History of Operating Systems
... creates new process terminates process opens file creates directory ...
... creates new process terminates process opens file creates directory ...
Lecture 11 Operating Systems • Free - VU LMS
... an OS Then came computer operators who ran multiple programs for multiple users one after the other – still, no need for an OS Later computers became powerful, & became able to run multiple programs, simultaneously. That’s when the need for OS’es arose for: – Managing the resources of the computers ...
... an OS Then came computer operators who ran multiple programs for multiple users one after the other – still, no need for an OS Later computers became powerful, & became able to run multiple programs, simultaneously. That’s when the need for OS’es arose for: – Managing the resources of the computers ...
Introduction to OS
... program needs to use I/O then its OS that decides when the program gets that access. Also, if required, the OS can take the I/O from the program before it completes execution. ...
... program needs to use I/O then its OS that decides when the program gets that access. Also, if required, the OS can take the I/O from the program before it completes execution. ...
IO Systems - monismith.info
... • This will prevent user processes from disrupting the OS • Protect memory-mapped and I/O memory port locations from user access, too • Kernel must provide a locking mechanism to allow only protected access to these features ...
... • This will prevent user processes from disrupting the OS • Protect memory-mapped and I/O memory port locations from user access, too • Kernel must provide a locking mechanism to allow only protected access to these features ...
Operating Systems
... It is a useful, memory-saving technique for multiprogrammed timesharing systems. A Reentrant Procedure is one in which multiple users can share a single copy of a program during the same period. Reentrancy has 2 key aspects: i.) The program code cannot modify itself, ii.) The local data for each use ...
... It is a useful, memory-saving technique for multiprogrammed timesharing systems. A Reentrant Procedure is one in which multiple users can share a single copy of a program during the same period. Reentrancy has 2 key aspects: i.) The program code cannot modify itself, ii.) The local data for each use ...
10-Software-Presentation
... program to hard disk or remove it Printer drivers – enable the computer to send the correct signals to the printer Email filter & web filters ...
... program to hard disk or remove it Printer drivers – enable the computer to send the correct signals to the printer Email filter & web filters ...
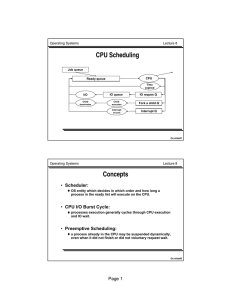
Page 1 • Scheduler: • CPU I/O Burst Cycle: • Preemptive Scheduling:
... • Scheduler: OS entity which decides in which order and how long a process in the ready list will execute on the CPU. ...
... • Scheduler: OS entity which decides in which order and how long a process in the ready list will execute on the CPU. ...
Operating System
... system itself. Systems with multiple users can gain efficiency by sharing the computer resources among the users. ...
... system itself. Systems with multiple users can gain efficiency by sharing the computer resources among the users. ...
Structure of Operating Systems
... • I/O subsystem and device drivers • Interrupts and traps • Protection, system calls and operating mode • OS structure • What happens when you boot a computer? ...
... • I/O subsystem and device drivers • Interrupts and traps • Protection, system calls and operating mode • OS structure • What happens when you boot a computer? ...
System Software
... the current status, i.e., the contents of the CPU registers, of the suspended process (in a structure called a process control block) in the memory so that the suspended process can resume execution seamlessly when it is allocated with more CPU time at a later stage. The storing of the status of a ...
... the current status, i.e., the contents of the CPU registers, of the suspended process (in a structure called a process control block) in the memory so that the suspended process can resume execution seamlessly when it is allocated with more CPU time at a later stage. The storing of the status of a ...
SE U 513 Exam
... 3 variables: A, B, C which are shared by thread T1 and thread T2 T1 computes C = A+B T2 transfers amount X from A to B o T2 must do: A = A -X and B = B+X (so that A+B is unchanged) But if T1 computes A+B after T2 has done A = A-X but before B = B+X then T1 will not obtain the correct result for C = ...
