Meiosis
... gametes contained two sets of chromosomes, the zygote resulting from their union would have four sets of chromosomes. The number of chromosomes would continue to double with each new generation, which could result in the extinction of the species. However, this does not usually happen; the number of ...
... gametes contained two sets of chromosomes, the zygote resulting from their union would have four sets of chromosomes. The number of chromosomes would continue to double with each new generation, which could result in the extinction of the species. However, this does not usually happen; the number of ...
Word file (68 KB )
... To screen for dominant suppressors of cdk7 and to map the suppressors (Figures 1, 2), cdk7ts1 virgins were crossed to balanced deficiency males. Eggs were laid at room temperature for four to eight hours and then transferred to the incubator where they were reared between 25°C and 26°C. The two clas ...
... To screen for dominant suppressors of cdk7 and to map the suppressors (Figures 1, 2), cdk7ts1 virgins were crossed to balanced deficiency males. Eggs were laid at room temperature for four to eight hours and then transferred to the incubator where they were reared between 25°C and 26°C. The two clas ...
Reebops: A "Model" Organism for Teaching Genetic Concepts
... Usually, we observe less variation among close relatives than among individuals who are not closely related. For example, members of the same family may share visible traits, such as similar eye color, height, hair color and body type. They also may share similar, less visible traits, such as high b ...
... Usually, we observe less variation among close relatives than among individuals who are not closely related. For example, members of the same family may share visible traits, such as similar eye color, height, hair color and body type. They also may share similar, less visible traits, such as high b ...
Molecular pathogenesis of liver adenomas and FNH - HAL
... remained negative, as well as Kupffer cells and other sinusoidal cells in the HCA that did not over-express SAA. These results suggested that the inflammatory pathway was intrinsically deregulated in tumor hepatocytes, and inflammatory infiltrates could be a secondary effect. According to this hypot ...
... remained negative, as well as Kupffer cells and other sinusoidal cells in the HCA that did not over-express SAA. These results suggested that the inflammatory pathway was intrinsically deregulated in tumor hepatocytes, and inflammatory infiltrates could be a secondary effect. According to this hypot ...
10_EukaryoticMapping (plain)
... It is critical to get both the parental genotypes and the gene order correct; many students muff the mapping if they assume the genes are in alphabetical order or the order printed on the page. The largest two classes of offspring represent the parentals; absence of crossover is the most common even ...
... It is critical to get both the parental genotypes and the gene order correct; many students muff the mapping if they assume the genes are in alphabetical order or the order printed on the page. The largest two classes of offspring represent the parentals; absence of crossover is the most common even ...
MUTATION STUDIES AT THE A, LOCUS IN MAIZE. I. A
... seed. The frequency of a" dots is, therefore, 97.5/0.24 or 406 times as great as a. This is misleading as a large portion of the am dots are very small indicating that they must have occurred at a later stage when the number of cells in the aleurone, and therefore the number of chances of mutation, ...
... seed. The frequency of a" dots is, therefore, 97.5/0.24 or 406 times as great as a. This is misleading as a large portion of the am dots are very small indicating that they must have occurred at a later stage when the number of cells in the aleurone, and therefore the number of chances of mutation, ...
Genetic Algorithms
... Select two parents from old generation; /* biased to the fitter ones */ Recombine parents for two offspring; Compute fitness of offspring; Insert offspring in new generation ...
... Select two parents from old generation; /* biased to the fitter ones */ Recombine parents for two offspring; Compute fitness of offspring; Insert offspring in new generation ...
AP Biology Meiosis Chapter 13 Guided Notes
... Inheritance of Genes • ______________ are the units of heredity, and are made up of segments of DNA • Genes are passed to the next generation via reproductive cells called __________ (sperm and eggs) • Each gene has a specific location called a ____________ on a certain chromosome • Most DNA is pac ...
... Inheritance of Genes • ______________ are the units of heredity, and are made up of segments of DNA • Genes are passed to the next generation via reproductive cells called __________ (sperm and eggs) • Each gene has a specific location called a ____________ on a certain chromosome • Most DNA is pac ...
