Micronutrients - Food a fact of life
... the condition called Beri-beri. This leads to symptoms such as fatigue, weakness of the legs and anorexia. ...
... the condition called Beri-beri. This leads to symptoms such as fatigue, weakness of the legs and anorexia. ...
Food Allergies and Intolerances and Their Importance to
... • “Anaphylactoid” ≠ “Anaphylaxis” • Certain foods can cause reactions that can mimic symptoms of allergic reactions ...
... • “Anaphylactoid” ≠ “Anaphylaxis” • Certain foods can cause reactions that can mimic symptoms of allergic reactions ...
nutrition in pediatric patients before liver transplantation
... longer molecules. They can be quickly utilised as an energy source but are also ketogenic. Although MCT have been used in the nutrition of cholestatic children for a long time, it is still difficult to indicate which ratio of MCT to LCT should be preferable. Some studies pointed to the risk of essen ...
... longer molecules. They can be quickly utilised as an energy source but are also ketogenic. Although MCT have been used in the nutrition of cholestatic children for a long time, it is still difficult to indicate which ratio of MCT to LCT should be preferable. Some studies pointed to the risk of essen ...
School Foodservice Fact Sheet
... nutrition. However, many processed foods do offer nutritional benefits. Processing can include canning, freezing, refrigeration…things our grandparents may have done to keep green beans on the table year-round. At ConAgra Foods, our employees make food from recipes our chefs create. We don’t think o ...
... nutrition. However, many processed foods do offer nutritional benefits. Processing can include canning, freezing, refrigeration…things our grandparents may have done to keep green beans on the table year-round. At ConAgra Foods, our employees make food from recipes our chefs create. We don’t think o ...
FREE Sample Here
... D. Chemical substances found in plants that affect body processes in humans and may benefit health E. Protein deficiency characterized by edema and loss of muscle mass F. Availability of safe, nutritious food is limited G. Access at all times to a sufficient supply of safe, nutritious food H. Fatty ...
... D. Chemical substances found in plants that affect body processes in humans and may benefit health E. Protein deficiency characterized by edema and loss of muscle mass F. Availability of safe, nutritious food is limited G. Access at all times to a sufficient supply of safe, nutritious food H. Fatty ...
The Dental Hygienist`s Guide to Nutritional Care
... Protein Deficiency in Relation to Oral Health • Protein malnutrition even of the subclinical type can and very likely will exacerbate oral infections and parotid enlargement. ...
... Protein Deficiency in Relation to Oral Health • Protein malnutrition even of the subclinical type can and very likely will exacerbate oral infections and parotid enlargement. ...
Wardlaws-Perspectives-in-Nutrition-10th-Edition-Byrd
... 4. People often have difficulty accurately estimating portion/serving sizes of foods they eat. To help students with this, have them estimate food portions in class. You can do this by bringing to class samples of commonly consumed foods, various-sized glasses, bowls, measuring cups, measuring spoon ...
... 4. People often have difficulty accurately estimating portion/serving sizes of foods they eat. To help students with this, have them estimate food portions in class. You can do this by bringing to class samples of commonly consumed foods, various-sized glasses, bowls, measuring cups, measuring spoon ...
Perspectives in Nutrition, 8th Edition
... Adequate nutrients within energy needs a. Consume a variety of nutrient-dense foods and beverages within and among the basic food groups while choosing foods that limit the intake of saturated and trans fat, cholesterol, added sugars, salt, and alcohol b. Meet recommended intakes within energy needs ...
... Adequate nutrients within energy needs a. Consume a variety of nutrient-dense foods and beverages within and among the basic food groups while choosing foods that limit the intake of saturated and trans fat, cholesterol, added sugars, salt, and alcohol b. Meet recommended intakes within energy needs ...
Click here to see the Document
... Avoiding an empty stomach Choosing foods that are well tolerated ...
... Avoiding an empty stomach Choosing foods that are well tolerated ...
