Limb Development: Hox Genes
... for normal formation of the mammalian heart) through alterations in gene expression (Chauzaud et al, 1999. Development 126: 2589-2596). For an excellent review of the development of the vertebrate heart see Fishman and Chien, 1997. Development 124: 2099-2117. While retinoic acid has specific effects ...
... for normal formation of the mammalian heart) through alterations in gene expression (Chauzaud et al, 1999. Development 126: 2589-2596). For an excellent review of the development of the vertebrate heart see Fishman and Chien, 1997. Development 124: 2099-2117. While retinoic acid has specific effects ...
Ch - Ranger College
... - recombination frequency data used to make chromosome maps – where genes are located on the chromosome - through evolutionary time alleles of genes that work well together came to be close together on chromosome Sex-link genes – if sex is determine by sex chromosomes Sex determination ...
... - recombination frequency data used to make chromosome maps – where genes are located on the chromosome - through evolutionary time alleles of genes that work well together came to be close together on chromosome Sex-link genes – if sex is determine by sex chromosomes Sex determination ...
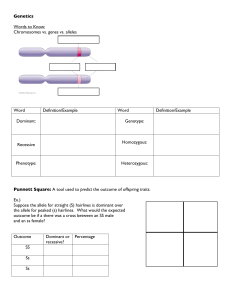
Genetics Vocabulary Spring 2011
... • The 23rd pair of paired chromsomes in an human somatic cell (The 1-22 pair are referred to as AUTOSOMES). • The sex chromsomes may be X or Y ; human males all have a 23rd pair that is XY, females are XX ...
... • The 23rd pair of paired chromsomes in an human somatic cell (The 1-22 pair are referred to as AUTOSOMES). • The sex chromsomes may be X or Y ; human males all have a 23rd pair that is XY, females are XX ...
8.2 Alleles and Genes Interact to Produce Phenotypes
... 8.2 Alleles and Genes Interact to Produce Phenotypes AP Biology Radjewski ...
... 8.2 Alleles and Genes Interact to Produce Phenotypes AP Biology Radjewski ...
No Slide Title
... 1. They will display the characteristic described by the dominant allele, a characteristic from a recessive allele is not expressed (e.g. blue eyes). 2. The offspring will show the effects of both alleles and will display a characteristic that is intermediate between those of offspring who are h ...
... 1. They will display the characteristic described by the dominant allele, a characteristic from a recessive allele is not expressed (e.g. blue eyes). 2. The offspring will show the effects of both alleles and will display a characteristic that is intermediate between those of offspring who are h ...
Gene Name
... not be affected by a small number of differentially expressed genes (eg. the Xchromosome genes or other sex-specific genes in our study). The array contains over 15K cDNA sets therefore we can assume overall autosomal gene expression is equal between female and male mouse tissue and ES cells (or emb ...
... not be affected by a small number of differentially expressed genes (eg. the Xchromosome genes or other sex-specific genes in our study). The array contains over 15K cDNA sets therefore we can assume overall autosomal gene expression is equal between female and male mouse tissue and ES cells (or emb ...
Red Line - iPlant Pods
... – 19 students used Red Line to visualize next-gen RNA-Seq data to investigate presence/absence variation (PAV) in maize – 12 hours effort, each student group annotated 100 kb and then imported next-gen RNA-Seq data from 5 different tissues in 30 maize inbred lines for a gene that they had previously ...
... – 19 students used Red Line to visualize next-gen RNA-Seq data to investigate presence/absence variation (PAV) in maize – 12 hours effort, each student group annotated 100 kb and then imported next-gen RNA-Seq data from 5 different tissues in 30 maize inbred lines for a gene that they had previously ...
BIOL/GEN 313_Wksht_032416
... A geneticist isolates two mutations in a bacteriophage. One mutation causes clear plaques (c), and the other produces minute plaques (m). Previous mapping experiments have established that the genes responsible for these two mutations are 8 m.u. apart. The geneticist mixes phages with genotype c+ m+ ...
... A geneticist isolates two mutations in a bacteriophage. One mutation causes clear plaques (c), and the other produces minute plaques (m). Previous mapping experiments have established that the genes responsible for these two mutations are 8 m.u. apart. The geneticist mixes phages with genotype c+ m+ ...
Document
... • Annotations for all organisms are still buggy • Few genes are 100% correct; expect multiple errors per gene • Most organisms’ gene annotations are probably much worse than for humans ...
... • Annotations for all organisms are still buggy • Few genes are 100% correct; expect multiple errors per gene • Most organisms’ gene annotations are probably much worse than for humans ...