... 3 variables: A, B, C which are shared by thread T1 and thread T2 T1 computes C = A+B T2 transfers amount X from A to B o T2 must do: A = A -X and B = B+X (so that A+B is unchanged) But if T1 computes A+B after T2 has done A = A-X but before B = B+X then T1 will not obtain the correct result for C = ...
What is an Operating System?
... with a program while it is running. Requires good responsiveness. What a job stalls waiting for I/O, another job can be run, giving good CPU utilization. The job pool is now under the control of the users. But memory is limited, so this requires swapping some jobs out to disk. One solution is ...
... with a program while it is running. Requires good responsiveness. What a job stalls waiting for I/O, another job can be run, giving good CPU utilization. The job pool is now under the control of the users. But memory is limited, so this requires swapping some jobs out to disk. One solution is ...
Introduction
... • Protection of files and directories, e.g. UNIX the rwx bits: 9 bits (owner/group/others) rwxr-xr-• File Descriptor: a number assigned to a file. • Mounting file systems. • Special files: block special files, character special files – standard input (fd=0), standard ...
... • Protection of files and directories, e.g. UNIX the rwx bits: 9 bits (owner/group/others) rwxr-xr-• File Descriptor: a number assigned to a file. • Mounting file systems. • Special files: block special files, character special files – standard input (fd=0), standard ...
Processes Process States
... Process States • Five states in general, with specific operating systems ...
... Process States • Five states in general, with specific operating systems ...
OSreviewS2004
... • Long-term scheduler (or job scheduler) – selects which processes should be brought into the ready queue. • Short-term scheduler (or CPU scheduler) – selects which process should be executed next and allocates CPU. • Midterm scheduler ...
... • Long-term scheduler (or job scheduler) – selects which processes should be brought into the ready queue. • Short-term scheduler (or CPU scheduler) – selects which process should be executed next and allocates CPU. • Midterm scheduler ...
Test1_soln
... Ans. If an OS has nothing to do, no event is scheduled to happen; it lies dormant as if in ‘sleep’. Only when it is awakened by a system call, or an event ‘happens’ it gets into work. In other words, an interrupt or an event schedule changes it from a ‘non-active state’ to an active ‘running’ state. ...
... Ans. If an OS has nothing to do, no event is scheduled to happen; it lies dormant as if in ‘sleep’. Only when it is awakened by a system call, or an event ‘happens’ it gets into work. In other words, an interrupt or an event schedule changes it from a ‘non-active state’ to an active ‘running’ state. ...
Process Control Block entity that defines a process to the OS
... Operating systems must interleave the execution of a number of processes to maximize processor use – while providing reasonable response rate ...
... Operating systems must interleave the execution of a number of processes to maximize processor use – while providing reasonable response rate ...
ppt
... space} to have multiple threads of control. • But for now – for simplicity and for historical reasons – consider each {process / address space} to have a single thread of control. ...
... space} to have multiple threads of control. • But for now – for simplicity and for historical reasons – consider each {process / address space} to have a single thread of control. ...
Introduction to Linux/Unix
... Redirection and Pipe File/Directory Permissions Process Management The nano Text Editor ...
... Redirection and Pipe File/Directory Permissions Process Management The nano Text Editor ...
Operating Systems
... computer is turned ON, and the last one to finish running when the computer is turned OFF • It manages the HW and SW resources of the computer system, often invisibly. These include the processor, memory, disk drives, etc. ...
... computer is turned ON, and the last one to finish running when the computer is turned OFF • It manages the HW and SW resources of the computer system, often invisibly. These include the processor, memory, disk drives, etc. ...
Distributed Systems Major Design Issues
... Processes Coordination required to achieve synchronization: Synchronization Types: ...
... Processes Coordination required to achieve synchronization: Synchronization Types: ...
Distributed Systems Major Design Issues
... Processes Coordination required to achieve synchronization: Synchronization Types: ...
... Processes Coordination required to achieve synchronization: Synchronization Types: ...