Applications of Doppler Effect: A stationary microphone records
... where vs is the velocity of the object (source of waves) with respect to the medium, and is the angle between the object's forward velocity and the line of sight from the object to the observer. Astronomy Redshift of spectral lines in theoptical spectrum of a supercluster of distant galaxies (right ...
... where vs is the velocity of the object (source of waves) with respect to the medium, and is the angle between the object's forward velocity and the line of sight from the object to the observer. Astronomy Redshift of spectral lines in theoptical spectrum of a supercluster of distant galaxies (right ...
Lab 9
... Objective: To demonstrate the classification of galaxies and to use a rational expression to figure out the distances to galaxies using redshift. The large-scale structure of the universe is governed by gravity. The Sun orbits the center of our galaxy, the Milky Way. The Milky Way, in turn, orbits t ...
... Objective: To demonstrate the classification of galaxies and to use a rational expression to figure out the distances to galaxies using redshift. The large-scale structure of the universe is governed by gravity. The Sun orbits the center of our galaxy, the Milky Way. The Milky Way, in turn, orbits t ...
1P04.pdf
... observational cosmology. We systematically explore which filter systems are optimal for estimating redshifts, and briefly introduce the ALHAMBRA survey, which will use a close-to-optimal filter set to obtain accurate estimates of redshifts and spectral types for several hundred thousand galaxies. fo ...
... observational cosmology. We systematically explore which filter systems are optimal for estimating redshifts, and briefly introduce the ALHAMBRA survey, which will use a close-to-optimal filter set to obtain accurate estimates of redshifts and spectral types for several hundred thousand galaxies. fo ...
ODU booklet 2 Teachers booklet Sept 2014 (7.5MB Word)
... Observations 1 and 2 are possible, but observation 3 is not because you cannot exceed the speed of light. ...
... Observations 1 and 2 are possible, but observation 3 is not because you cannot exceed the speed of light. ...
The Island Universe of Immanuel Kant - EU-HOU
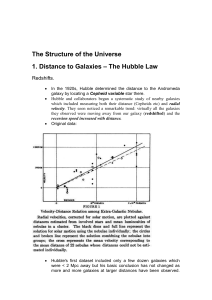
... much farther galaxies could be measured. As can be easily noticed in the previous slide (right panel), Hubble law works very well: velocity/distance ratio remains constant in a wide range of these two quantities, particularly for more distant galaxies where the proper motions velocities become negli ...
... much farther galaxies could be measured. As can be easily noticed in the previous slide (right panel), Hubble law works very well: velocity/distance ratio remains constant in a wide range of these two quantities, particularly for more distant galaxies where the proper motions velocities become negli ...
5.9MB Word - Clydeview Academy
... Observations 1 and 2 are possible, but observation 3 is not because you cannot exceed the speed of light. ...
... Observations 1 and 2 are possible, but observation 3 is not because you cannot exceed the speed of light. ...
MSL Electromagnetic Spectrum
... Doppler Effect Summary Motion toward or away from an observer causes a shift in the observed wavelength of light: • blueshift (shorter wavelength) motion toward you ...
... Doppler Effect Summary Motion toward or away from an observer causes a shift in the observed wavelength of light: • blueshift (shorter wavelength) motion toward you ...
Light: The Cosmic Messenger
... 26 April 2007, L-3 Communications, Waco Texas: SOFIA takes to the air for its first test flight after completion of modifications ...
... 26 April 2007, L-3 Communications, Waco Texas: SOFIA takes to the air for its first test flight after completion of modifications ...
– 1 – 1. Feedback From The First Stars
... by gas or dust, and hence GRBs should in principle be detected from the reionization era. Furthermore GRBs at maximum are very luminous, and their intrinsic emission, ignoring absorption from the IGM, is featureless, unlike QSOs. This requires an X-ray satellite to detect the GRB, ideally something ...
... by gas or dust, and hence GRBs should in principle be detected from the reionization era. Furthermore GRBs at maximum are very luminous, and their intrinsic emission, ignoring absorption from the IGM, is featureless, unlike QSOs. This requires an X-ray satellite to detect the GRB, ideally something ...
SISSA lect 1 28/02/11 and 03/03/11 - INAF
... 1 – Linear theory + Press & Schechter: simple tool to get abundance of collapsed haloes at any redshift 2- Sheth & Tormen and other fitting N-body based formulae Importance of describing the number of haloes at high redshift as a potentially ...
... 1 – Linear theory + Press & Schechter: simple tool to get abundance of collapsed haloes at any redshift 2- Sheth & Tormen and other fitting N-body based formulae Importance of describing the number of haloes at high redshift as a potentially ...
MB mirror - Institute of Astronomy
... headquarter of NAOC, and its main workforce distributed in the Nanjing Institute of Astronomical Optics and Technology /NAOC in Nanjing, the Beijing part of NAOC and in the University of Science and Technology of China in Hefei. The project has its board and scientific and technical committee as usu ...
... headquarter of NAOC, and its main workforce distributed in the Nanjing Institute of Astronomical Optics and Technology /NAOC in Nanjing, the Beijing part of NAOC and in the University of Science and Technology of China in Hefei. The project has its board and scientific and technical committee as usu ...
Calculating Distance
... This gives you the angle of a right triangle, you already know the opposite side (distance to the Sun), so the distance to the star can be calculated (1 AU / tanq). Because the angle gets extremely small to measure farther and farther stars, distance can only be determined out to about 150 ly (the n ...
... This gives you the angle of a right triangle, you already know the opposite side (distance to the Sun), so the distance to the star can be calculated (1 AU / tanq). Because the angle gets extremely small to measure farther and farther stars, distance can only be determined out to about 150 ly (the n ...
Redshift
In physics, redshift happens when light or other electromagnetic radiation from an object is increased in wavelength, or shifted to the red end of the spectrum. In general, whether or not the radiation is within the visible spectrum, ""redder"" means an increase in wavelength – equivalent to a lower frequency and a lower photon energy, in accordance with, respectively, the wave and quantum theories of light.Some redshifts are an example of the Doppler effect, familiar in the change of apparent pitches of sirens and frequency of the sound waves emitted by speeding vehicles. A redshift occurs whenever a light source moves away from an observer. Another kind of redshift is cosmological redshift, which is due to the expansion of the universe, and sufficiently distant light sources (generally more than a few million light years away) show redshift corresponding to the rate of increase in their distance from Earth. Finally, gravitational redshift is a relativistic effect observed in electromagnetic radiation moving out of gravitational fields. Conversely, a decrease in wavelength is called blueshift and is generally seen when a light-emitting object moves toward an observer or when electromagnetic radiation moves into a gravitational field. However, redshift is a more common term and sometimes blueshift is referred to as negative redshift.Knowledge of redshifts and blueshifts has been applied to develop several terrestrial technologies such as Doppler radar and radar guns. Redshifts are also seen in the spectroscopic observations of astronomical objects. Its value is represented by the letter z.A special relativistic redshift formula (and its classical approximation) can be used to calculate the redshift of a nearby object when spacetime is flat. However, in many contexts, such as black holes and Big Bang cosmology, redshifts must be calculated using general relativity. Special relativistic, gravitational, and cosmological redshifts can be understood under the umbrella of frame transformation laws. There exist other physical processes that can lead to a shift in the frequency of electromagnetic radiation, including scattering and optical effects; however, the resulting changes are distinguishable from true redshift and are not generally referred to as such (see section on physical optics and radiative transfer).