Option D1: Human nutrition - Ms. Richards IB Biology HL
... Skin becomes dry and bruises easily. Blood pressure is reduced, with slow heart rate and poor circulation. Infertility with no ovulation. Heart muscle deteriorates • If untreated, anorexia can result in death ...
... Skin becomes dry and bruises easily. Blood pressure is reduced, with slow heart rate and poor circulation. Infertility with no ovulation. Heart muscle deteriorates • If untreated, anorexia can result in death ...
NUTRITION OVERVIEW
... Related to too little iron – and thus too little hemoglobin in the blood. 5% of women of childbearing age. Symptoms: Sensitivity to cold., chronic fatigue, edginess, depression, sleeplessness, and susceptibility to colds and infection. ...
... Related to too little iron – and thus too little hemoglobin in the blood. 5% of women of childbearing age. Symptoms: Sensitivity to cold., chronic fatigue, edginess, depression, sleeplessness, and susceptibility to colds and infection. ...
Draft Summary of the 3rd OECD Food Chain Network meeting
... composition has changed with an increased consumption of fats, sugars and refined carbohydrates. In addition technological advances have reduced energy requirements for work and daily tasks. This set of changes, commonly referred to as the nutrition or dietary transition, characterize most countries ...
... composition has changed with an increased consumption of fats, sugars and refined carbohydrates. In addition technological advances have reduced energy requirements for work and daily tasks. This set of changes, commonly referred to as the nutrition or dietary transition, characterize most countries ...
Unit N - Public Schools of Robeson County
... 4. B vitamins and Vitamin C are water soluble, can’t be stored, excess excreted G. Fiber 1. Found in plant foods like whole grain breads, cereals, beans, peas, other vegetables and fruit 2. Important for proper bowel functioning, may lower risk of heart disease and some cancers ...
... 4. B vitamins and Vitamin C are water soluble, can’t be stored, excess excreted G. Fiber 1. Found in plant foods like whole grain breads, cereals, beans, peas, other vegetables and fruit 2. Important for proper bowel functioning, may lower risk of heart disease and some cancers ...
Unit 12.1 web
... Iron is part of heme which is critical for the transport of oxygen by hemoglobin and the temporary storage of oxygen in heart muscles by myoglobin. RNI: 8 - 10mg/day (higher for pregnant women) Deficiency: anemia( the red blood cells are low in hemoglobin and thus carry a decreased oxygen supply), f ...
... Iron is part of heme which is critical for the transport of oxygen by hemoglobin and the temporary storage of oxygen in heart muscles by myoglobin. RNI: 8 - 10mg/day (higher for pregnant women) Deficiency: anemia( the red blood cells are low in hemoglobin and thus carry a decreased oxygen supply), f ...
Chemistry/Biology Warm-up
... • heifers fed wheat-based diets produced calves at lower rates than those fed corn diets • assumption: something toxic in wheat • analysis: nothing toxic in tissues • reality: vitamin deficiency • scientific methods for formulating feeds were inadequate • research diets eventually simplified/purifie ...
... • heifers fed wheat-based diets produced calves at lower rates than those fed corn diets • assumption: something toxic in wheat • analysis: nothing toxic in tissues • reality: vitamin deficiency • scientific methods for formulating feeds were inadequate • research diets eventually simplified/purifie ...
Biochemical Functions of Micronutrients
... Micronutrient deficiencies are globally important problems which are not always clinically apparent or dependent on food supply and consumption patterns. They might be associated with physiologic effects that can be lifethreatening or more commonly damaging to optimal health and functions of the bod ...
... Micronutrient deficiencies are globally important problems which are not always clinically apparent or dependent on food supply and consumption patterns. They might be associated with physiologic effects that can be lifethreatening or more commonly damaging to optimal health and functions of the bod ...
Is keeping a child at the table during mealtimes
... Expanding Children’s Diets by Suzanne Evans Morris 2009 “Children need to learn about new foods in an unthreatening way…Mealtimes frequently are associated with expectations for eating and drinking. Many children are on guard and spend a great deal of energy protecting themselves from new sensory ex ...
