(Traditional) estimators based on gene frequencies
... as the group of single migration parameter models with two or n islands, stepping stone models, and multi-parameter models such as the migration matrix model. In this lecture I will concentrate on approaches using gene frequencies, and will neglect complicating evolutionary forces such as selection ...
... as the group of single migration parameter models with two or n islands, stepping stone models, and multi-parameter models such as the migration matrix model. In this lecture I will concentrate on approaches using gene frequencies, and will neglect complicating evolutionary forces such as selection ...
Chapter 14: Mendel and the Gene Idea
... • Mendel developed a hypothesis to explain the 3:1 inheritance pattern he observed in F2 offspring • Four related concepts make up this model • These concepts can be related to what we now know about genes and chromosomes • The first concept is that ___________________________ of genes account for v ...
... • Mendel developed a hypothesis to explain the 3:1 inheritance pattern he observed in F2 offspring • Four related concepts make up this model • These concepts can be related to what we now know about genes and chromosomes • The first concept is that ___________________________ of genes account for v ...
Mutation analysis of bigH3 gene in patients with corneal dystrophy
... the CYP1B1 gene in the GLC3A locus have been found in about 50% of PCG patients. No genetic locus has been identified for PCAG, but there is a possible site on chromosome 10. For POAG, more than 10 chromosomal loci have been mapped. But there are only 2 confirmed genes, MYOC and OPTN. Over 60 MYOC m ...
... the CYP1B1 gene in the GLC3A locus have been found in about 50% of PCG patients. No genetic locus has been identified for PCAG, but there is a possible site on chromosome 10. For POAG, more than 10 chromosomal loci have been mapped. But there are only 2 confirmed genes, MYOC and OPTN. Over 60 MYOC m ...
Beadle and Tatum 2
... determined during development by an interaction between its genetic make-up (genotype) and the environment. ...
... determined during development by an interaction between its genetic make-up (genotype) and the environment. ...
Diagnostic Genetic Testing of a Potentially Affected Individual
... Request is for Genetic testing for diagnostic purposes Check all that apply to the individual: Individual has symptoms of a genetic disorder Individual is at risk for a late onset genetic disorder or slowly evolving genetic disorder Individual has melanoma (hereditary) Individual has amyotrophic lat ...
... Request is for Genetic testing for diagnostic purposes Check all that apply to the individual: Individual has symptoms of a genetic disorder Individual is at risk for a late onset genetic disorder or slowly evolving genetic disorder Individual has melanoma (hereditary) Individual has amyotrophic lat ...
Chapter 11 Genetics - Duxbury Public Schools
... Describe the basic process of DNA replication and how it relates to the transmission and conservation of the genetic code. Explain the basic processes of transcription and translation, and how they result in the expression of genes. Distinguish among the end products of replication, transcription, a ...
... Describe the basic process of DNA replication and how it relates to the transmission and conservation of the genetic code. Explain the basic processes of transcription and translation, and how they result in the expression of genes. Distinguish among the end products of replication, transcription, a ...
Section 11–3 Exploring Mendelian Genetics
... shape segregate independently of those for seed color? He observed F2 offspring that had combinations of phenotypes—and therefore combinations of alleles—not found in either parent. ...
... shape segregate independently of those for seed color? He observed F2 offspring that had combinations of phenotypes—and therefore combinations of alleles—not found in either parent. ...
BREEDING, GENETICS, AND PHYSIOLOGY Molecular
... germplasm, specifically in the areas of disease resistance and cooking quality. Simple sequence repeat (SSR) and single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers linked to these specific traits are used to predict the cooking quality of milled grain and screen for the presence of rice blast [Magnaportha ...
... germplasm, specifically in the areas of disease resistance and cooking quality. Simple sequence repeat (SSR) and single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers linked to these specific traits are used to predict the cooking quality of milled grain and screen for the presence of rice blast [Magnaportha ...
Mendelian Inheritance
... Chin (C or c) Hairline (W or w) Earlobes (E or e) PTC (T or t) Thumb (B or b) Little Finger (L or l) Mid-Digit Hair (H or h) Dimples (D or d) 3. Choose one of your traits, and use Punnett squares to predict the genotypes of your parents. What are possible combinations that could have given you that ...
... Chin (C or c) Hairline (W or w) Earlobes (E or e) PTC (T or t) Thumb (B or b) Little Finger (L or l) Mid-Digit Hair (H or h) Dimples (D or d) 3. Choose one of your traits, and use Punnett squares to predict the genotypes of your parents. What are possible combinations that could have given you that ...
Mendelian Inheritance
... mild mental retardation, hyperphagia leading to obesity, short stature, and dysmorphic features (21). It is now known that the Prader-Willi syndrome is caused by any mechanism that leads to the loss of the paternal contribution of a gene(s) in the chromosome region of 15ql 1—13. A completely differe ...
... mild mental retardation, hyperphagia leading to obesity, short stature, and dysmorphic features (21). It is now known that the Prader-Willi syndrome is caused by any mechanism that leads to the loss of the paternal contribution of a gene(s) in the chromosome region of 15ql 1—13. A completely differe ...
Task One: Determining Possible Genetic Diseases
... Step 1: Figure out the amino acid sequence for each DNA site. Rewrite the sections of DNA in the space provided: ________________________________________________________________________ Transcribe the section of DNA into mRNA in the space provided: ___________________________________________________ ...
... Step 1: Figure out the amino acid sequence for each DNA site. Rewrite the sections of DNA in the space provided: ________________________________________________________________________ Transcribe the section of DNA into mRNA in the space provided: ___________________________________________________ ...
