Mackay, T. F. C. and R. R. H. Anholt (2007).
... polymorphisms at many interacting loci, with effects that are sensitive to the environment (Box 1). Understanding the genetic and environmental influences on the manifestation of behavior is important from the dual perspectives of human health and evolutionary biology. Psychiatric disorders such as ...
... polymorphisms at many interacting loci, with effects that are sensitive to the environment (Box 1). Understanding the genetic and environmental influences on the manifestation of behavior is important from the dual perspectives of human health and evolutionary biology. Psychiatric disorders such as ...
Chapter13 Section03 cell transformation ppt
... Transforming Animal Cells Many egg cells are large enough that DNA can be directly injected into the nucleus. Enzymes may help to insert the foreign DNA into the chromosomes of the injected cell. DNA molecules used for transformation of animal and plant cells contain marker genes. ...
... Transforming Animal Cells Many egg cells are large enough that DNA can be directly injected into the nucleus. Enzymes may help to insert the foreign DNA into the chromosomes of the injected cell. DNA molecules used for transformation of animal and plant cells contain marker genes. ...
Gene Section MRC1 (mannose receptor, C type 1)
... The protein encoded by the MRC1 gene is classified as a type I transmembrane receptor since the protein COOH terminus is located on the cytoplasmic side of the membrane. MRC1 is a membrane receptor containing: - a ricin b-type lectin domain (RICIN), that is a cysteinrich (CysR) domain located at the ...
... The protein encoded by the MRC1 gene is classified as a type I transmembrane receptor since the protein COOH terminus is located on the cytoplasmic side of the membrane. MRC1 is a membrane receptor containing: - a ricin b-type lectin domain (RICIN), that is a cysteinrich (CysR) domain located at the ...
3 Cell Transformation
... Transforming Animal Cells Many egg cells are large enough that DNA can be directly injected into the nucleus. Enzymes may help to insert the foreign DNA into the chromosomes of the injected cell. DNA molecules used for transformation of animal and plant cells contain marker genes. ...
... Transforming Animal Cells Many egg cells are large enough that DNA can be directly injected into the nucleus. Enzymes may help to insert the foreign DNA into the chromosomes of the injected cell. DNA molecules used for transformation of animal and plant cells contain marker genes. ...
Document
... products, drugs, toxins, pesticides, carcinogens • All DMEs have endogenous compounds as natural substrates (used in natural process of breaking down compounds) • Located in every eukaryotic cell, most prokaryotes ...
... products, drugs, toxins, pesticides, carcinogens • All DMEs have endogenous compounds as natural substrates (used in natural process of breaking down compounds) • Located in every eukaryotic cell, most prokaryotes ...
Modeling Chromosome Maintenance as a Property of Cell Cycle in
... without using the Poisson distribution to quantify the rates of mutation per colony. Screening MORF Library Plasmids for Identifying Candidate Chromosome Instability Genes Plasmid DNA comprising the entire MORF library was partitioned into sets including about 384 individual MORF plasmid DNA prepara ...
... without using the Poisson distribution to quantify the rates of mutation per colony. Screening MORF Library Plasmids for Identifying Candidate Chromosome Instability Genes Plasmid DNA comprising the entire MORF library was partitioned into sets including about 384 individual MORF plasmid DNA prepara ...
Genes and physical fitness
... a type of association of two polymorphisms located close to each other on the same chromosome and inherited as a haplotype. If there is then an association of a polymorphism with a trait, it does not functionally affect the development of this trait, but most probably remains in the linkage disequil ...
... a type of association of two polymorphisms located close to each other on the same chromosome and inherited as a haplotype. If there is then an association of a polymorphism with a trait, it does not functionally affect the development of this trait, but most probably remains in the linkage disequil ...
SSSA_Poster_Straathof_finalv
... • Further investigation to determine treatment effect on cumulative N2O emissions • Molecular quantification of several additional genes responsible for nitrification and denitrification (N2O production) at various points of the N-cycle including amo, nirK, nosZ, norB and ammonia-oxidizing archaea • ...