... Expanding Children’s Diets by Suzanne Evans Morris 2009 “Children need to learn about new foods in an unthreatening way…Mealtimes frequently are associated with expectations for eating and drinking. Many children are on guard and spend a great deal of energy protecting themselves from new sensory ex ...
PDF
... of the incidence of protein-calorie-deficiency disease throughout Egypt is unknown but there is evidence concerning its presence among the low income rural population (Partwardhan and Darby, p. 151). Anemia, defined as hemoglobin concentrations of less than 10 grams per 100 ml for ages 6-23 months a ...
... of the incidence of protein-calorie-deficiency disease throughout Egypt is unknown but there is evidence concerning its presence among the low income rural population (Partwardhan and Darby, p. 151). Anemia, defined as hemoglobin concentrations of less than 10 grams per 100 ml for ages 6-23 months a ...
28 NUTRITION AND HEALTH MODULE - 4
... glucose is changed into glycogen which is stored in the liver for subsequent use. (For detail refer to lesson 13) Cellulose is a fibrous substance which is not digested by human body. However, it serves as roughage and facilitates bowel (stool) movement. A normal person needs about 400-500 grams of ...
... glucose is changed into glycogen which is stored in the liver for subsequent use. (For detail refer to lesson 13) Cellulose is a fibrous substance which is not digested by human body. However, it serves as roughage and facilitates bowel (stool) movement. A normal person needs about 400-500 grams of ...
Ulcerative Colitis and Colectomy
... able to call down and order food when he felt like it. Objective: Patient will call down and order something from ...
... able to call down and order food when he felt like it. Objective: Patient will call down and order something from ...
Document
... prevent deficiencies by providing the vital vitamins and minerals needed to boost good health. So who needs ‘em?. ...
... prevent deficiencies by providing the vital vitamins and minerals needed to boost good health. So who needs ‘em?. ...
Goals and Objectives for this rotation are identical across all PL years
... 5. Provide informative and accurate nutritional counseling to parents and patients suspected of a nutritional deficiency or with exogenous obesity. 6. Describe intervention approaches with proven efficacy in helping children, adolescents and families alter their eating and exercise habits, in order ...
... 5. Provide informative and accurate nutritional counseling to parents and patients suspected of a nutritional deficiency or with exogenous obesity. 6. Describe intervention approaches with proven efficacy in helping children, adolescents and families alter their eating and exercise habits, in order ...
1 - contentextra
... oranges were grown in Scotland. Exercise and eating healthily are the best prevention but the Campaign to End Obesity in the USA states 52% of adults do not meet minimum physical activity recommendations while only 35.8% of high-school students are physically active for an hour or more every day. Th ...
... oranges were grown in Scotland. Exercise and eating healthily are the best prevention but the Campaign to End Obesity in the USA states 52% of adults do not meet minimum physical activity recommendations while only 35.8% of high-school students are physically active for an hour or more every day. Th ...
Response of the Ministry of Health def versie
... should there be a maximum set to the levels of these vitamins or minerals in foods? − If the risk of adverse effects, even at high levels, of the intake of vitamins and minerals is low or non-existent, should there be a maximum set to the levels of these vitamins and minerals in foods? − If a maximu ...
... should there be a maximum set to the levels of these vitamins or minerals in foods? − If the risk of adverse effects, even at high levels, of the intake of vitamins and minerals is low or non-existent, should there be a maximum set to the levels of these vitamins and minerals in foods? − If a maximu ...
A.1.4 Outline the consequences of protein
... There is also variation in the structure of unsaturated fatty acids. cis- isomers have the hydrogen atoms on the same side of the C=C double bond, whereas trans-isomers have the hydrogen atoms on opposite sides. Most trans- fats are created artificially. In unsaturated fatty acids, the omega-number ...