Gene Conversion in Human Genetic Disease
... Gene conversion refers to the unidirectional transfer of genetic material from a ‘donor’ sequence to a highly homologous ‘acceptor’. It is one of four pathways of homologous recombination, the other three being non-allelic homologous recombination (NAHR), break-induced replication (BIR) and single-s ...
... Gene conversion refers to the unidirectional transfer of genetic material from a ‘donor’ sequence to a highly homologous ‘acceptor’. It is one of four pathways of homologous recombination, the other three being non-allelic homologous recombination (NAHR), break-induced replication (BIR) and single-s ...
AP Biology Practice Exam #1
... a) It produces cells with the haploid number of chromosomes. b) It follows DNA replication. c) It occurs only in reproductive structures. d) It produces four genetically identical gametes. e) It serves as a factor in bringing about variation among offspring. _____19. If 2n=48 for a particular cell, ...
... a) It produces cells with the haploid number of chromosomes. b) It follows DNA replication. c) It occurs only in reproductive structures. d) It produces four genetically identical gametes. e) It serves as a factor in bringing about variation among offspring. _____19. If 2n=48 for a particular cell, ...
Section 11–3 Exploring Mendelian Genetics (pages 270–274)
... shape segregate independently of those for seed color? He observed F2 offspring that had combinations of phenotypes—and therefore combinations of alleles—not found in either parent. ...
... shape segregate independently of those for seed color? He observed F2 offspring that had combinations of phenotypes—and therefore combinations of alleles—not found in either parent. ...
document
... 7. The less differentiated a cancer cell is, the more: A) benign it will be. B) embryonic it will appear. C) similar it will appear to its tissue of origin. D) all of the above. 8. Tumor markers can be found in: A) blood. B) cerebrospinal fluid. C) urine. D) all of the above. 9. Tumor cell markers c ...
... 7. The less differentiated a cancer cell is, the more: A) benign it will be. B) embryonic it will appear. C) similar it will appear to its tissue of origin. D) all of the above. 8. Tumor markers can be found in: A) blood. B) cerebrospinal fluid. C) urine. D) all of the above. 9. Tumor cell markers c ...
14 - BioEYES Assessment Task
... Question One It can be said that an organism’s genetic make-up is a combination of its parents’ DNA and the fact that we inherit 2 copies of each gene in our genome. a. Explain how we receive 2 copies of each gene. You must use the following key terms in your response: chromosomes, fertilization, ho ...
... Question One It can be said that an organism’s genetic make-up is a combination of its parents’ DNA and the fact that we inherit 2 copies of each gene in our genome. a. Explain how we receive 2 copies of each gene. You must use the following key terms in your response: chromosomes, fertilization, ho ...
Did you ever get a message from a friend that was in code
... Crucial during development of a fertilized egg to an organism. b. Cells move from mitosis to differentiate (change) into different cells. c. Important to determine the body plan of an organism. d. Controls the transcription of specific genes at specific times and in specific locations e. One mutatio ...
... Crucial during development of a fertilized egg to an organism. b. Cells move from mitosis to differentiate (change) into different cells. c. Important to determine the body plan of an organism. d. Controls the transcription of specific genes at specific times and in specific locations e. One mutatio ...
Meiosis 1 - Learning on the Loop
... • Understand the process of meiosis • Understand the need to undergo meiosis as sexual organisms – to produce change or variation ...
... • Understand the process of meiosis • Understand the need to undergo meiosis as sexual organisms – to produce change or variation ...
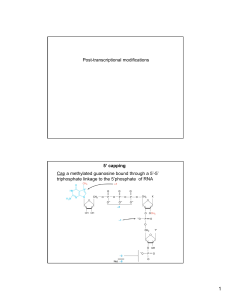
Post-transcriptional modifications Cap a
... move from cell-to-cell or even over long distances in the plant. Several current models hold that silencing signals are “aberrant” RNAs (aRNA), that differ in some way from normal mRNAs. The most likely candidates are small antisense RNAs (asRNA) and double-stranded RNAs (dsRNA). Most current models ...
... move from cell-to-cell or even over long distances in the plant. Several current models hold that silencing signals are “aberrant” RNAs (aRNA), that differ in some way from normal mRNAs. The most likely candidates are small antisense RNAs (asRNA) and double-stranded RNAs (dsRNA). Most current models ...
8 Expression and Modification of Recombinant Proteins
... plasmid and ligated with ligase * New (engineered) plasmid inserted into bacterium (transform) ...
... plasmid and ligated with ligase * New (engineered) plasmid inserted into bacterium (transform) ...
1 - contentextra
... Gene therapy involves replacing a defective gene with an effective gene which will make a correct protein. Genes are delivered to cells by vectors (e.g. a virus). If the vector delivers the gene to a gamete cell, it is germ-line therapy; if the gene is delivered to a body cell, it is somatic therapy ...
... Gene therapy involves replacing a defective gene with an effective gene which will make a correct protein. Genes are delivered to cells by vectors (e.g. a virus). If the vector delivers the gene to a gamete cell, it is germ-line therapy; if the gene is delivered to a body cell, it is somatic therapy ...
Antibody structure : the early studies
... • You have about a trillion different antibodies able to react with millions of different types of Ag • b butt you only l have h about b t 30,000-40,000 30 000 40 000 genes which hi h code d for f all ll the proteins you need in your entire body, most of which are not Ab • so there cannot be one gen ...
... • You have about a trillion different antibodies able to react with millions of different types of Ag • b butt you only l have h about b t 30,000-40,000 30 000 40 000 genes which hi h code d for f all ll the proteins you need in your entire body, most of which are not Ab • so there cannot be one gen ...