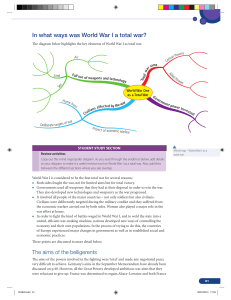
World War I
... how to overcome the defensive advantage provided by trenches. For the first year the only strategy tried by the general was sending large waves of soldiers through no man’s land. This unfortunately only resulted in a large number of casualties. ...
... how to overcome the defensive advantage provided by trenches. For the first year the only strategy tried by the general was sending large waves of soldiers through no man’s land. This unfortunately only resulted in a large number of casualties. ...
Causes, Practices and Effects of War Pearson Baccaularete for IB
... The role of civilians The impact of the fighting on civilians As you have read earlier in this chapter, civilians were also affected by the actual fighting, and there were many casualties as a result of the new technologies available to both sides. Paris was shelled from a distance of 126km by the ...
... The role of civilians The impact of the fighting on civilians As you have read earlier in this chapter, civilians were also affected by the actual fighting, and there were many casualties as a result of the new technologies available to both sides. Paris was shelled from a distance of 126km by the ...
WWI Trenches Reading Activity
... the earth and two holding and tying the bags. The men stacking the filled bags worked in pairs and were expected to move sixty bags an hour. Research by the British Army suggested that a typical bullet used in the First World War would only penetrate fifteen inches into a sandbag. Soldiers were inst ...
... the earth and two holding and tying the bags. The men stacking the filled bags worked in pairs and were expected to move sixty bags an hour. Research by the British Army suggested that a typical bullet used in the First World War would only penetrate fifteen inches into a sandbag. Soldiers were inst ...
The United States in World War I
... supported the Allies, as a large number of German immigrants lived throughout the United States. On August 4, 1914 President Woodrow Wilson issued a proclamation of American neutrality in the war. From American Neutrality to Intervention Even though many Americans were sympathetic to the cause of th ...
... supported the Allies, as a large number of German immigrants lived throughout the United States. On August 4, 1914 President Woodrow Wilson issued a proclamation of American neutrality in the war. From American Neutrality to Intervention Even though many Americans were sympathetic to the cause of th ...
World War 1 Main Idea:
... its forces in the east. Meanwhile, the war on the Western Front settled into a stalemate. By early 1915, opposing armies on the Western Front had dug miles of parallel trenches to protect themselves from enemy fire. This set the stage for what became known as trench warfare. The German commander, Ge ...
... its forces in the east. Meanwhile, the war on the Western Front settled into a stalemate. By early 1915, opposing armies on the Western Front had dug miles of parallel trenches to protect themselves from enemy fire. This set the stage for what became known as trench warfare. The German commander, Ge ...
World War I
... and through the barbed wire, which was supposed to have been cut, but it hadn't. We had very little artillery bombardment before we went over. ...Some of our chaps were dropping down at the side of me, but I kept going. I got to the German barbed wire, I got through that all right, and jumped into ...
... and through the barbed wire, which was supposed to have been cut, but it hadn't. We had very little artillery bombardment before we went over. ...Some of our chaps were dropping down at the side of me, but I kept going. I got to the German barbed wire, I got through that all right, and jumped into ...
US History Top 100
... May 1915 – U-boats sink the Lusitania Sept. 1915 – Germany promises not to sink unarmed ships March 1916 – Germany sinks the Sussex May 1916 – Germany promises not to sink unarmed ships Jan. 1917 – Zimmerman note is intercepted Feb. 1917 – Germany resumes unrestricted submarine warfare • April 1917 ...
... May 1915 – U-boats sink the Lusitania Sept. 1915 – Germany promises not to sink unarmed ships March 1916 – Germany sinks the Sussex May 1916 – Germany promises not to sink unarmed ships Jan. 1917 – Zimmerman note is intercepted Feb. 1917 – Germany resumes unrestricted submarine warfare • April 1917 ...
World History Text: Patterns of Interaction Cha
... Why It Matters Now: Ethnic conflict in the Balkan region, which helped start the war, continued to erupt in that area in the 1990s.. Section 2: War Consumes Europe Main Idea: One European nation after another was drawn into a large and industrialized war that resulted in many casualties. Why It Matt ...