View/Open
... XY placentas being significantly larger than XX placentas and that such differences are independent of androgen effects [37]. Although the possession of one X chromosome rather than two leads to an increase in placental size, the underlying mechanism is still to be determined [37]. In mice and cattl ...
... XY placentas being significantly larger than XX placentas and that such differences are independent of androgen effects [37]. Although the possession of one X chromosome rather than two leads to an increase in placental size, the underlying mechanism is still to be determined [37]. In mice and cattl ...
Traits and Families
... A gene is a recipe for a protein. It is used by the cell to make that protein. In achondroplasia, the normal allele (FGRF3) codes for a protein (fibroblast growth factor) that is part of the structure of normal bones, including those of the arms and legs. The achondroplasia allele produces a protein ...
... A gene is a recipe for a protein. It is used by the cell to make that protein. In achondroplasia, the normal allele (FGRF3) codes for a protein (fibroblast growth factor) that is part of the structure of normal bones, including those of the arms and legs. The achondroplasia allele produces a protein ...
early RNs, crossing over initiates, then synapsis begins Chiasmata
... •Ac transposable element is autonomous: it encodes the gene for the transposase enzyme that allows it to jump. Some maize lines have active Ac. •Ds element is non -autonomous: it is a derivative of Ac but its transposase gene does not function. However, when Ac is present in same genome, Ds can jump ...
... •Ac transposable element is autonomous: it encodes the gene for the transposase enzyme that allows it to jump. Some maize lines have active Ac. •Ds element is non -autonomous: it is a derivative of Ac but its transposase gene does not function. However, when Ac is present in same genome, Ds can jump ...
Introduction to Genetics
... Early light microscope work on dividing cells revealed small (usually) rod-shaped structures that appear to pair during cell division. These are chromosomes. It was soon postulated that Genes are carried on chromosomes, because chromosomes behaved in a fashion that would generate Mendel’s laws. We n ...
... Early light microscope work on dividing cells revealed small (usually) rod-shaped structures that appear to pair during cell division. These are chromosomes. It was soon postulated that Genes are carried on chromosomes, because chromosomes behaved in a fashion that would generate Mendel’s laws. We n ...
Genetics Part I
... what degree they are inherited is still not clear in the case of certain traits. For example, there have been efforts to find a gene for criminality or addictive personalities, but none have been proven to date. Sometimes we blame genetics for something that in reality has nothing to do with genes. ...
... what degree they are inherited is still not clear in the case of certain traits. For example, there have been efforts to find a gene for criminality or addictive personalities, but none have been proven to date. Sometimes we blame genetics for something that in reality has nothing to do with genes. ...
Pairing of homologous regions in the mouse genome is associated
... cluster are expressed from the maternal allele, while a long noncoding RNA expressed from the paternal allele covers the locus to create a repressive compartment [15–17]. The maternal allele carries a germline methylation mark in the locus control region (KvDMR1), and monoallelic expression of the n ...
... cluster are expressed from the maternal allele, while a long noncoding RNA expressed from the paternal allele covers the locus to create a repressive compartment [15–17]. The maternal allele carries a germline methylation mark in the locus control region (KvDMR1), and monoallelic expression of the n ...
Chapter 10: Sexual Reproduction and Genetics
... Haploid and diploid cells In order to maintain the same chromosome number from generation to generation, an organism produces gametes, which are sex cells that have half the number of chromosomes. Although the number of chromosomes varies from one species to another, in humans each gamete contains ...
... Haploid and diploid cells In order to maintain the same chromosome number from generation to generation, an organism produces gametes, which are sex cells that have half the number of chromosomes. Although the number of chromosomes varies from one species to another, in humans each gamete contains ...
UNIT 3 - davis.k12.ut.us
... Some organisms reproduce by asexual reproduction, while others reproduce by sexual reproduction. The life cycles of still other organisms might involve both asexual and sexual reproduction. During asexual reproduction, the organism inherits all of its chromosomes from a single parent. Therefore, the ...
