Answer key for the worksheets
... b. If these people become parents, what are the chances that their children will have CF? What about the chances they will be carriers? no chance of having the disease; 50% chance of carriers c. Does it make any difference if the children are male or female? no Huntington’s disease results from a g ...
... b. If these people become parents, what are the chances that their children will have CF? What about the chances they will be carriers? no chance of having the disease; 50% chance of carriers c. Does it make any difference if the children are male or female? no Huntington’s disease results from a g ...
Mendelian Genetics
... The F1 plants must have inherited genetic factors from both parents Therefore, each plant must possess two genetic factors (alleles) for each characteristic The two alleles in each plant separate when gametes are formed This occurs with equal probability One allele is the dominant form; th ...
... The F1 plants must have inherited genetic factors from both parents Therefore, each plant must possess two genetic factors (alleles) for each characteristic The two alleles in each plant separate when gametes are formed This occurs with equal probability One allele is the dominant form; th ...
PROBABILITY
... Dominant traits usually appear more often in a population (except widows peak and cleft chin). For example, having free earlobes is the dominant form of the trait; so it will show up more often in a population. When there is at least one dominant gene in the pair, then the dominant allele masks, or ...
... Dominant traits usually appear more often in a population (except widows peak and cleft chin). For example, having free earlobes is the dominant form of the trait; so it will show up more often in a population. When there is at least one dominant gene in the pair, then the dominant allele masks, or ...
Quantitative genetics
... • G - Genetic factors, E - environmental factors, GxE interactions, A - additive effects, D – dominance (alleles at one locus), E – epistasis (alles at different loci), C common and E - non-shared environment (children in one family are different) • EEE... ...
... • G - Genetic factors, E - environmental factors, GxE interactions, A - additive effects, D – dominance (alleles at one locus), E – epistasis (alles at different loci), C common and E - non-shared environment (children in one family are different) • EEE... ...
Genetics Chapter 10
... alleles will be passed on during reproduction by each parent. Thus, we separate the parental gametes in order to produce offspring that have the normal 2 alleles per gene. Each offspring has it’s own unique combination of alleles, so chance has no memory in genetics and all offspring have equal chan ...
... alleles will be passed on during reproduction by each parent. Thus, we separate the parental gametes in order to produce offspring that have the normal 2 alleles per gene. Each offspring has it’s own unique combination of alleles, so chance has no memory in genetics and all offspring have equal chan ...
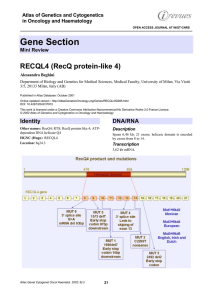
Gene Section RECQL4 (RecQ protein-like 4) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... helicases and contains from aa 476 to 824 an helicase domain with a potential ATP binding site from aa 502 to 509, and the DEAH box from aa 605 to 608. ...
... helicases and contains from aa 476 to 824 an helicase domain with a potential ATP binding site from aa 502 to 509, and the DEAH box from aa 605 to 608. ...
File - Wk 1-2
... Alters the subsequent reading frame by inserting or deleting one or more bases (within a set of three). This alters the reading frame (triplet grouping) of the genetic message, causing an entirely new series of AA’s to be coded after the site of the mutation. All nucleotides downstream of the mutati ...
... Alters the subsequent reading frame by inserting or deleting one or more bases (within a set of three). This alters the reading frame (triplet grouping) of the genetic message, causing an entirely new series of AA’s to be coded after the site of the mutation. All nucleotides downstream of the mutati ...
Codominance/Incomplete Dominance
... Determining the effect of any one of these genes is difficult. Due to independent assortment and crossover during meiosis, many different combinations appear in offspring. Familiar examples include growth rate, fertility, and carcass merit. All of these characteristics have a degree of intermediate ...
... Determining the effect of any one of these genes is difficult. Due to independent assortment and crossover during meiosis, many different combinations appear in offspring. Familiar examples include growth rate, fertility, and carcass merit. All of these characteristics have a degree of intermediate ...
ESSAY 1: CONCEPTION
... segments that are coding for enzymes that tell the body what to do, and even those short segments are sometimes controlled by external factors. The segments simply code for proteins and send them around the body, but the particular combinations of proteins cannot be predicted. There are also many ‘s ...
... segments that are coding for enzymes that tell the body what to do, and even those short segments are sometimes controlled by external factors. The segments simply code for proteins and send them around the body, but the particular combinations of proteins cannot be predicted. There are also many ‘s ...
скачати - ua
... The interaction between genetic variation and natural selection is one of the most important concepts in modern biology. The product of this interaction, evolution, which is a change in a population?s allele frequency, is responsible for the great complexity and diversity of life seen on earth today ...
... The interaction between genetic variation and natural selection is one of the most important concepts in modern biology. The product of this interaction, evolution, which is a change in a population?s allele frequency, is responsible for the great complexity and diversity of life seen on earth today ...
Chapter 9
... The following slides present data which supports the views taken in Figures 9-4 and 9-6 of the textbook. These data present empirical evidence supporting 1) the existence of modifier or minor effect genes, 2) the fact that they outnumber the major effect genes, and 3) the important role they play in ...
... The following slides present data which supports the views taken in Figures 9-4 and 9-6 of the textbook. These data present empirical evidence supporting 1) the existence of modifier or minor effect genes, 2) the fact that they outnumber the major effect genes, and 3) the important role they play in ...
