No Slide Title
... A consequence of human mobility Biotic effects on natural species assemblies Parasite release Particularly problematic on islands Introduction of natural enemies may work, but .. ...
... A consequence of human mobility Biotic effects on natural species assemblies Parasite release Particularly problematic on islands Introduction of natural enemies may work, but .. ...
Slide 1
... Separation of the two strands of the DNA double helix. After the two strands are separated, new matching DNA strand is formed one base at a time for each of the old DNA strands. The result is two identical DNA double helixes. DNA splits apart ...
... Separation of the two strands of the DNA double helix. After the two strands are separated, new matching DNA strand is formed one base at a time for each of the old DNA strands. The result is two identical DNA double helixes. DNA splits apart ...
Cloning
... Possible reasons for these results include: Epigenetic changes in chromatin (acetylation of ...
... Possible reasons for these results include: Epigenetic changes in chromatin (acetylation of ...
B2.7 Inheritance and Speciation Objectives
... 5. Be able to suggest reasons why scientists cannot be certain about how life began on Earth, including the uncertainty arising from the lack of enough valid and reliable evidence 6. Know that extinction may be caused by: changes to the environment over geological time new predators new diseas ...
... 5. Be able to suggest reasons why scientists cannot be certain about how life began on Earth, including the uncertainty arising from the lack of enough valid and reliable evidence 6. Know that extinction may be caused by: changes to the environment over geological time new predators new diseas ...
a5_1_1-1_done
... 20. Tumor-suppressing genes code for proteins with what function? Preventing uncontrolled cell division. Cancer can be caused by a mutation in a tumor-suppressing gene that causes there to be too little or too much of the tumor-suppressing protein made? Too little. 21. Explain how mutations that occ ...
... 20. Tumor-suppressing genes code for proteins with what function? Preventing uncontrolled cell division. Cancer can be caused by a mutation in a tumor-suppressing gene that causes there to be too little or too much of the tumor-suppressing protein made? Too little. 21. Explain how mutations that occ ...
HGNC future plans
... Manually curate gene families with complicated orthology relationships across vertebrate species, develop new synteny and BLAST filtering tools, begin with UGT and GST families. ...
... Manually curate gene families with complicated orthology relationships across vertebrate species, develop new synteny and BLAST filtering tools, begin with UGT and GST families. ...
Booklet 3
... (b) Complete the genetic diagram below to show how two parents who do not have PKU can have some children who have PKU and some children who do not. Use the letters G and g to represent the alleles. parental phenotypes: ...
... (b) Complete the genetic diagram below to show how two parents who do not have PKU can have some children who have PKU and some children who do not. Use the letters G and g to represent the alleles. parental phenotypes: ...
MUTATIONS
... Mutations are the source of the altered versions of genes that provide the raw material for evolution. Most mutations have no effect on the organism, especially among the eukaryotes, because a large portion of the DNA is not in genes and thus does not affect the organism’s phenotype. Only a sm ...
... Mutations are the source of the altered versions of genes that provide the raw material for evolution. Most mutations have no effect on the organism, especially among the eukaryotes, because a large portion of the DNA is not in genes and thus does not affect the organism’s phenotype. Only a sm ...
Ch 24 - LPS.org
... • Speciation, the origin of new species, is at the focal point of evolutionary theory • Evolutionary theory must explain how new species originate and how populations evolve • Microevolution consists of adaptations that evolve within a population, confined to one gene pool • Macroevolution refers t ...
... • Speciation, the origin of new species, is at the focal point of evolutionary theory • Evolutionary theory must explain how new species originate and how populations evolve • Microevolution consists of adaptations that evolve within a population, confined to one gene pool • Macroevolution refers t ...
Punnett Squares
... PUNNETT SQUARES A punnett square is a diagram used to predict the outcome of a breeding experiment. ...
... PUNNETT SQUARES A punnett square is a diagram used to predict the outcome of a breeding experiment. ...
1 - Acpsd.net
... offspring would be Red and white in the same flower. Incomplete dominance- offspring is in-between that of the parents. Ex. Cross between Red and white makes a Pink flower. Complete dominance – One allele will be completely dominant over the recessive. Ex. Red parent crossed with a white parent and ...
... offspring would be Red and white in the same flower. Incomplete dominance- offspring is in-between that of the parents. Ex. Cross between Red and white makes a Pink flower. Complete dominance – One allele will be completely dominant over the recessive. Ex. Red parent crossed with a white parent and ...
11.2 Worksheet
... Where two or more alleles for a gene exist, some may be dominant and others recessive. In sexually reproducing organisms, offspring receive a copy of each gene from each parent. The alleles segregate when forming gametes. Alleles for different genes usually segregate independently. ...
... Where two or more alleles for a gene exist, some may be dominant and others recessive. In sexually reproducing organisms, offspring receive a copy of each gene from each parent. The alleles segregate when forming gametes. Alleles for different genes usually segregate independently. ...
013368718X_CH11_159
... Where two or more alleles for a gene exist, some may be dominant and others recessive. In sexually reproducing organisms, offspring receive a copy of each gene from each parent. The alleles segregate when forming gametes. Alleles for different genes usually segregate independently. ...
... Where two or more alleles for a gene exist, some may be dominant and others recessive. In sexually reproducing organisms, offspring receive a copy of each gene from each parent. The alleles segregate when forming gametes. Alleles for different genes usually segregate independently. ...
mbv4160_mbv9160_exam_2011_final
... 7) What is the genetic cause of the hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer syndrome (also called Lynch syndrome)? 8) What type of DNA sequences is prone for mutations if the mismatch repair system is defect? How can such mutations indirectly cause cancer? IV High-throughput sequencing 9) What is ...