... Some organisms reproduce by asexual reproduction, while others reproduce by sexual reproduction. The life cycles of still other organisms might involve both asexual and sexual reproduction. During asexual reproduction, the organism inherits all of its chromosomes from a single parent. Therefore, the ...
alpha-thalassemia-pdf
... An individual with one abnormal alpha globin gene is said to be a silent carrier of alpha thalassemia. This condition, in which one of the four alpha globin genes is missing or defective, generally causes no health problems because the lack of alpha globin protein is so small that there is no anemia ...
... An individual with one abnormal alpha globin gene is said to be a silent carrier of alpha thalassemia. This condition, in which one of the four alpha globin genes is missing or defective, generally causes no health problems because the lack of alpha globin protein is so small that there is no anemia ...
Chapter 10: Sexual Reproduction and Genetics
... to another, in humans each gamete contains 23 chromosomes. The symbol n can be used to represent the number of chromosomes in a gamete. A cell with n number of chromosomes is called a haploid cell. Haploid comes from the Greek word haploos, meaning single. The process by which one haploid gamete com ...
... to another, in humans each gamete contains 23 chromosomes. The symbol n can be used to represent the number of chromosomes in a gamete. A cell with n number of chromosomes is called a haploid cell. Haploid comes from the Greek word haploos, meaning single. The process by which one haploid gamete com ...
slides
... • Mitochondria are only passed along from the mother, because they are present in the egg at fer/liza/on, while the sperm contributes only its nucleus to the egg (no cytoplasm, and thus no organelles ...
... • Mitochondria are only passed along from the mother, because they are present in the egg at fer/liza/on, while the sperm contributes only its nucleus to the egg (no cytoplasm, and thus no organelles ...
Low X/Y divergence in four pairs of papaya sex
... MSY is 8–9 Mbp based on size estimates for the remaining three gaps (Q.Y., P.H.M., J.J., A.H.P and R.M., unpublished data). Isolation of X chromosome BACs corresponding to the MSY region Because an X chromosome is present in all three sex forms, male (XY), female (XX) and hermaphrodite (XYh), isolat ...
... MSY is 8–9 Mbp based on size estimates for the remaining three gaps (Q.Y., P.H.M., J.J., A.H.P and R.M., unpublished data). Isolation of X chromosome BACs corresponding to the MSY region Because an X chromosome is present in all three sex forms, male (XY), female (XX) and hermaphrodite (XYh), isolat ...
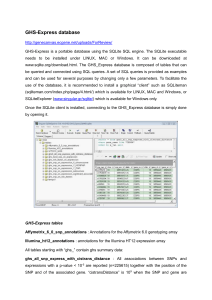
GHS-Express database http://genecanvas.ecgene.net/uploads/Fo
... SNP and of the associated gene. “cistransDistance” is 109 when the SNP and gene are ...
... SNP and of the associated gene. “cistransDistance” is 109 when the SNP and gene are ...
Slide 1
... A locus (plural, loci) is the position of a gene. Different versions of a gene (called alleles) may be found at the same locus on maternal and paternal chromosomes. © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... A locus (plural, loci) is the position of a gene. Different versions of a gene (called alleles) may be found at the same locus on maternal and paternal chromosomes. © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
PowerPoint Notes
... A. Mendel’s principles form the basis of modern genetics. Mendel’s principles include the following: 1. The inheritance of traits is determined by individual units known as ___________. ...
... A. Mendel’s principles form the basis of modern genetics. Mendel’s principles include the following: 1. The inheritance of traits is determined by individual units known as ___________. ...
Chromosome numbers in female and male gametes: One
... have triploid embryos. No plump kernels with 4n zygotes were found. These would occur if the pollen of el plants consisted of a mixture of diploid and haploid grains and the diploid grains effected fertilization. However, haploid grains have a competitive advantage over diploid pollen in pollen mixt ...
... have triploid embryos. No plump kernels with 4n zygotes were found. These would occur if the pollen of el plants consisted of a mixture of diploid and haploid grains and the diploid grains effected fertilization. However, haploid grains have a competitive advantage over diploid pollen in pollen mixt ...