... There is also variation in the structure of unsaturated fatty acids. cis- isomers have the hydrogen atoms on the same side of the C=C double bond, whereas trans-isomers have the hydrogen atoms on opposite sides. Most trans- fats are created artificially. In unsaturated fatty acids, the omega-number ...
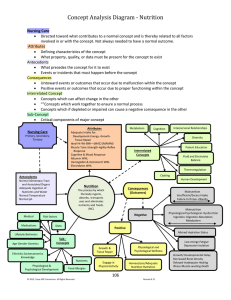
Concept Analysis Diagram
... Explanation of Nutrition Diagram: Nursing - Directed toward what contribution nursing would make to the concept and a positive consequence. Related to all factors involved in or with the concept. Not always needed to have a normal outcome. For example an individual may work with an outpatient dietic ...
... Explanation of Nutrition Diagram: Nursing - Directed toward what contribution nursing would make to the concept and a positive consequence. Related to all factors involved in or with the concept. Not always needed to have a normal outcome. For example an individual may work with an outpatient dietic ...
2105Lecture 11abc powerpoint
... Potentially lethal lung infection Nasogastric feeding or gastrostomy or jejunostomy which allows the lower esophageal sphincter to remain closed -all this helps to reduce aspiration risk ...
... Potentially lethal lung infection Nasogastric feeding or gastrostomy or jejunostomy which allows the lower esophageal sphincter to remain closed -all this helps to reduce aspiration risk ...
Vitamin supplementation: the Lingering Questions in wound Healing
... Enriched and Fortified Foods In recent years, a thorough dietary assessment has become all-the-more critical because of the trend among food companies to add nutrients to a wide variety of foods that do not naturally contain these compounds. This change in food manufacturing practice has created a s ...
... Enriched and Fortified Foods In recent years, a thorough dietary assessment has become all-the-more critical because of the trend among food companies to add nutrients to a wide variety of foods that do not naturally contain these compounds. This change in food manufacturing practice has created a s ...
chapter_12_child_and_preadolescent_nutrition
... • All foods available in schools should be consistent with the U.S. Dietary Guidelines & Dietary Reference Intakes • Sound nutrition policies need community & school environment support • Community leaders should support the school’s nutrition policy • The School Health Index (SHI) should be ...
... • All foods available in schools should be consistent with the U.S. Dietary Guidelines & Dietary Reference Intakes • Sound nutrition policies need community & school environment support • Community leaders should support the school’s nutrition policy • The School Health Index (SHI) should be ...
PSE4U - 14 - Canada Food Guide - CHOW
... Advice for women of childbearing age • All women who could become pregnant and those who are pregnant or breastfeeding need a multivitamin containing folic acid every day. • Pregnant women need to ensure that their multivitamin also contains iron. ...
... Advice for women of childbearing age • All women who could become pregnant and those who are pregnant or breastfeeding need a multivitamin containing folic acid every day. • Pregnant women need to ensure that their multivitamin also contains iron. ...
NUTRITION AND HEALTH
... glucose is changed into glycogen which is stored in the liver for subsequent use. (For detail refer to lesson 13) Cellulose is a fibrous substance which is not digested by human body. However, it serves as roughage and facilitates bowel (stool) movement. A normal person needs about 400-500 grams of ...
... glucose is changed into glycogen which is stored in the liver for subsequent use. (For detail refer to lesson 13) Cellulose is a fibrous substance which is not digested by human body. However, it serves as roughage and facilitates bowel (stool) movement. A normal person needs about 400-500 grams of ...
Nutrition Therapy for Clients with Disordered Eating
... Recurrent episodes of binge eating characterized by both of the following:(1) Eating, in a discrete period of time (eg, within any 2-hour period), an amount of food that is larger than most would eat during a similar period of time and under similar circumstances.(2) A sense of lack of control over ...
... Recurrent episodes of binge eating characterized by both of the following:(1) Eating, in a discrete period of time (eg, within any 2-hour period), an amount of food that is larger than most would eat during a similar period of time and under similar circumstances.(2) A sense of lack of control over ...