Extended Nutrition Competency Framework (NCF
... Fuel metabolism and homeostasis of carbohydrates, fats and protein Hormonal control of hunger and satiety Biochemical demand and contributors to energy intake and energy expenditure in the body across the life course Nutritional requirements across the lifespan including infancy, childhood, adolesce ...
... Fuel metabolism and homeostasis of carbohydrates, fats and protein Hormonal control of hunger and satiety Biochemical demand and contributors to energy intake and energy expenditure in the body across the life course Nutritional requirements across the lifespan including infancy, childhood, adolesce ...
營養資料標籤 有助你作出有依據的食物選擇
... Choose a variety of food and eat cereals as the largest portion of food in every meal. Eat a lot of vegetables and fruit. Reduce the consumption of foodstuffs with high salt, fat and sugar content as well as those which are preserved. A daily fluid intake of 6 to 8 glasses (including clear soup, fru ...
... Choose a variety of food and eat cereals as the largest portion of food in every meal. Eat a lot of vegetables and fruit. Reduce the consumption of foodstuffs with high salt, fat and sugar content as well as those which are preserved. A daily fluid intake of 6 to 8 glasses (including clear soup, fru ...
Chap 34 Lesson Plan
... health of each that the mother increases her nutritional intake and gain weight while the child is growing in order to preserve the mother’s health and ensure a healthy newborn. 2. What foods should Wanda encourage Anita to eat? The need during pregnancy in not just for extra calories but for speci ...
... health of each that the mother increases her nutritional intake and gain weight while the child is growing in order to preserve the mother’s health and ensure a healthy newborn. 2. What foods should Wanda encourage Anita to eat? The need during pregnancy in not just for extra calories but for speci ...
NS 220: Nutritional Planning and Management
... www.fitday.com access using NS270KU as the username and password, go to data for 7/23/09 Use same password and username for www.mypyramid.gov under pyramid tracker ...
... www.fitday.com access using NS270KU as the username and password, go to data for 7/23/09 Use same password and username for www.mypyramid.gov under pyramid tracker ...
Functional soy food based on flaxseed and quinoa and enriched
... The definition of functional food established by Ordinance n.18 of the 30th April 1999, published by the Health Surveillance Agency of the Ministry of Health, says that any food or ingredient that alleges functional or health propriety must be safe for consumption, without the need of medical prescr ...
... The definition of functional food established by Ordinance n.18 of the 30th April 1999, published by the Health Surveillance Agency of the Ministry of Health, says that any food or ingredient that alleges functional or health propriety must be safe for consumption, without the need of medical prescr ...
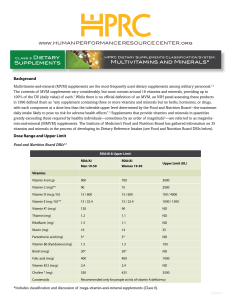
Supplements Multivitamins and Minerals*
... Multivitamin-and-mineral (MVM) supplements are the most frequently used dietary supplements among military personnel.1,2 The contents of MVM supplements vary considerably, but most contain around 18 vitamins and minerals, providing up to 100% of the DV (daily value) of each.3 While there is no offic ...
... Multivitamin-and-mineral (MVM) supplements are the most frequently used dietary supplements among military personnel.1,2 The contents of MVM supplements vary considerably, but most contain around 18 vitamins and minerals, providing up to 100% of the DV (daily value) of each.3 While there is no offic ...
... 2089 kCal/day [4]. Stunting and underweight in children under five years is still high at 35 % and 16.5%, respectively [5]. As in other low income countries many people are also exposed to food insecurity resulting from a diet low in dietary variety and energy. This in turn leads to stunting, underw ...
Nutrition and Diet Manual
... from each of six food groups: grains, vegetables, fruits, milk products, meat and beans, and oils. These foods contain six kinds of nutrients: proteins (2), carbohydrates (3), fats (4), minerals (5), vitamins (6), and water (8). A person should regularly eat or drink enough of all of these nutrients ...
