lecture12-BW
... Counters the differences between two populations that result from mutation, natural selection, and genetic drift ...
... Counters the differences between two populations that result from mutation, natural selection, and genetic drift ...
slides - University of Colorado-MCDB
... carrier for both diseases? a. 1 (100%) b. 3/4 4 possible genotypes of offspring c. 1/2 only one way to get AaBb, so ¼; d. 1/4 Or, think about it this way: ½ chance of getting Aa x ½ chance of ...
... carrier for both diseases? a. 1 (100%) b. 3/4 4 possible genotypes of offspring c. 1/2 only one way to get AaBb, so ¼; d. 1/4 Or, think about it this way: ½ chance of getting Aa x ½ chance of ...
Question Report - Blue Valley Schools
... 18 In this diagram of chromatin structure, the letter B indicates A histones. B supercoils. C a nucleosome. D a DNA double helix. 19 Which of the following statements about prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic genetic material is FALSE? A Both genomes have introns. B Both genomes consist of a combination of ...
... 18 In this diagram of chromatin structure, the letter B indicates A histones. B supercoils. C a nucleosome. D a DNA double helix. 19 Which of the following statements about prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic genetic material is FALSE? A Both genomes have introns. B Both genomes consist of a combination of ...
BIOL 101 - University of South Carolina
... 7. Identify basic mechanisms of communication within and among cells and describe how they combine to perform a cellular/organismal function 8. Describe the mechanisms and regulation of the molecular and biochemical workings of cells with emphasis on genetic code, cell proliferation, regulation of ...
... 7. Identify basic mechanisms of communication within and among cells and describe how they combine to perform a cellular/organismal function 8. Describe the mechanisms and regulation of the molecular and biochemical workings of cells with emphasis on genetic code, cell proliferation, regulation of ...
Unit 3
... inherited together. Linked genes do not assort independently, because they are on the same chromosome and move together through meiosis and fertilization. Since independent assortment does not occur, a dihybrid cross following two linked genes will not produce an F 2 phenotypic ratio of 9:3:3:1. - E ...
... inherited together. Linked genes do not assort independently, because they are on the same chromosome and move together through meiosis and fertilization. Since independent assortment does not occur, a dihybrid cross following two linked genes will not produce an F 2 phenotypic ratio of 9:3:3:1. - E ...
TRANSPOSABLE ELEMENTS IN BACTERIA Transposable
... (transposase) that catalyses the transposition event. Thus, transposition requires that the IS element carry a promoter recognized by the RNA polymerase of the host cell. Typically the gene for the transposase is the only gene within the element. Molecules of the transposase bind to the ITR sequence ...
... (transposase) that catalyses the transposition event. Thus, transposition requires that the IS element carry a promoter recognized by the RNA polymerase of the host cell. Typically the gene for the transposase is the only gene within the element. Molecules of the transposase bind to the ITR sequence ...
Global Agenda Council on Genetics
... (separation of surrounding cellular material), and, in many cases, multiplication of the DNA sequence of interest. Patents can only be granted if the patent application relates to patentable subject matter and all patentability criteria are cumulatively met. National patent law generally distinguish ...
... (separation of surrounding cellular material), and, in many cases, multiplication of the DNA sequence of interest. Patents can only be granted if the patent application relates to patentable subject matter and all patentability criteria are cumulatively met. National patent law generally distinguish ...
Genetics of Quantitative Variation in Human Gene Expression
... The extent of variation among individuals at the DNA sequence level has been well characterized. The goal of many genetic studies is to determine the consequences of these sequence variants, for both normal and disease phenotypes. We have extended the study of genome variation from the sequence to m ...
... The extent of variation among individuals at the DNA sequence level has been well characterized. The goal of many genetic studies is to determine the consequences of these sequence variants, for both normal and disease phenotypes. We have extended the study of genome variation from the sequence to m ...
CANCER`S Wandering GENE
... that enzyme in blood. A Tay-Sachs carrier expressed about half the normal amount of the enzyme, enough to preclude the disease; an affected child showed no enzyme at all. Population screening for the enzyme began in the early 1970s. First in Baltimore and Washington, D.C., and then in other cities, ...