Document
... #ways to obtain that outcome / total # possible outcomes 2. The product rule = the "AND" rule For 2 independent events, the probability of observing 2 particular outcomes (outcome 1 AND outcome 2) is the PRODUCT of their independent probabilities. 3. The addition rule = the "OR" rule The probability ...
... #ways to obtain that outcome / total # possible outcomes 2. The product rule = the "AND" rule For 2 independent events, the probability of observing 2 particular outcomes (outcome 1 AND outcome 2) is the PRODUCT of their independent probabilities. 3. The addition rule = the "OR" rule The probability ...
Allopatric and sympatric speciation
... thought to be rare in animals? • The problem is how to avoid intermediate genotypes that will function as bridges for gene flow, which would eliminate the difference. • Needed: polymorphism and assortative mating. • Problem: if these two are not genetically coupled, recombination will eliminate the ...
... thought to be rare in animals? • The problem is how to avoid intermediate genotypes that will function as bridges for gene flow, which would eliminate the difference. • Needed: polymorphism and assortative mating. • Problem: if these two are not genetically coupled, recombination will eliminate the ...
Chapter 3bF
... greater spatial ability is associated with her sneak egg laying behavior in the nests of other bird species. ...
... greater spatial ability is associated with her sneak egg laying behavior in the nests of other bird species. ...
Chapter 14: Mendel and the Gene Idea
... • Because of the different effects of dominant and recessive alleles, an organism’s traits do not always reveal its genetic composition • Therefore, we distinguish between an organism’s ____________________, or physical appearance, and its _________________________, or genetic makeup • In the exampl ...
... • Because of the different effects of dominant and recessive alleles, an organism’s traits do not always reveal its genetic composition • Therefore, we distinguish between an organism’s ____________________, or physical appearance, and its _________________________, or genetic makeup • In the exampl ...
Chapter 8 Human Genetics and Biotechnology Worksheets
... The remaining pair of human chromosomes consists of the sex chromosomes, X and Y. Females have two X chromosomes, and males have one X and one Y chromosome. In females, one of the X chromosomes in each cell is inactivated and known as a Barr body. This ensures that females, like males, have only one ...
... The remaining pair of human chromosomes consists of the sex chromosomes, X and Y. Females have two X chromosomes, and males have one X and one Y chromosome. In females, one of the X chromosomes in each cell is inactivated and known as a Barr body. This ensures that females, like males, have only one ...
molecular diagnosis in lgmd2a: mutation analysis or
... very high when patients show a complete calpain-3 deficiency (84.4%) and progressively decreases with the amount of protein; this new data offers an important tool for genetic counseling when only protein data are available. A total of 47 different CAPN-3 gene mutations were detected, 22 of which ar ...
... very high when patients show a complete calpain-3 deficiency (84.4%) and progressively decreases with the amount of protein; this new data offers an important tool for genetic counseling when only protein data are available. A total of 47 different CAPN-3 gene mutations were detected, 22 of which ar ...
Principles & Patterns of inheritance ppt
... • hybrid offspring - receives different forms of a genetic trait from each parent ...
... • hybrid offspring - receives different forms of a genetic trait from each parent ...
coding and non-coding functions of the genome
... “That made research very easy, because we could focus on the 2% of the genome that is made up of genes and discard the other 98%. But we were wrong,” he said. Although scientists had suspected this was a mistake for some time, a large international consortium turned this dogma on its head in 2012. T ...
... “That made research very easy, because we could focus on the 2% of the genome that is made up of genes and discard the other 98%. But we were wrong,” he said. Although scientists had suspected this was a mistake for some time, a large international consortium turned this dogma on its head in 2012. T ...
Midterm 2 key
... What micro-evolutionary process could be responsible for causing the differences in the relative amount of expression of the two genes that you indicated in your answer above? (2) Mutation, specifically to the regulatory gene that controls how long each gene is turned on Bird beak morphology has a l ...
... What micro-evolutionary process could be responsible for causing the differences in the relative amount of expression of the two genes that you indicated in your answer above? (2) Mutation, specifically to the regulatory gene that controls how long each gene is turned on Bird beak morphology has a l ...
Biology Final Study Guide
... other factors are necessary? Explain how natural selection causes some traits to become more common in a population over several generations. 49. Why are “useless” (vestigial) body parts (like leg and pelvic bones in a whale) significant, in light of evolution? 50. Why is mutation important for evol ...
... other factors are necessary? Explain how natural selection causes some traits to become more common in a population over several generations. 49. Why are “useless” (vestigial) body parts (like leg and pelvic bones in a whale) significant, in light of evolution? 50. Why is mutation important for evol ...
Does evolutionary theory need a rethink?
... its first appearance5,6. In other words, often it is the trait that comes The core of current evolutionary theory was forged in the 1930s and first; genes that cement it follow, sometimes several generations later5. 1940s. It combined natural selection, genetics and other fields into a Studies of fi ...
... its first appearance5,6. In other words, often it is the trait that comes The core of current evolutionary theory was forged in the 1930s and first; genes that cement it follow, sometimes several generations later5. 1940s. It combined natural selection, genetics and other fields into a Studies of fi ...
COMMENT
... its first appearance5,6. In other words, often it is the trait that comes The core of current evolutionary theory was forged in the 1930s and first; genes that cement it follow, sometimes several generations later5. 1940s. It combined natural selection, genetics and other fields into a Studies of fi ...
... its first appearance5,6. In other words, often it is the trait that comes The core of current evolutionary theory was forged in the 1930s and first; genes that cement it follow, sometimes several generations later5. 1940s. It combined natural selection, genetics and other fields into a Studies of fi ...