G030163-03 - DCC
... Only visible in gravitational radiation Strong field gravity and fast motion Rich (unknown) waveforms for black hole plunge and merger ...
... Only visible in gravitational radiation Strong field gravity and fast motion Rich (unknown) waveforms for black hole plunge and merger ...
Life Before the Fall: Group Galaxy Evolution Prior to Cluster Assembly
... Comparison with properties of both local clusters (Coma) and CL 1358 (z=0.33) ...
... Comparison with properties of both local clusters (Coma) and CL 1358 (z=0.33) ...
PowerPoint Presentation - 18. The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard
... The idea is that matter under the influence of an intense gravitational field loses energy and releases enormous quantities of radiation in the process. Just as water goes over Niagara Falls, losing its potential energy while providing us with power to drive electric generators, so can material fall ...
... The idea is that matter under the influence of an intense gravitational field loses energy and releases enormous quantities of radiation in the process. Just as water goes over Niagara Falls, losing its potential energy while providing us with power to drive electric generators, so can material fall ...
the magellanic clouds newsletter - Keele University Astrophysics
... age distribution of the LMC Cepheids is found to have a peak at log Age = 8.2 ± 0.1. This suggests that major star formation event took place at about 125–200 Myr ago which may have been triggered by a close encounter between the SMC and the LMC. Cepheids are found to be asymmetrically distributed t ...
... age distribution of the LMC Cepheids is found to have a peak at log Age = 8.2 ± 0.1. This suggests that major star formation event took place at about 125–200 Myr ago which may have been triggered by a close encounter between the SMC and the LMC. Cepheids are found to be asymmetrically distributed t ...
ppt
... Measurements of - or upper limits on - the stellar continuum constrains the IMF Sources expected to cover a range of metallicity from Z ~ 0 to 10-3 ...
... Measurements of - or upper limits on - the stellar continuum constrains the IMF Sources expected to cover a range of metallicity from Z ~ 0 to 10-3 ...
astrocoursespring2012lec2-6
... Continuous radiation viewed through a low density gas results in an absorption-line spectrum. What's happening here is that radiation emitted by gas under high pressure deep within the star is being absorbed by low density gas in the star's outer layers. We can show this in the lab: Using a slit and ...
... Continuous radiation viewed through a low density gas results in an absorption-line spectrum. What's happening here is that radiation emitted by gas under high pressure deep within the star is being absorbed by low density gas in the star's outer layers. We can show this in the lab: Using a slit and ...
Galactic sources science with AGILE The case of the Carina Region
... variable Galactic sources since it hosts massive star forming regions, star clusters, young hot stars and a wealth of spectacular nebular structures. An extremely peculiar system in the region and one of the most interesting objects of our Galaxy is the Z Carinae binary [5,6], where the primary star ...
... variable Galactic sources since it hosts massive star forming regions, star clusters, young hot stars and a wealth of spectacular nebular structures. An extremely peculiar system in the region and one of the most interesting objects of our Galaxy is the Z Carinae binary [5,6], where the primary star ...
3 The lives of galaxies
... galaxies, rotation velocity starts off low and rises as you Figure 29: Measuring rotation from the move outwards, then it flattens off and stays flat out to very Doppler shift of spectral features. large distances from the centre. Is this what we expect ? Types of rotation curve. (1) A solid body, r ...
... galaxies, rotation velocity starts off low and rises as you Figure 29: Measuring rotation from the move outwards, then it flattens off and stays flat out to very Doppler shift of spectral features. large distances from the centre. Is this what we expect ? Types of rotation curve. (1) A solid body, r ...
Neutron stars - Institut de Physique Nucleaire de Lyon
... Theory before the discovery T.E.Sterne (1933) – first model EOS (equation of state) of nuclear matter; prediction of the neutronization with increasing density. F.Zwicky [“On collapsed neutron stars,” Astrophys. J. 88 (1938) 522] – estimate of the maximum binding energy of a neutron star; – diffe ...
... Theory before the discovery T.E.Sterne (1933) – first model EOS (equation of state) of nuclear matter; prediction of the neutronization with increasing density. F.Zwicky [“On collapsed neutron stars,” Astrophys. J. 88 (1938) 522] – estimate of the maximum binding energy of a neutron star; – diffe ...
Sardinia_SA - Mullard Space Science Laboratory
... • The form of the spectral energy distribution, and particularly the relationship between the direct component of emission (X-ray thermal bremsstrahlung + cyclotron) and the reprocessed component been the topic of much debate. ...
... • The form of the spectral energy distribution, and particularly the relationship between the direct component of emission (X-ray thermal bremsstrahlung + cyclotron) and the reprocessed component been the topic of much debate. ...
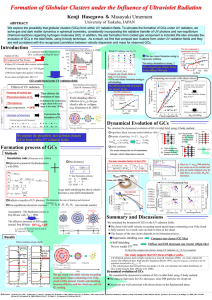
Poster - unist
... We explore the possibility that globular clusters (GCs) form within UV radiation fields. To simulate the formation of GCs under UV radiation, we solve gas and dark matter dynamics in spherical symmetry, consistently incorporating the radiative transfer of UV photons and non-equilibrium chemical reac ...
... We explore the possibility that globular clusters (GCs) form within UV radiation fields. To simulate the formation of GCs under UV radiation, we solve gas and dark matter dynamics in spherical symmetry, consistently incorporating the radiative transfer of UV photons and non-equilibrium chemical reac ...
systems - Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics
... sufficiently far away and a variable red source at the dynamical center of the galaxy could unambiguously be identified (Genzel et al. 2003; Ghez et al. 2004, see also Fig. 1). Ever since its discovery it was claimed that Sgr A*’s variability is accompanied by a quasiperiodicity (QPO) of ∼20 min. Ho ...