... 7) What is the genetic cause of the hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer syndrome (also called Lynch syndrome)? 8) What type of DNA sequences is prone for mutations if the mismatch repair system is defect? How can such mutations indirectly cause cancer? IV High-throughput sequencing 9) What is ...
Pattern recognition Using Genetic Algorithm
... which leads to a decision. The quality of this decision can only be measured by statistic relating to the number of "good" and "bad" classifications. Also pattern recognition can be defined as an area of science concerned with discriminating objects on the basis of information available about them. ...
... which leads to a decision. The quality of this decision can only be measured by statistic relating to the number of "good" and "bad" classifications. Also pattern recognition can be defined as an area of science concerned with discriminating objects on the basis of information available about them. ...
Chapter 7 Darwin, Mendel and Theories of Inheritance
... • Discontinuous Variation – In general, alleles represent specific DNA sequences, and are passed unchanged from one generation to the next, so long as no mutations occur within the sequence – However, there can be variation in the phenotype, even when the genotype is constant • Other genes (alleles ...
... • Discontinuous Variation – In general, alleles represent specific DNA sequences, and are passed unchanged from one generation to the next, so long as no mutations occur within the sequence – However, there can be variation in the phenotype, even when the genotype is constant • Other genes (alleles ...
reading guide
... There seem to be two categories of genes involved in cancer: oncogenes, which code for proteins to regulate cell growth, and should not be stuck “on,” much like the accelerator in a car; and tumor-suppressor genes, which work like the brakes on a car and must function! Let’s begin with a look at the ...
... There seem to be two categories of genes involved in cancer: oncogenes, which code for proteins to regulate cell growth, and should not be stuck “on,” much like the accelerator in a car; and tumor-suppressor genes, which work like the brakes on a car and must function! Let’s begin with a look at the ...
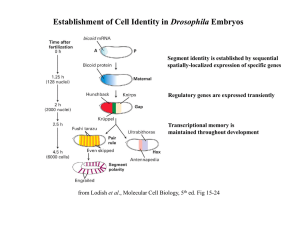
NOTE: The provided figures may be useful and beneficial
... 2. Explain the Inquiry & Experiment in Figure 15.4. Include in your answer an explanation regarding why only the males have white eyes. Is it possible for females to have white eyes? Provide a Punnett square as evidence to support your answer. (CUES: dominant, recessive, sex-linked.) 3. Steroid horm ...
... 2. Explain the Inquiry & Experiment in Figure 15.4. Include in your answer an explanation regarding why only the males have white eyes. Is it possible for females to have white eyes? Provide a Punnett square as evidence to support your answer. (CUES: dominant, recessive, sex-linked.) 3. Steroid horm ...
Volume 8, 10 December 2009, Article number63 Mutations in the
... investigated in the similar pattern. Single mutation of V255M in the HNF4α gene was detected. This known mutation was found in 8 of 30 patients and 3 of 21 individuals in relatives. Fifty healthy control subjects did not show any mutation. Here, it is indicated that the prevalence of HNF4α mutation ...
... investigated in the similar pattern. Single mutation of V255M in the HNF4α gene was detected. This known mutation was found in 8 of 30 patients and 3 of 21 individuals in relatives. Fifty healthy control subjects did not show any mutation. Here, it is indicated that the prevalence of HNF4α mutation ...
lecture2
... The human Y chromosome contains 7 sets of genes — each set containing from 2 to 6 nearlyidentical genes — oriented back-to-back or head-to-head; that is, they are inverted repeats like the portion shown here. (The dashes represent the thousands of base pairs that separate adjacent palindromes.) 5' . ...
... The human Y chromosome contains 7 sets of genes — each set containing from 2 to 6 nearlyidentical genes — oriented back-to-back or head-to-head; that is, they are inverted repeats like the portion shown here. (The dashes represent the thousands of base pairs that separate adjacent palindromes.) 5' . ...
Epigenetics-2015
... Prevents changes in cell identity by preserving transcription patterns Chromatin is altered in a heritable manner ...
... Prevents changes in cell identity by preserving transcription patterns Chromatin is altered in a heritable manner ...
Keystone Review Packet Selected Topics Winter 2015 #4 Keystone
... B. reduced pesticide and herbicide use C. improved agricultural yield and profit D. increased genetic variation and diversity 12. A cell in the process of cell division contains the normal chromosome number. Each chromosome consists of two identical sister chromatids. During which stages and process ...
... B. reduced pesticide and herbicide use C. improved agricultural yield and profit D. increased genetic variation and diversity 12. A cell in the process of cell division contains the normal chromosome number. Each chromosome consists of two identical sister chromatids. During which stages and process ...
p2 - Glenelg High School
... does each of these formulas mean, and how are the formulas derived? p + q = 1: If you add all the dominant alleles for a gene to all the recessive alleles for the gene, you get all of the alleles for that gene, or 100% of the alleles for the gene. (Note: This assumes the gene has only two alleles.) ...
... does each of these formulas mean, and how are the formulas derived? p + q = 1: If you add all the dominant alleles for a gene to all the recessive alleles for the gene, you get all of the alleles for that gene, or 100% of the alleles for the gene. (Note: This assumes the gene has only two alleles.) ...