... Why It Matters Now: Ethnic conflict in the Balkan region, which helped start the war, continued to erupt in that area in the 1990s.. Section 2: War Consumes Europe Main Idea: One European nation after another was drawn into a large and industrialized war that resulted in many casualties. Why It Matt ...
First world war
... preceding years began to give way, as the allies combined infantry, artillery, tanks, and aircraft more effectively, demonstrated in the Australian capture of Hamel spur on 4 July 1918. The allied offensive, beginning on 8 August at Amiens, also contributed to Australian successes at Mont St Quent ...
... preceding years began to give way, as the allies combined infantry, artillery, tanks, and aircraft more effectively, demonstrated in the Australian capture of Hamel spur on 4 July 1918. The allied offensive, beginning on 8 August at Amiens, also contributed to Australian successes at Mont St Quent ...
World War I The Great War
... German offered to support Austria-Hungary Austria sent Serbia and ultimatum ...
... German offered to support Austria-Hungary Austria sent Serbia and ultimatum ...
The Road to War • Main Idea 1: Many factors contributed to the
... The French army blocked the German advance at the Marne River, east of Paris, in September 1914. ...
... The French army blocked the German advance at the Marne River, east of Paris, in September 1914. ...
powerpoint slides
... April 1917: Entry of the United States The United States tried to remain neutral Naval Conflict between Germany and Britain Sinking of the Lusitania, May 7, 1915 Return to unrestricted submarine warfare, January 1917 United States enters the war, April 6, 1917 Bolshevik Revolution, 1917 Italian defe ...
... April 1917: Entry of the United States The United States tried to remain neutral Naval Conflict between Germany and Britain Sinking of the Lusitania, May 7, 1915 Return to unrestricted submarine warfare, January 1917 United States enters the war, April 6, 1917 Bolshevik Revolution, 1917 Italian defe ...
File - Mr. Costanzo
... Clemnceau of France, and Vittorio Orlando of Italy? 3. What types of new weapons were the Germans not allowed to have in their Army and Navy due to the Treaty of Versailles? 4. How did Germans, especially Adolph Hitler feel about the Treaty of Versailles? ...
... Clemnceau of France, and Vittorio Orlando of Italy? 3. What types of new weapons were the Germans not allowed to have in their Army and Navy due to the Treaty of Versailles? 4. How did Germans, especially Adolph Hitler feel about the Treaty of Versailles? ...
The War Effort at Home
... In the spring of 1918, Germany began an allout offensive on the Western Front. More American soldiers began to arrive, and U.S. troops carried more of the burden of fighting. ...
... In the spring of 1918, Germany began an allout offensive on the Western Front. More American soldiers began to arrive, and U.S. troops carried more of the burden of fighting. ...
The United States and World War I
... The war began with Allies versus the Central Powers and six neutral countries. The Allies: 1. France 2. United Kingdom 3. Italy 4. Serbia 5. Russia 6. Romania 7. Greece 8. Portugal 9. Japan The Neutral 1. Spain 2. Norway 3. Belgium 4. Switzerland 5. Sweden 6. Denmark The Central Powers 1. Austria-H ...
... The war began with Allies versus the Central Powers and six neutral countries. The Allies: 1. France 2. United Kingdom 3. Italy 4. Serbia 5. Russia 6. Romania 7. Greece 8. Portugal 9. Japan The Neutral 1. Spain 2. Norway 3. Belgium 4. Switzerland 5. Sweden 6. Denmark The Central Powers 1. Austria-H ...
Harry Harrington
... For these activities they were equipped with a variety of explosives (including the first issues of plastic high explosive) timing devices and detonators. They were not, however, expected to attack enemy forces in strength, the small arms, revolvers and Sten guns, provided were for defence rather th ...
... For these activities they were equipped with a variety of explosives (including the first issues of plastic high explosive) timing devices and detonators. They were not, however, expected to attack enemy forces in strength, the small arms, revolvers and Sten guns, provided were for defence rather th ...
America joins the fight
... what country were most battles of the war on the Western Front fought? • 2. About how far were the Germans pushed back by the time of the armistice? How long did that take? ...
... what country were most battles of the war on the Western Front fought? • 2. About how far were the Germans pushed back by the time of the armistice? How long did that take? ...
00 Key Terms - 4-1
... Causes – in 1914, nationalism, militarism, imperialism, and entangling alliances combined with other factors to lead the nations of Europe into a brutal, global war Nationalism – devotion to one’s nation; in the late 19th century many Europeans began to reject the earlier idea of a nation as a colle ...