Nutritional Report to the PAM HCR meeting 07
... among the Saharawis. The weaning food is normal food that can be prepared at home but it maybe demands some nutritional and practical skills. Usually the young mothers inherit these skills from their mothers or grandmothers, but sometimes this it is difficult, for example if the availability of the ...
... among the Saharawis. The weaning food is normal food that can be prepared at home but it maybe demands some nutritional and practical skills. Usually the young mothers inherit these skills from their mothers or grandmothers, but sometimes this it is difficult, for example if the availability of the ...
Malnutrition
Malnutrition or malnourishment is a condition that results from eating a diet in which nutrients are either not enough or are too much such that the diet causes health problems. It may involve calories, protein, carbohydrates, vitamins or minerals. Not enough nutrients is called undernutrition or undernourishment while too much is called overnutrition. Malnutrition is often used specifically to refer to undernutrition where there is not enough calories, protein, or micronutrients. If undernutrition occurs during pregnancy, or before two years of age, it may result in permanent problems with physical and mental development. Extreme undernourishment, known as starvation, may have symptoms that include: a short height, thin body, very poor energy levels, and swollen legs and abdomen. People also often get infections and are frequently cold. The symptoms of micronutrient deficiencies depend on the micronutrient that is lacking.Undernourishment is most often due to not enough high-quality food being available to eat. This is often related to high food prices and poverty. A lack of breast feeding may contribute, as may a number of infectious diseases such as: gastroenteritis, pneumonia, malaria, and measles, which increase nutrient requirements. There are two main types of undernutrition: protein-energy malnutrition and dietary deficiencies. Protein-energy malnutrition has two severe forms: marasmus (a lack of protein and calories) and kwashiorkor (a lack of just protein). Common micronutrient deficiencies include: a lack of iron, iodine, and vitamin A. During pregnancy, due to the body's increased need, deficiencies may become more common. In some developing countries, overnutrition in the form of obesity is beginning to present within the same communities as undernutrition. Other causes of malnutrition include anorexia nervosa and bariatric surgery.Efforts to improve nutrition are some of the most effective forms of development aid. Breastfeeding can reduce rates of malnutrition and death in children, and efforts to promote the practice increase the rates of breastfeeding. In young children, providing food (in addition to breastmilk) between six months and two years of age improves outcomes. There is also good evidence supporting the supplementation of a number of micronutrients to women during pregnancy and among young children in the developing world. To get food to people who need it most, both delivering food and providing money so people can buy food within local markets are effective. Simply feeding students at school is insufficient. Management of severe malnutrition within the person's home with ready-to-use therapeutic foods is possible much of the time. In those who have severe malnutrition complicated by other health problems, treatment in a hospital setting is recommended. This often involves managing low blood sugar and body temperature, addressing dehydration, and gradual feeding. Routine antibiotics are usually recommended due to the high risk of infection. Longer-term measures include: improving agricultural practices, reducing poverty, improving sanitation, and the empowerment of women.There were 925 million undernourished people in the world in 2010. This is an increase of 80 million people since 1990 or a 2.5% drop in the percentage of undernourished people. Another billion people are estimated to have a lack of vitamins and minerals. In 2013, protein-energy malnutrition was estimated to have resulted in 469,000 deaths—down from 510,000 deaths in 1990. Other nutritional deficiencies, which include iodine deficiency and iron deficiency anemia, result in another 84,000 deaths. In 2010, malnutrition was the cause of 1.4% of all disability adjusted life years. About a third of deaths in children are believed to be due to undernutrition, although the deaths are rarely labelled as such. In 2010, it was estimated to have contributed to about 1.5 million deaths in women and children, though some estimate the number may be greater than 3 million. An additional 165 million children have stunted growth from malnutrition. Undernutrition is more common in developing countries. Certain groups have higher rates of undernutrition, including women—in particular while pregnant or breastfeeding—children under five years of age, and the elderly. In the elderly, undernutrition becomes more common due to physical, psychological, and social factors.