BIOL 1406-61313 CHAPTER 14 AND 15 Dr
... 3. In general, the frequency that crossing over occurs between two linked genes depends on _____. how far apart they are on the chromosome the phase of meiosis in which the crossing over occurs whether the genes are on the X or some other chromosome whether the genes are dominant or recessive the ch ...
... 3. In general, the frequency that crossing over occurs between two linked genes depends on _____. how far apart they are on the chromosome the phase of meiosis in which the crossing over occurs whether the genes are on the X or some other chromosome whether the genes are dominant or recessive the ch ...
Making Reebops: a model for meiosis
... Reebops are imagined animals, made from marshmallows, pins and cocktail sticks. They have 16 chromosomes (in 8 homologous pairs) in their body cells. It is important that you understand what happens to form the gametes or sex cells. Have a look at the parents – Mum and Dad Reebop. Note their charact ...
... Reebops are imagined animals, made from marshmallows, pins and cocktail sticks. They have 16 chromosomes (in 8 homologous pairs) in their body cells. It is important that you understand what happens to form the gametes or sex cells. Have a look at the parents – Mum and Dad Reebop. Note their charact ...
Chapter 13 – Genetic Engineering
... – Ex – bananas, citrus fruit, strawberries, many ornamental flowers Diploid corn Tetraploid corn ...
... – Ex – bananas, citrus fruit, strawberries, many ornamental flowers Diploid corn Tetraploid corn ...
Document
... All cells come from other cells Eukaryotic cells that go through the process of mitosis make EXACT copies of themselves (one skin cell divides to form two identical skin cells, etc.) Sex cells (sperm and egg cells) are different from all other cells in the body because they have half as many chromos ...
... All cells come from other cells Eukaryotic cells that go through the process of mitosis make EXACT copies of themselves (one skin cell divides to form two identical skin cells, etc.) Sex cells (sperm and egg cells) are different from all other cells in the body because they have half as many chromos ...
Section 7.1 Chromosomes and Phenotype Relate dominant
... gene. However, the two copies of a gene may be different alleles. Both copies of a gene can affect phenotype. Much of what has been learned about human genes comes from studies of genetic disorders. Many genetic disorders are caused by recessive alleles on autosomes. People who have one dominant all ...
... gene. However, the two copies of a gene may be different alleles. Both copies of a gene can affect phenotype. Much of what has been learned about human genes comes from studies of genetic disorders. Many genetic disorders are caused by recessive alleles on autosomes. People who have one dominant all ...
MEIOSIS AND CROSSING OVER
... When cells divide by mitosis, the new cells have exactly the same number and kind of chromosomes as the original cells. Imagine if mitosis were the only means of cell division. IF the parent organism has 14 chromosomes, it would produce gametes that contained a complete set of 14 chromosomes The off ...
... When cells divide by mitosis, the new cells have exactly the same number and kind of chromosomes as the original cells. Imagine if mitosis were the only means of cell division. IF the parent organism has 14 chromosomes, it would produce gametes that contained a complete set of 14 chromosomes The off ...
Ch. 13 Genetic Engineering, Chapter Summary Date
... 6. a techniques scientist used to make many copies of a certain gene. 8. produced by combining DNA from different species or different sources. 14. a technique that breed specific animals and plants with desired traits. This technique takes advantage of naturally occurring genetic variation in a gro ...
... 6. a techniques scientist used to make many copies of a certain gene. 8. produced by combining DNA from different species or different sources. 14. a technique that breed specific animals and plants with desired traits. This technique takes advantage of naturally occurring genetic variation in a gro ...
12.4 Mutations
... • Changes in the number or structure of chromosomes • Can change locations of genes on chromosomes or number of copies of some genes ...
... • Changes in the number or structure of chromosomes • Can change locations of genes on chromosomes or number of copies of some genes ...
9. Biodiversity& Species
... Polyploidy is a common mechanism for sympatric speciation: Hybrid polyploids (allopolyploids) have characteristics of both parents. They have more genes and enzymes to deal with changes in the environment and thus are often better adapted than the parent species. Since their chromosome numbers are ...
... Polyploidy is a common mechanism for sympatric speciation: Hybrid polyploids (allopolyploids) have characteristics of both parents. They have more genes and enzymes to deal with changes in the environment and thus are often better adapted than the parent species. Since their chromosome numbers are ...