... Causes – in 1914, nationalism, militarism, imperialism, and entangling alliances combined with other factors to lead the nations of Europe into a brutal, global war Nationalism – devotion to one’s nation; in the late 19th century many Europeans began to reject the earlier idea of a nation as a colle ...
Chapter 19 Notes—World War I (1914
... control as both countries experienced multiple revolts from within their military structures. B. The war ended in the late fall of 1918, after the member countries of the Central Powers signed peace agreements. Germany was the last on November 11, 1918. As a result of these agreements, Austria-Hunga ...
... control as both countries experienced multiple revolts from within their military structures. B. The war ended in the late fall of 1918, after the member countries of the Central Powers signed peace agreements. Germany was the last on November 11, 1918. As a result of these agreements, Austria-Hunga ...
Modern American Fiction and World War I
... American soldiers found themselves in a unique position, war had changed them into men while their parents still saw them as boys----Most were unable to support themselves because the war had interrupted their lives. Now they came home after tasting the harsh reality of war and the freedom they foun ...
... American soldiers found themselves in a unique position, war had changed them into men while their parents still saw them as boys----Most were unable to support themselves because the war had interrupted their lives. Now they came home after tasting the harsh reality of war and the freedom they foun ...
World War I- The Great War
... British and French troops defeat Germany in the Battle of the Marne. The battle of the Marne pushed back the German offensive and destroyed Germany’s hopes for a quick victory on the Western Front. ...
... British and French troops defeat Germany in the Battle of the Marne. The battle of the Marne pushed back the German offensive and destroyed Germany’s hopes for a quick victory on the Western Front. ...
World War I - Ms. Mac`s Class
... the Ottoman Empire (Central Powers) Italy was part of the Triple Alliance with Germany, but joined the Entente after a secret agreement guaranteeing land from AustriaHungary ...
... the Ottoman Empire (Central Powers) Italy was part of the Triple Alliance with Germany, but joined the Entente after a secret agreement guaranteeing land from AustriaHungary ...
WWI
... the Somme River-1916 (France) • Trench warfare was deadly and neither side ever gained much ground • Verdun- French vs. Germans (over 300,000 killed) • Somme- British/French vs. Germans (approx. 1 million killed), only a few miles gained by each side ...
... the Somme River-1916 (France) • Trench warfare was deadly and neither side ever gained much ground • Verdun- French vs. Germans (over 300,000 killed) • Somme- British/French vs. Germans (approx. 1 million killed), only a few miles gained by each side ...
c. capitalism - Northview Middle School
... a. U.S. manufacturers build warships and airplanes. b. families make up for wages lost when their men went to war. c. U.S. soldiers who were fighting in France. d. the Allied war effort in the form of billions of dollars in loans. 9. Which of the following was a factor leading to a shortage of labor ...
... a. U.S. manufacturers build warships and airplanes. b. families make up for wages lost when their men went to war. c. U.S. soldiers who were fighting in France. d. the Allied war effort in the form of billions of dollars in loans. 9. Which of the following was a factor leading to a shortage of labor ...
Technology during World War I

Technology during World War I reflected a trend toward industrialism and the application of mass production methods to weapons and to the technology of warfare in general. This trend began fifty years prior to World War I during the U.S. Civil War, and continued through many smaller conflicts in which new weapons were tested.August 1914 marked the end of a relatively peaceful century in Europe with unprecedented invention and new science. The 19th-century vision of a peaceful future fed by ever-increasing prosperity through technology was largely shattered by the war's end; after the technological escalation during World War II, it was apparent that whatever the gains in prosperity and comfort due to technology applied to civilian use would always be under the shadow of the horrors of technology applied to warfare.The earlier years of the First World War can be characterized as a clash of 20th-century technology with 19th-century warfare in the form of ineffective battles with huge numbers of casualties on both sides. It was not until the final year of the war that the major armies made effective steps in revolutionizing matters of command and control and tactics to adapt to the modern battlefield, and started to harness the myriad new technologies to effective military purposes. Tactical reorganizations (such as shifting the focus of command from the 100+ man company to the 10+ man squad) went hand-in-hand with armored cars, the first submachine guns, and automatic rifles that could be carried and used by one man.