Chapter 3-1 • Definitions: - Genetics: the scientific study of heredity
... - Purebred: an organism that always produces offspring with the same form of a trait as the parent - Gene: factor that controls traits - Allele: different forms of a gene - Dominant Allele: its trait always shows when the allele is present - Recessive Allele: is masked by the dominant allele - Hybri ...
... - Purebred: an organism that always produces offspring with the same form of a trait as the parent - Gene: factor that controls traits - Allele: different forms of a gene - Dominant Allele: its trait always shows when the allele is present - Recessive Allele: is masked by the dominant allele - Hybri ...
MENDELIAN INHERITANCE
... genes are located on gonosoms which Mendelian principle is broken? which condition is broken? 1) complete sex-linked - genes are located on heterologous regions of sex chromosome (crossing-over is impossible) 2) incomplete sex-linked - genes are located on homologous (pseudoautosomal) regions of ...
... genes are located on gonosoms which Mendelian principle is broken? which condition is broken? 1) complete sex-linked - genes are located on heterologous regions of sex chromosome (crossing-over is impossible) 2) incomplete sex-linked - genes are located on homologous (pseudoautosomal) regions of ...
Honors BIOLOGY
... males get only one X chromosome (always from mom), if that gene is faulty then there is no allele on the Y to override it and the male is affected. Because females get two X’s, they have two chances to be normal. Sex-linked genotypes always use the XX or XY sex genotypes “carrying” the linked trait ...
... males get only one X chromosome (always from mom), if that gene is faulty then there is no allele on the Y to override it and the male is affected. Because females get two X’s, they have two chances to be normal. Sex-linked genotypes always use the XX or XY sex genotypes “carrying” the linked trait ...
11-1 The Work of Mendel
... • Probability of head 3 times in a row = ½ x ½ x ½ = _____ • The ________ the number or trials, the closer to the expected ratio • _______ outcomes do not affect _______ outcomes • Alleles segregate randomly (like a coin) ...
... • Probability of head 3 times in a row = ½ x ½ x ½ = _____ • The ________ the number or trials, the closer to the expected ratio • _______ outcomes do not affect _______ outcomes • Alleles segregate randomly (like a coin) ...
Genetic determination of diseases
... due to the process during 1st meiotic division = crossing-over and recombination thus alleles originally coming from different grandparents can appear in one ...
... due to the process during 1st meiotic division = crossing-over and recombination thus alleles originally coming from different grandparents can appear in one ...
What happens to the repressor when lactose is present?
... sequence is found directly before the RNA Polymerase starting point for __________________. This region is known as the TATA _______ Box ...
... sequence is found directly before the RNA Polymerase starting point for __________________. This region is known as the TATA _______ Box ...
X-Linked Recessive Inheritance
... Cytoplasmic inheritance follows the pattern of inheritance of mitochondria or chloroplasts In genomic imprinting, the allele inherited from one of the parents is expressed while the other allele is silent ...
... Cytoplasmic inheritance follows the pattern of inheritance of mitochondria or chloroplasts In genomic imprinting, the allele inherited from one of the parents is expressed while the other allele is silent ...
Heredity
... • Chromosomes are made up of many genes joined together like beads on a string. • The chromosomes in a pair may have different alleles for some genes and the same allele for others. ...
... • Chromosomes are made up of many genes joined together like beads on a string. • The chromosomes in a pair may have different alleles for some genes and the same allele for others. ...
Estimating the Number of Mouse Genes and the Duplicated Regions
... genome and to measure the degree of redundancy in the genome in various species. The number of human protein-coding genes was recently estimated as 35,000-40,000, though it is still controversial. Also, traces of ancient duplications of extensive chromosomal regions were being discovered within the ...
... genome and to measure the degree of redundancy in the genome in various species. The number of human protein-coding genes was recently estimated as 35,000-40,000, though it is still controversial. Also, traces of ancient duplications of extensive chromosomal regions were being discovered within the ...
Heredity and the Environment
... • Mitosis—Exact replication of 22 non-sex linked chromosomes (autosomes) • Meiosis—When sex cells (egg & sperm) replicate, genetic material is shuffled and each chromosome has 23 single stranded chromosomes; when sperm and egg unite, there is a unique pairing of chromosomes, thus genetic diversity i ...
... • Mitosis—Exact replication of 22 non-sex linked chromosomes (autosomes) • Meiosis—When sex cells (egg & sperm) replicate, genetic material is shuffled and each chromosome has 23 single stranded chromosomes; when sperm and egg unite, there is a unique pairing of chromosomes, thus genetic diversity i ...