Hierarchical Reflection
... other hand we want the set of normal forms to be as small as possible. We achieve this by requiring the polynomials and monomials to be sorted ; furthermore, no two monomials in a polynomial can have exactly the same set of variables. Thus normal forms for polynomials will be unique. For this we hav ...
... other hand we want the set of normal forms to be as small as possible. We achieve this by requiring the polynomials and monomials to be sorted ; furthermore, no two monomials in a polynomial can have exactly the same set of variables. Thus normal forms for polynomials will be unique. For this we hav ...
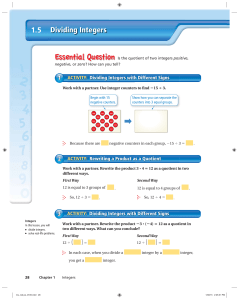
Dividing Integers 1.5
... 15. IN YOUR OWN WORDS Is the quotient of two integers positive, negative, or zero? How can you tell? 16. STRUCTURE Write general rules for dividing (a) two integers with the same sign and (b) two integers with different signs. ...
... 15. IN YOUR OWN WORDS Is the quotient of two integers positive, negative, or zero? How can you tell? 16. STRUCTURE Write general rules for dividing (a) two integers with the same sign and (b) two integers with different signs. ...
The Essential Dimension of Finite Group Schemes Corso di Laurea Magistrale in Matematica
... In the second chapter we will develop the elementary theory of algebraic groups (here meaning affine group schemes of finite type over a field) concentrating on the parts of interest for our aim: action of algebraic groups over varieties and representations. In the third the definition of essential ...
... In the second chapter we will develop the elementary theory of algebraic groups (here meaning affine group schemes of finite type over a field) concentrating on the parts of interest for our aim: action of algebraic groups over varieties and representations. In the third the definition of essential ...
4 Ideals in commutative rings
... ideal in I bigger than I, not necessarily that I contains every ideal in I. ...
... ideal in I bigger than I, not necessarily that I contains every ideal in I. ...
Solving Problems with Magma
... met by the books An Introduction to Magma and Handbook of Magma Functions. Even the most keen inductive learners will not learn all there is to know about Magma from the present work. What Solving Problems with Magma does offer is a large collection of real-world algebraic problems, solved using the ...
... met by the books An Introduction to Magma and Handbook of Magma Functions. Even the most keen inductive learners will not learn all there is to know about Magma from the present work. What Solving Problems with Magma does offer is a large collection of real-world algebraic problems, solved using the ...
here - Halfaya
... Lemma 2.1.1. If a ring R has characteristic n, then (n) = 0, and Z/nZ ,→ R. Proof. This is immediate. Note also if the ring has characteristic zero, then Z/0Z = Z ,→ R. Lemma 2.1.2. If a ring R is a domain, then either it has characteristic 0 or charistic p, for some prime p ∈ N. Proof. Suppose doma ...
... Lemma 2.1.1. If a ring R has characteristic n, then (n) = 0, and Z/nZ ,→ R. Proof. This is immediate. Note also if the ring has characteristic zero, then Z/0Z = Z ,→ R. Lemma 2.1.2. If a ring R is a domain, then either it has characteristic 0 or charistic p, for some prime p ∈ N. Proof. Suppose doma ...
9 Solutions for Section 2
... Choose a ∈ I with a 6= 0. Since every non-zero element of R is invertible we have 1 = aa−1 ∈ I and hence I = R (for then, if r ∈ R we have r = 1r = a(a−1 r ∈ I). Conversely if there are no right ideals except {0} and R, take a ∈ R with a 6= 0. Certainly the right ideal, aR, generated by a is non-ze ...
... Choose a ∈ I with a 6= 0. Since every non-zero element of R is invertible we have 1 = aa−1 ∈ I and hence I = R (for then, if r ∈ R we have r = 1r = a(a−1 r ∈ I). Conversely if there are no right ideals except {0} and R, take a ∈ R with a 6= 0. Certainly the right ideal, aR, generated by a is non-ze ...