... • Further investigation to determine treatment effect on cumulative N2O emissions • Molecular quantification of several additional genes responsible for nitrification and denitrification (N2O production) at various points of the N-cycle including amo, nirK, nosZ, norB and ammonia-oxidizing archaea • ...
16-2 Evolution as Genetic Change PowerPoint
... If an individual dies without reproducing, it does not contribute its alleles to the population’s gene pool. If an individual produces many offspring, its alleles stay in the gene pool and may increase in frequency. ...
... If an individual dies without reproducing, it does not contribute its alleles to the population’s gene pool. If an individual produces many offspring, its alleles stay in the gene pool and may increase in frequency. ...
Mathematical Modeling of Population Genetics
... The alleles from each gamete may di¤er from each other. Both parents each give one set of chromosomes to the o¤spring. The chromosome’s alleles need not be the same. If the alleles di¤er, the resulting cell is considered a heterozygote. If the alleles do not di¤er, the resulting cell is considered a ...
... The alleles from each gamete may di¤er from each other. Both parents each give one set of chromosomes to the o¤spring. The chromosome’s alleles need not be the same. If the alleles di¤er, the resulting cell is considered a heterozygote. If the alleles do not di¤er, the resulting cell is considered a ...
Table of Contents - Milan Area Schools
... transcriptase (RT) to make complementary DNA (cDNA). The cDNA is amplified by PCR prior to hybridization. The amplified cDNA is coupled to a fluorescent dye and then hybridized to the chip. A scanner detects glowing spots on the array. The combinations of these spots differ with different types ...
... transcriptase (RT) to make complementary DNA (cDNA). The cDNA is amplified by PCR prior to hybridization. The amplified cDNA is coupled to a fluorescent dye and then hybridized to the chip. A scanner detects glowing spots on the array. The combinations of these spots differ with different types ...
The Fishy Frequencies Lab
... Introduction to Hardy-Weinberg The Hardy-Weinberg Principle states that allele frequencies in a population will remain constant unless one or more factors cause those frequencies to change. The situation in which allele frequencies remain constant is called genetic equilibrium. Five conditions are r ...
... Introduction to Hardy-Weinberg The Hardy-Weinberg Principle states that allele frequencies in a population will remain constant unless one or more factors cause those frequencies to change. The situation in which allele frequencies remain constant is called genetic equilibrium. Five conditions are r ...
Mitosis, Meiosis and Fertilization Teacher Prep Notes
... chromosomes out on the table, so students can more easily see the multiple different possible combinations. We recommend that this activity be followed by our Genetics activity, so the students will see how understanding meiosis and fertilization is the basis for understanding genetics. Teaching poi ...
... chromosomes out on the table, so students can more easily see the multiple different possible combinations. We recommend that this activity be followed by our Genetics activity, so the students will see how understanding meiosis and fertilization is the basis for understanding genetics. Teaching poi ...
Welcome Back to School - Glen Ridge Public Schools
... To return to the chapter summary click escape or close this document. ...
... To return to the chapter summary click escape or close this document. ...
Recombinant Paper Plasmids Cut-and
... complementary sticky ends. By using enzymes that will cut the DNA on either side of the gene, the gene can be clipped out of the DNA strand. Once scientists obtain the gene they are looking for, they must somehow get it into the host cell. The workhorse of this transfer step is the plasmid, a small ...
... complementary sticky ends. By using enzymes that will cut the DNA on either side of the gene, the gene can be clipped out of the DNA strand. Once scientists obtain the gene they are looking for, they must somehow get it into the host cell. The workhorse of this transfer step is the plasmid, a small ...
Natural selection in rats
... their features on. B: A mutation in a rat’s sex cells make its offspring resistant to warfarin. A: The mutated gene is passed on and is common in the rat population. C: The number of resistant rats ...
... their features on. B: A mutation in a rat’s sex cells make its offspring resistant to warfarin. A: The mutated gene is passed on and is common in the rat population. C: The number of resistant rats ...