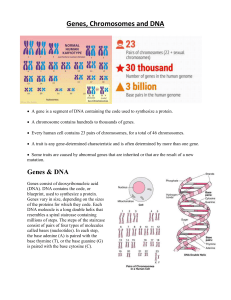
Genes Chromosomes and DNA
... A gene is a segment of DNA containing the code used to synthesize a protein. A chromosome contains hundreds to thousands of genes. Every human cell contains 23 pairs of chromosomes, for a total of 46 chromosomes. A trait is any gene-determined characteristic and is often determined by more t ...
... A gene is a segment of DNA containing the code used to synthesize a protein. A chromosome contains hundreds to thousands of genes. Every human cell contains 23 pairs of chromosomes, for a total of 46 chromosomes. A trait is any gene-determined characteristic and is often determined by more t ...
Biology Final Study Guide
... a food web or chain and why? 14. What are the three types of symbiotic relationships and give an example of each? 15. Draw logistic and exponential growth models. 16. Compare & contrast chloroplast & mitochondria (job, what cell types have it, equation) 17. What are the main steps in the water, carb ...
... a food web or chain and why? 14. What are the three types of symbiotic relationships and give an example of each? 15. Draw logistic and exponential growth models. 16. Compare & contrast chloroplast & mitochondria (job, what cell types have it, equation) 17. What are the main steps in the water, carb ...
Unit 5 Test Review
... Structure found only in animal cells that the spindle fibers come from Event during Prophase I, when parts of homologous chromosomes trade pieces Reproduction involving only one parent Structure of two homologous chromosomes together during meiosis; has 4 chromatids Alternates between interphase and ...
... Structure found only in animal cells that the spindle fibers come from Event during Prophase I, when parts of homologous chromosomes trade pieces Reproduction involving only one parent Structure of two homologous chromosomes together during meiosis; has 4 chromatids Alternates between interphase and ...
Chapter 15 - The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance
... Fetus can survive an extra copy of a chromosome, ...
... Fetus can survive an extra copy of a chromosome, ...
meiosis_and_sexual_life_cycles
... In an unfertilized egg (ovum), the sex chromosome is X. In a sperm cell, the sex chromosome may be either X or Y. ...
... In an unfertilized egg (ovum), the sex chromosome is X. In a sperm cell, the sex chromosome may be either X or Y. ...
Biology Final Study Guide
... a food web or chain and why? 14. What are the three types of symbiotic relationships and give an example of each? 15. Draw logistic and exponential growth models. 16. Compare & contrast chloroplast & mitochondria (job, what cell types have it, equation) 17. What are the main steps in the water, carb ...
... a food web or chain and why? 14. What are the three types of symbiotic relationships and give an example of each? 15. Draw logistic and exponential growth models. 16. Compare & contrast chloroplast & mitochondria (job, what cell types have it, equation) 17. What are the main steps in the water, carb ...
Control of Chromosome Pairing and Genome Evolution in Disomic
... Another control population is made from the cross of DSCnn1A to Chinese Spring (CS). DSCnn1A is identical to Chinese Spring except its chromosome 1A pair is from the cultivar Cheyenne. This allows measurement of recombination between homologous chromosomes 1A in the presence of Ph1. To study the eff ...
... Another control population is made from the cross of DSCnn1A to Chinese Spring (CS). DSCnn1A is identical to Chinese Spring except its chromosome 1A pair is from the cultivar Cheyenne. This allows measurement of recombination between homologous chromosomes 1A in the presence of Ph1. To study the eff ...
Transcript
... sperm. So we will have X bearing sperm on the top, and Y bearing sperm on the bottom. And now these sperm have to go in search of eggs, let's roll the video. Now they're fired up, in the experiment on the top the X bearing sperm in purple are going to win, down below the Y bearing sperm, we end u ...
... sperm. So we will have X bearing sperm on the top, and Y bearing sperm on the bottom. And now these sperm have to go in search of eggs, let's roll the video. Now they're fired up, in the experiment on the top the X bearing sperm in purple are going to win, down below the Y bearing sperm, we end u ...
Chapter 15 Study Questions
... features; cry sounds like a mewing cat Increased # of white blood cells ...
... features; cry sounds like a mewing cat Increased # of white blood cells ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 13. _______ inversion in which the rearrangement of genes is confined to single arm of the chromosome 14. ----------------- introns are located in the protein encoding genes of the nucleus. 15. ----------------- discovered that new species arise as a result of natural selection. IV. Answer all, each ...