... from each of six food groups: grains, vegetables, fruits, milk products, meat and beans, and oils. These foods contain six kinds of nutrients: proteins (2), carbohydrates (3), fats (4), minerals (5), vitamins (6), and water (8). A person should regularly eat or drink enough of all of these nutrients ...
maternal-nutrition-in-developing-countries
... Dietary Iron Requirements Throughout the Life Cycle ...
... Dietary Iron Requirements Throughout the Life Cycle ...
Chapter 16 – Life Cycle Nutrition Infancy
... b. Lower blood pressure as adults. c. Lower blood cholesterol as adults. 8. Other Potential Benefits a. May protect against obesity later in life. b. Indications of positive effect on later intelligence. 9. Breast Milk Banks a. Donated milk can be provided to those who are unable to provide sufficie ...
... b. Lower blood pressure as adults. c. Lower blood cholesterol as adults. 8. Other Potential Benefits a. May protect against obesity later in life. b. Indications of positive effect on later intelligence. 9. Breast Milk Banks a. Donated milk can be provided to those who are unable to provide sufficie ...
Chapter 1 – Perspectives on Health and Nutrition
... 17. Your friend always refers to meat as protein. You try to correct her by stating that: a. practically all foods contain mixtures of the energy-yielding nutrients. b. protein is not the predominant nutrient in meat. c. protein-rich foods are always high in fat. d. meat contains more carbohydrate t ...
... 17. Your friend always refers to meat as protein. You try to correct her by stating that: a. practically all foods contain mixtures of the energy-yielding nutrients. b. protein is not the predominant nutrient in meat. c. protein-rich foods are always high in fat. d. meat contains more carbohydrate t ...
vol11 issue 2 - Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Nutrition
... postmenopausal women aged 50-65 years in Kuala Lumpur. The results showed that the mean calcium intake from the dietary records was 447 ± 168 mg/day and 499 ± 211 mg/day from the FFQ. The mean difference in intake by the two methods was 51.3 mg (95% CI = - 30.8 - 77.9; SD = 181.2, P> 0.05), which di ...
... postmenopausal women aged 50-65 years in Kuala Lumpur. The results showed that the mean calcium intake from the dietary records was 447 ± 168 mg/day and 499 ± 211 mg/day from the FFQ. The mean difference in intake by the two methods was 51.3 mg (95% CI = - 30.8 - 77.9; SD = 181.2, P> 0.05), which di ...
Food Labeling 2 PPT
... 40 or more square inches of available label space and approximately 3 inches or more of continuous vertical space. Exact specifications of the basic label format can be found in 21 CFR 101.9 (d) and 9 CFR 317.309 (d). ...
... 40 or more square inches of available label space and approximately 3 inches or more of continuous vertical space. Exact specifications of the basic label format can be found in 21 CFR 101.9 (d) and 9 CFR 317.309 (d). ...
Lesson 3
... Nutrition and Older Adults • Most older adults can get all the calories and nutrients they need by following the recommendations in the Dietary Guidelines and the Food Guide Pyramid. • In certain cases, health care providers might recommend a dietary supplement to help meet older adults’ nutrient ne ...
... Nutrition and Older Adults • Most older adults can get all the calories and nutrients they need by following the recommendations in the Dietary Guidelines and the Food Guide Pyramid. • In certain cases, health care providers might recommend a dietary supplement to help meet older adults’ nutrient ne ...
The Epidemiology of Global Micronutrient Deficiencies
... the Determinants of Undernutrition (fig. 2) [6]. The underlying causes that contribute to the immediate causes include food insecurity, inadequate care or feeding practices, and an unhealthy environment with inadequate access to health services. Nutritional status is greatly impacted by infection [9 ...
... the Determinants of Undernutrition (fig. 2) [6]. The underlying causes that contribute to the immediate causes include food insecurity, inadequate care or feeding practices, and an unhealthy environment with inadequate access to health services. Nutritional status is greatly impacted by infection [9 ...