... sufficiently far away and a variable red source at the dynamical center of the galaxy could unambiguously be identified (Genzel et al. 2003; Ghez et al. 2004, see also Fig. 1). Ever since its discovery it was claimed that Sgr A*’s variability is accompanied by a quasiperiodicity (QPO) of ∼20 min. Ho ...
22. The Milky Way Galaxy
... Composition unknown. Probably mostly exotic particles that don't interact with ordinary matter at all (except gravity). Some may be brown dwarfs, cold white dwarfs … Most likely it's a dark halo surrounding the Milky Way. Or we need a new theory of gravity. ...
... Composition unknown. Probably mostly exotic particles that don't interact with ordinary matter at all (except gravity). Some may be brown dwarfs, cold white dwarfs … Most likely it's a dark halo surrounding the Milky Way. Or we need a new theory of gravity. ...
The Most Massive LMC Star Sk
... formed together. The fainter components (c-f) are probably early-type 0 250-1,000 MG' Cassinelli et al. (1981) stars, as the formation of low mass stars from the IUE data concluded that R 136 a is a single supermassive star of needs a longer time scale. This may be a general trend of massive star fo ...
... formed together. The fainter components (c-f) are probably early-type 0 250-1,000 MG' Cassinelli et al. (1981) stars, as the formation of low mass stars from the IUE data concluded that R 136 a is a single supermassive star of needs a longer time scale. This may be a general trend of massive star fo ...
presentation source
... (right) shows about 50 small, bright, young globular clusters formed as a result of the collision. NGC 1275 is also a strong source of X rays and radio waves ...
... (right) shows about 50 small, bright, young globular clusters formed as a result of the collision. NGC 1275 is also a strong source of X rays and radio waves ...
A systematic study of X-ray variability in the ROSAT all
... Key words. surveys – X-rays: general – stars: activity – stars: flares ...
... Key words. surveys – X-rays: general – stars: activity – stars: flares ...
What does the EUV and thin film group do?
... http://wave.xray.mpe.mpg.de/roentgen/roentgen-1.gif ...
... http://wave.xray.mpe.mpg.de/roentgen/roentgen-1.gif ...
The brightest ULIRG: watching the birth of a quasar
... In the early 1980’s, the IRAS satellite discovered a number of unexpectedly bright far-infrared (FIR) sources. A number of groups around the world (Aaronson & Olszewski 1984; Houck et al. 1985; Allen et al. 1985) quickly found that they were at high redshifts, and thus of enormous total luminosity, ...
... In the early 1980’s, the IRAS satellite discovered a number of unexpectedly bright far-infrared (FIR) sources. A number of groups around the world (Aaronson & Olszewski 1984; Houck et al. 1985; Allen et al. 1985) quickly found that they were at high redshifts, and thus of enormous total luminosity, ...
Lecture 26 Pre-Main Sequence Evolution
... Completely embedded objects have SEDs with positive spectral index in the far-IR: the youngest sources emit the bulk of their energy in the sub-mm & mm ...
... Completely embedded objects have SEDs with positive spectral index in the far-IR: the youngest sources emit the bulk of their energy in the sub-mm & mm ...
Age patterns in a sample of spiral galaxies
... The most common SF diagnostics use far ultra-violet (FUV), far-infrared (FIR), or nebular recombination lines [15]. UV emission is mainly dominated by O-B type stars, with lifetimes . 108 yr [13, 15]. In contrast, the Hα line is strong only in the presence of the most massive, hot O stars (masses > ...
... The most common SF diagnostics use far ultra-violet (FUV), far-infrared (FIR), or nebular recombination lines [15]. UV emission is mainly dominated by O-B type stars, with lifetimes . 108 yr [13, 15]. In contrast, the Hα line is strong only in the presence of the most massive, hot O stars (masses > ...
arXiv:1502.04693v1 [gr
... As confusion with lensing B-modes begins to limit experiments that search for primordial B-mode polarization, robust methods for delensing the CMB polarization sky are becoming increasingly important. We investigate in detail the possibility of delensing the CMB with the cosmic infrared background ( ...
... As confusion with lensing B-modes begins to limit experiments that search for primordial B-mode polarization, robust methods for delensing the CMB polarization sky are becoming increasingly important. We investigate in detail the possibility of delensing the CMB with the cosmic infrared background ( ...
Dark Matter Search
... • In early March, the LAT skywatchers found a new, flaring gamma-ray source in the Cygnus region. ...
... • In early March, the LAT skywatchers found a new, flaring gamma-ray source in the Cygnus region. ...
Astrophysical X-ray source

Astrophysical X-ray sources are astronomical objects with physical properties which result in the emission of X-rays.There are a number of types of astrophysical objects which emit X-rays, from galaxy clusters, through black holes in active galactic nuclei (AGN) to galactic objects such as supernova remnants, stars, and binary stars containing a white dwarf (cataclysmic variable stars and super soft X-ray sources), neutron star or black hole (X-ray binaries). Some solar system bodies emit X-rays, the most notable being the Moon, although most of the X-ray brightness of the Moon arises from reflected solar X-rays. A combination of many unresolved X-ray sources is thought to produce the observed X-ray background. The X-ray continuum can arise from bremsstrahlung, either magnetic or ordinary Coulomb, black-body radiation, synchrotron radiation, inverse Compton scattering of lower-energy photons be relativistic electrons, knock-on collisions of fast protons with atomic electrons, and atomic recombination, with or without additional electron transitions.Furthermore, celestial entities in space are discussed as celestial X-ray sources. The origin of all observed astronomical X-ray sources is in, near to, or associated with a coronal cloud or gas at coronal cloud temperatures for however long or brief a period.