... 13. _______ inversion in which the rearrangement of genes is confined to single arm of the chromosome 14. ----------------- introns are located in the protein encoding genes of the nucleus. 15. ----------------- discovered that new species arise as a result of natural selection. IV. Answer all, each ...
A change in ocean current causes the climate on an island to
... What controls cell processes and contains genetic instructions? A cell that has lost its chromosomes will be unable to do what? How many chromosomes are present in a normal human reproductive cell? How would a gene be described? ...
... What controls cell processes and contains genetic instructions? A cell that has lost its chromosomes will be unable to do what? How many chromosomes are present in a normal human reproductive cell? How would a gene be described? ...
4.3.5 Sex Chromosomes and Sex Linkage Questions
... Each person normally has one pair of sex chromosomes in each cell. Females have two X chromosomes, while males have one X and one Y chromosome. The X chromosome contains about 1000 genes, including the genes for haemophilia and colour blindness. For this reason these genes are said to be sex-linked. ...
... Each person normally has one pair of sex chromosomes in each cell. Females have two X chromosomes, while males have one X and one Y chromosome. The X chromosome contains about 1000 genes, including the genes for haemophilia and colour blindness. For this reason these genes are said to be sex-linked. ...
Genetics student notes. File
... Use the terms you have just learned to label the diagram. Each term/number is used only once, and all terms/numbers are used. ...
... Use the terms you have just learned to label the diagram. Each term/number is used only once, and all terms/numbers are used. ...
Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance
... Is the Disorder an Autosomal Recessive Disorder or Is It Sex Linked? ...
... Is the Disorder an Autosomal Recessive Disorder or Is It Sex Linked? ...
Genetics Unit final
... shaped red blood cells can treat but not successful • Inherited as an autosomal recessive trait • Most common in African Americans originating from Africa, and white Americans who come from around the Mediterranean sea. • One out of twelve African Americans have the heterozygous form… • Caused by a ...
... shaped red blood cells can treat but not successful • Inherited as an autosomal recessive trait • Most common in African Americans originating from Africa, and white Americans who come from around the Mediterranean sea. • One out of twelve African Americans have the heterozygous form… • Caused by a ...
Polyploid
Polyploid cells and organisms are those containing more than two paired (homologous) sets of chromosomes. Most species whose cells have nuclei (Eukaryotes) are diploid, meaning they have two sets of chromosomes—one set inherited from each parent. However, polyploidy is found in some organisms and is especially common in plants. In addition, polyploidy occurs in some tissues of animals that are otherwise diploid, such as human muscle tissues. This is known as endopolyploidy. Species whose cells do not have nuclei, that is, Prokaryotes, may be polyploid organisms, as seen in the large bacterium Epulopicium fishelsoni [1]. Hence ploidy is defined with respect to a cell. Most eukaryotes have diploid somatic cells, but produce haploid gametes (eggs and sperm) by meiosis. A monoploid has only one set of chromosomes, and the term is usually only applied to cells or organisms that are normally diploid. Male bees and other Hymenoptera, for example, are monoploid. Unlike animals, plants and multicellular algae have life cycles with two alternating multicellular generations. The gametophyte generation is haploid, and produces gametes by mitosis, the sporophyte generation is diploid and produces spores by meiosis.Polyploidy refers to a numerical change in a whole set of chromosomes. Organisms in which a particular chromosome, or chromosome segment, is under- or overrepresented are said to be aneuploid (from the Greek words meaning ""not"", ""good"", and ""fold""). Therefore the distinction between aneuploidy and polyploidy is that aneuploidy refers to a numerical change in part of the chromosome set, whereas polyploidy refers to a numerical change in the whole set of chromosomes.Polyploidy may occur due to abnormal cell division, either during mitosis, or commonly during metaphase I in meiosis.Polyploidy occurs in some animals, such as goldfish, salmon, and salamanders, but is especially common among ferns and flowering plants (see Hibiscus rosa-sinensis), including both wild and cultivated species. Wheat, for example, after millennia of hybridization and modification by humans, has strains that are diploid (two sets of chromosomes), tetraploid (four sets of chromosomes) with the common name of durum or macaroni wheat, and hexaploid (six sets of chromosomes) with the common name of bread wheat. Many agriculturally important plants of the genus Brassica are also tetraploids.Polyploidy can be induced in plants and cell cultures by some chemicals: the best known is colchicine, which can result in chromosome doubling, though its use may have other less obvious consequences as well. Oryzalin will also double the existing chromosome content.