... that enzyme in blood. A Tay-Sachs carrier expressed about half the normal amount of the enzyme, enough to preclude the disease; an affected child showed no enzyme at all. Population screening for the enzyme began in the early 1970s. First in Baltimore and Washington, D.C., and then in other cities, ...
William’s syndrome: gene expression is related to ORIGINAL ARTICLE
... As an approach toward understanding the role of the deleted genes in WS, we have characterized WS subjects according to genetic, social/ emotional, neurocognitive, neurophysiological and neuroanatomical features. Previous work from this laboratory also used molecular cytogenetic, microsatellite and ...
... As an approach toward understanding the role of the deleted genes in WS, we have characterized WS subjects according to genetic, social/ emotional, neurocognitive, neurophysiological and neuroanatomical features. Previous work from this laboratory also used molecular cytogenetic, microsatellite and ...
Viral Mediated Gene Delivery
... Representing the Adenoviridae family is the familiar adenovirus. An icosahedral, nonenveloped virus with broad tropism, adenovirus can infect both dividing and quiescent cells. This large, double-stranded DNA virus does not integrate into the genome, making it limited to transient, episomal expressi ...
... Representing the Adenoviridae family is the familiar adenovirus. An icosahedral, nonenveloped virus with broad tropism, adenovirus can infect both dividing and quiescent cells. This large, double-stranded DNA virus does not integrate into the genome, making it limited to transient, episomal expressi ...
Beyond Dominant and Recessive Alleles
... • Many traits are produced by the interaction of several genes. • Traits controlled by two or more genes are said to be polygenic traits. • Skin color in humans is caused by multiple genes that code for melanin in the skin. • Many genetic disorders are polygenic such as autism, diabetes, and cancer. ...
... • Many traits are produced by the interaction of several genes. • Traits controlled by two or more genes are said to be polygenic traits. • Skin color in humans is caused by multiple genes that code for melanin in the skin. • Many genetic disorders are polygenic such as autism, diabetes, and cancer. ...
Overview of Recombinant DNA Experiments Covered by
... The deliberate transfer of recombinant DNA, or DNA or RNA derived from recombinant DNA, into one or more human research participants are subject to the NIH Guidelines. This includes the transfer of DNA with defective viral vectors, such as retroviral, adenoviral and lentiviral vectors, along with th ...
... The deliberate transfer of recombinant DNA, or DNA or RNA derived from recombinant DNA, into one or more human research participants are subject to the NIH Guidelines. This includes the transfer of DNA with defective viral vectors, such as retroviral, adenoviral and lentiviral vectors, along with th ...
blueprint of life
... ADAPTIVE RADIATION: the process by which an organism adapts to its niche over millions of years. Darwin and Wallace’s theory of natural selection and isolation accounts for divergent evolution. For example when a species is occupying a certain environment it will be exposed to those environmental pr ...
... ADAPTIVE RADIATION: the process by which an organism adapts to its niche over millions of years. Darwin and Wallace’s theory of natural selection and isolation accounts for divergent evolution. For example when a species is occupying a certain environment it will be exposed to those environmental pr ...
Mesoderm tissue development in Drosophila melanogaster Abstract
... regions for CG11148.7 In D. melanogaster, the dot chromosome has become mostly heterochromatin, which means the DNA has become tightly coiled and the information in these areas is not transcribed, in contrast to the high amount of euchromatin, or loosely coiled DNA that is transcribed actively into ...
... regions for CG11148.7 In D. melanogaster, the dot chromosome has become mostly heterochromatin, which means the DNA has become tightly coiled and the information in these areas is not transcribed, in contrast to the high amount of euchromatin, or loosely coiled DNA that is transcribed actively into ...
Metaphors in multilevel concepts of genetics
... introduced word acts as the filename in hypertext - for "click to display" from outside the appropriate block of knowledge, both images and texts. Maybe the future neurobiology, along with the computer science, will show us how it occurs physically - in the intact creative brain. ...
... introduced word acts as the filename in hypertext - for "click to display" from outside the appropriate block of knowledge, both images and texts. Maybe the future neurobiology, along with the computer science, will show us how it occurs physically - in the intact creative brain. ...
