You may have heard the terms saturated and unsaturated in rela
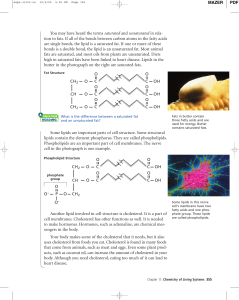
... are single bonds, the lipid is a saturated fat. If one or more of these bonds is a double bond, the lipid is an unsaturated fat. Most animal fats are saturated, and most oils from plants are unsaturated. Diets high in saturated fats have been linked to heart disease. Lipids in the butter in the phot ...
... are single bonds, the lipid is a saturated fat. If one or more of these bonds is a double bond, the lipid is an unsaturated fat. Most animal fats are saturated, and most oils from plants are unsaturated. Diets high in saturated fats have been linked to heart disease. Lipids in the butter in the phot ...
week 7_lipid - UniMAP Portal
... obtained by the ingestion of LDL by foam cells- directly correlated with high risk for coronary heart disease. High plasma HDL- low risk for coronary artery disease. Liver cells are the only cells that possess HDL receptors. ...
... obtained by the ingestion of LDL by foam cells- directly correlated with high risk for coronary heart disease. High plasma HDL- low risk for coronary artery disease. Liver cells are the only cells that possess HDL receptors. ...
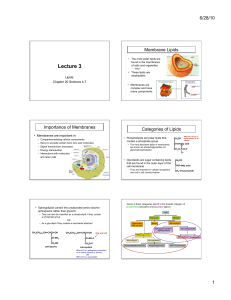
Lecture 3
... •! Leading cause of death •! High levels of cholesterol increase the chances of developing these types of disease •! These diseases are more prevalent as people age, one reason is that the rate at which cholesterol is metabolized, decreases with age •! Females have lower levels of cholesterol ...
... •! Leading cause of death •! High levels of cholesterol increase the chances of developing these types of disease •! These diseases are more prevalent as people age, one reason is that the rate at which cholesterol is metabolized, decreases with age •! Females have lower levels of cholesterol ...
Mutation in the EGFP domain of LDL receptor
... Laboratory Medicine, Genetics, and Immunobiology, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Conn; and Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran. Mutation in the EGFP domain of LDL receptor-related protein 6 (LRP6R611C) is associated with hypercholesterolemia and early-onset atherosc ...
... Laboratory Medicine, Genetics, and Immunobiology, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Conn; and Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran. Mutation in the EGFP domain of LDL receptor-related protein 6 (LRP6R611C) is associated with hypercholesterolemia and early-onset atherosc ...