Instructor`s Guide
... caused by reactive oxygen molecules called free radicals. ATP: Adenosine Triphosphate. The form of energy that cells can use. electroyltes: Substances that help maintain the body’s fluid balance. enrichment: Process of adding back nutrients into foods that lost them during processing. Could also ind ...
... caused by reactive oxygen molecules called free radicals. ATP: Adenosine Triphosphate. The form of energy that cells can use. electroyltes: Substances that help maintain the body’s fluid balance. enrichment: Process of adding back nutrients into foods that lost them during processing. Could also ind ...
Malnutrition
Malnutrition or malnourishment is a condition that results from eating a diet in which nutrients are either not enough or are too much such that the diet causes health problems. It may involve calories, protein, carbohydrates, vitamins or minerals. Not enough nutrients is called undernutrition or undernourishment while too much is called overnutrition. Malnutrition is often used specifically to refer to undernutrition where there is not enough calories, protein, or micronutrients. If undernutrition occurs during pregnancy, or before two years of age, it may result in permanent problems with physical and mental development. Extreme undernourishment, known as starvation, may have symptoms that include: a short height, thin body, very poor energy levels, and swollen legs and abdomen. People also often get infections and are frequently cold. The symptoms of micronutrient deficiencies depend on the micronutrient that is lacking.Undernourishment is most often due to not enough high-quality food being available to eat. This is often related to high food prices and poverty. A lack of breast feeding may contribute, as may a number of infectious diseases such as: gastroenteritis, pneumonia, malaria, and measles, which increase nutrient requirements. There are two main types of undernutrition: protein-energy malnutrition and dietary deficiencies. Protein-energy malnutrition has two severe forms: marasmus (a lack of protein and calories) and kwashiorkor (a lack of just protein). Common micronutrient deficiencies include: a lack of iron, iodine, and vitamin A. During pregnancy, due to the body's increased need, deficiencies may become more common. In some developing countries, overnutrition in the form of obesity is beginning to present within the same communities as undernutrition. Other causes of malnutrition include anorexia nervosa and bariatric surgery.Efforts to improve nutrition are some of the most effective forms of development aid. Breastfeeding can reduce rates of malnutrition and death in children, and efforts to promote the practice increase the rates of breastfeeding. In young children, providing food (in addition to breastmilk) between six months and two years of age improves outcomes. There is also good evidence supporting the supplementation of a number of micronutrients to women during pregnancy and among young children in the developing world. To get food to people who need it most, both delivering food and providing money so people can buy food within local markets are effective. Simply feeding students at school is insufficient. Management of severe malnutrition within the person's home with ready-to-use therapeutic foods is possible much of the time. In those who have severe malnutrition complicated by other health problems, treatment in a hospital setting is recommended. This often involves managing low blood sugar and body temperature, addressing dehydration, and gradual feeding. Routine antibiotics are usually recommended due to the high risk of infection. Longer-term measures include: improving agricultural practices, reducing poverty, improving sanitation, and the empowerment of women.There were 925 million undernourished people in the world in 2010. This is an increase of 80 million people since 1990 or a 2.5% drop in the percentage of undernourished people. Another billion people are estimated to have a lack of vitamins and minerals. In 2013, protein-energy malnutrition was estimated to have resulted in 469,000 deaths—down from 510,000 deaths in 1990. Other nutritional deficiencies, which include iodine deficiency and iron deficiency anemia, result in another 84,000 deaths. In 2010, malnutrition was the cause of 1.4% of all disability adjusted life years. About a third of deaths in children are believed to be due to undernutrition, although the deaths are rarely labelled as such. In 2010, it was estimated to have contributed to about 1.5 million deaths in women and children, though some estimate the number may be greater than 3 million. An additional 165 million children have stunted growth from malnutrition. Undernutrition is more common in developing countries. Certain groups have higher rates of undernutrition, including women—in particular while pregnant or breastfeeding—children under five years of age, and the elderly. In the elderly, undernutrition becomes more common due to physical, psychological, and social factors.