Stature in adolescent twins - UCSD Genetics Training Program
... Linkage disequilibrium (LD). Marker trait Marker marker In population genetics, linkage disequilibrium is the non-random association of alleles at two or more loci. Linkage disequilibrium describes a situation in which some combinations of alleles or genetic markers occur more or less frequentl ...
... Linkage disequilibrium (LD). Marker trait Marker marker In population genetics, linkage disequilibrium is the non-random association of alleles at two or more loci. Linkage disequilibrium describes a situation in which some combinations of alleles or genetic markers occur more or less frequentl ...
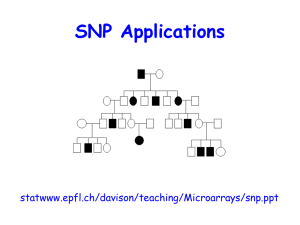
SNP Applications
... may provide exploitable diversity • Rapid and efficient to genotype • Increased stability over other types of ...
... may provide exploitable diversity • Rapid and efficient to genotype • Increased stability over other types of ...
Functional Consequences of a SDHB Gene Mutation in an
... D1S 244), PC2 (D1S228 to D1S507), and PC3 (D1S507 toward the centromere) were deleted. They contain candidate regions for putative tumor suppressor loci implicated in several cancer such as neuroblastoma (13). It will be of interest to determine the precise role of 1p in SDHB and SDHD-inherited pheo ...
... D1S 244), PC2 (D1S228 to D1S507), and PC3 (D1S507 toward the centromere) were deleted. They contain candidate regions for putative tumor suppressor loci implicated in several cancer such as neuroblastoma (13). It will be of interest to determine the precise role of 1p in SDHB and SDHD-inherited pheo ...
From DNA to Protein
... Proteins are made from subunits called amino acids Hundreds of thousands of different proteins made by all living things are remarkably similar in their construction All proteins in living things are assembled from only 20 different amino acids The Structure of Proteins These 20 amino acids ...
... Proteins are made from subunits called amino acids Hundreds of thousands of different proteins made by all living things are remarkably similar in their construction All proteins in living things are assembled from only 20 different amino acids The Structure of Proteins These 20 amino acids ...
Document
... 4. Fertilization is the union of a sperm and an egg to form a zygote, or a fertilized egg. Reproductive cells are called gametes. 5. Gametes must have half the number of chromosomes, or one chromosome from each pair. Cells with half the number of chromosomes are called haploid (N). 6. In order for c ...
... 4. Fertilization is the union of a sperm and an egg to form a zygote, or a fertilized egg. Reproductive cells are called gametes. 5. Gametes must have half the number of chromosomes, or one chromosome from each pair. Cells with half the number of chromosomes are called haploid (N). 6. In order for c ...
Genetic tasks V: GENE INTERACTIONS
... 12. In pumpkin, the shape is determined by two genes. Dominant allele of gene A or B determines round shape, dominant alleles of both genes determine discoid shape, while homozygous genotype aabb determines elongated shape. a) Use colours in Punnet square (or branching method) to differentiate phen ...
... 12. In pumpkin, the shape is determined by two genes. Dominant allele of gene A or B determines round shape, dominant alleles of both genes determine discoid shape, while homozygous genotype aabb determines elongated shape. a) Use colours in Punnet square (or branching method) to differentiate phen ...
Basic genetics - Informatics: Indiana University
... • Instead of masking the effects of another gene, a gene can modify the expression of a second gene. In mice, coat color is controlled by the B gene. The B allele conditions black coat color and is dominant to the b allele that produces a brown coat. The intensity of the color, either black or brown ...
... • Instead of masking the effects of another gene, a gene can modify the expression of a second gene. In mice, coat color is controlled by the B gene. The B allele conditions black coat color and is dominant to the b allele that produces a brown coat. The intensity of the color, either black or brown ...
MeiosisPPT
... B. Sex cells, or gametes contain half of the normal amount of chromosomes 1. Meiosis is the process of creating haploid (N) gametes from diploid (2N) cells ...
... B. Sex cells, or gametes contain half of the normal amount of chromosomes 1. Meiosis is the process of creating haploid (N) gametes from diploid (2N) cells ...