Autism Spectrum Disorders
... Pathophysiology more likely to lead to new drugs than genetics Elucidate basis of autistic regression Devise a rational treatment for autistic regression ...
... Pathophysiology more likely to lead to new drugs than genetics Elucidate basis of autistic regression Devise a rational treatment for autistic regression ...
Part 3 – Theoretical Genetics
... Therefore, the homozygous tall plant was either TT, or Tt (genotypes). The homozygous dwarf plants had to be genotype (tt). What would be the possible gametes? 3. First Filial Offspring (F1) from the cross of parental (P) Mendel found that the offspring were all tall plants. This lead him to concl ...
... Therefore, the homozygous tall plant was either TT, or Tt (genotypes). The homozygous dwarf plants had to be genotype (tt). What would be the possible gametes? 3. First Filial Offspring (F1) from the cross of parental (P) Mendel found that the offspring were all tall plants. This lead him to concl ...
Population Genetics
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
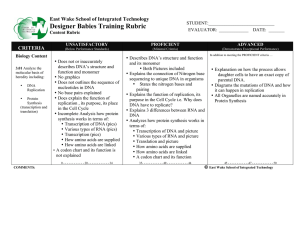
Designer Babies Training Rubric
... or not Designer babies should be placed on the market and why ...
... or not Designer babies should be placed on the market and why ...
Complex Chromosome Rearrangement of 6p25.3-.p23
... stroke secondary to moyamoya syndrome, a progressive cerebrovascular occlusive disorder of uncertain but likely multifactorial etiology. Past medical history revealed hearing loss and developmental delay/ intellectual disability. Routine karyotype demonstrated extra chromosomal material on 6p. Singl ...
... stroke secondary to moyamoya syndrome, a progressive cerebrovascular occlusive disorder of uncertain but likely multifactorial etiology. Past medical history revealed hearing loss and developmental delay/ intellectual disability. Routine karyotype demonstrated extra chromosomal material on 6p. Singl ...
The Determination of the Genetic Order and Genetic Map
... dominant genes. This then yielded a F1 generation in which the males were all recessive mutants and the females were wild type. An F2 generation was then bred and created by crossing a wild type female and recessive male. This cross then yielded eight different phenotypes whose recombination frequen ...
... dominant genes. This then yielded a F1 generation in which the males were all recessive mutants and the females were wild type. An F2 generation was then bred and created by crossing a wild type female and recessive male. This cross then yielded eight different phenotypes whose recombination frequen ...
Genetics - Monroe County Schools
... Instructions for specifying characteristics are carried in nucleic acids. Mulitcellular organisms, including humans, form from cells that contain two copies of each chromosome. This explains many features of heredity. ...
... Instructions for specifying characteristics are carried in nucleic acids. Mulitcellular organisms, including humans, form from cells that contain two copies of each chromosome. This explains many features of heredity. ...
Title CHROMOSOMAL ASSIGNMENT OF
... from the sorted chrom~.omes, digested by EcoRI, and subjected to Southern blot analysis using P-labeled human gastrin gene (12) as a probe. Lane T: total human lymphocyte DNA. Lanes A to H; DNA from each sorted chromosome fraction. The arrow indicates the position of the DNA fragment hybridizing to ...
... from the sorted chrom~.omes, digested by EcoRI, and subjected to Southern blot analysis using P-labeled human gastrin gene (12) as a probe. Lane T: total human lymphocyte DNA. Lanes A to H; DNA from each sorted chromosome fraction. The arrow indicates the position of the DNA fragment hybridizing to ...
Dropping Your Genes
... dropping them simultaneously. Only one allele on each chromosome will be facing up and the two alleles will represent the genotype of a gamete. Again, work with a lab partner who should choose the same two chromosomes from his or her genome. Each of you should produce 40 gametes and, by gametic unio ...
... dropping them simultaneously. Only one allele on each chromosome will be facing up and the two alleles will represent the genotype of a gamete. Again, work with a lab partner who should choose the same two chromosomes from his or her genome. Each of you should produce 40 gametes and, by gametic unio ...