previous studies have revealed a s ...
PSYC 2314 Chapter 3
... • X-linked Genes: genes that are on the X chromosome. – If an X-linked gene is recessive—as are the genes for most forms of color-blindness, many allergies, several diseases, and some learning disabilities—the fact that it is on the X chromosome is critical. ...
... • X-linked Genes: genes that are on the X chromosome. – If an X-linked gene is recessive—as are the genes for most forms of color-blindness, many allergies, several diseases, and some learning disabilities—the fact that it is on the X chromosome is critical. ...