Circuit Defects
... The total circuit resistance (equivalent resistance) is less than the value of the lowest resistance. The equivalent resistance for two resistance's in parallel is equal to the product divided by the sum ...
... The total circuit resistance (equivalent resistance) is less than the value of the lowest resistance. The equivalent resistance for two resistance's in parallel is equal to the product divided by the sum ...
Parallel circuits - Journal of Pyrotechnics
... • The total resistance always increases as more elements are added to the circuit. As a result, the total amount of current flowing always decreases. • To maintain the same current as more elements are added, greater and greater voltage will be needed from the power source. • If the wire size is suf ...
... • The total resistance always increases as more elements are added to the circuit. As a result, the total amount of current flowing always decreases. • To maintain the same current as more elements are added, greater and greater voltage will be needed from the power source. • If the wire size is suf ...
- Krest Technology
... A high-performance ultrahigh-frequency amplitude shift keying (ASK) detector for lowpower radio-frequency (RF) receivers is proposed. The circuit is based on a high-gain common-source topology with a feedback loop that provides adaptive biasing. Hence, high sensitivity and rail-to-rail input operati ...
... A high-performance ultrahigh-frequency amplitude shift keying (ASK) detector for lowpower radio-frequency (RF) receivers is proposed. The circuit is based on a high-gain common-source topology with a feedback loop that provides adaptive biasing. Hence, high sensitivity and rail-to-rail input operati ...
Series and Parallel Circuits Computer Lab
... Measure the current with the ammeter. Compare the current reading when there were two bulbs present in the circuit. Measure the voltage with the voltmeter. Compare the voltage reading when there were two bulbs present. ...
... Measure the current with the ammeter. Compare the current reading when there were two bulbs present in the circuit. Measure the voltage with the voltmeter. Compare the voltage reading when there were two bulbs present. ...
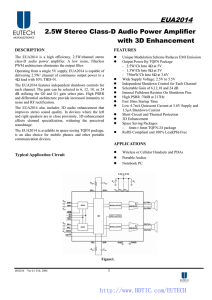
EUA2014 2.5W Stereo Class-D Audio Power Amplifier with 3D Enhancement
... The EUA2014 is a high efficiency, 2.5W/channel stereo class-D audio power amplifier. A low noise, filterless PWM architecture eliminates the output filter. Operating from a single 5V supply, EUA2014 is capable of delivering 2.5W/ channel of continuous output power to a 4Ω load with 10% THD+N. The EU ...
... The EUA2014 is a high efficiency, 2.5W/channel stereo class-D audio power amplifier. A low noise, filterless PWM architecture eliminates the output filter. Operating from a single 5V supply, EUA2014 is capable of delivering 2.5W/ channel of continuous output power to a 4Ω load with 10% THD+N. The EU ...
Electric Circuit Lab
... Procedure for Series Lab: Connect the given resistors in series. One 100 , one 250 . Measure the voltage across each resistor and the current in the circuit. Use a 6 V battery as your power source. Before connecting the battery make sure to show your circuit to the teacher for approval. Circuit ...
... Procedure for Series Lab: Connect the given resistors in series. One 100 , one 250 . Measure the voltage across each resistor and the current in the circuit. Use a 6 V battery as your power source. Before connecting the battery make sure to show your circuit to the teacher for approval. Circuit ...
solar street light - mv3
... A 12V,75Ah@C10 battery backup providing 5 days autonomy 4m height pole ...
... A 12V,75Ah@C10 battery backup providing 5 days autonomy 4m height pole ...
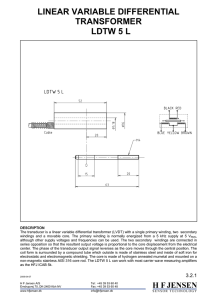
LINEAR VARIABLE DIFFERENTIAL TRANSFORMER LDTW 5 L
... The transducer is a linear variable differential transformer (LVDT) with a single primary winding, two secondary windings and a movable core. The primary winding is normally energized from a 5 kHz supply at 5 VRMS, although other supply voltages and frequencies can be used. The two secondary winding ...
... The transducer is a linear variable differential transformer (LVDT) with a single primary winding, two secondary windings and a movable core. The primary winding is normally energized from a 5 kHz supply at 5 VRMS, although other supply voltages and frequencies can be used. The two secondary winding ...
physics 202 - La Salle University
... high voltages. But most of the devices we will be interested in need direct current (DC) at relatively small voltages. One first reduces the voltage by using a transformer. A transformer changes the voltage and the current in such a way that the power is not significantly diminished. First let us bu ...
... high voltages. But most of the devices we will be interested in need direct current (DC) at relatively small voltages. One first reduces the voltage by using a transformer. A transformer changes the voltage and the current in such a way that the power is not significantly diminished. First let us bu ...
open saved file with Word to simulate
... Construct the circuit of Figure 1 in Multisim. Make required measurements, then plot, then comment. Construct the circuit of Figure 1 using a protoboard and resistor and two digital meters. Make required measurements, then plot, then comment. ...
... Construct the circuit of Figure 1 in Multisim. Make required measurements, then plot, then comment. Construct the circuit of Figure 1 using a protoboard and resistor and two digital meters. Make required measurements, then plot, then comment. ...
NTE6410 Unijunction Transistor UJT
... Note 3. Intrinsic standoff ratio, is defined in terms of peak–point voltage, VP, by means of the equation: VP = η VB2B1 VF, where VF is approximately 0.49 volts at +25°C @ IF = 10µA and decreases with temperature at approximately 2.5mV/°C. Components R1, C1, and the UJT form a relaxation oscillator, ...
... Note 3. Intrinsic standoff ratio, is defined in terms of peak–point voltage, VP, by means of the equation: VP = η VB2B1 VF, where VF is approximately 0.49 volts at +25°C @ IF = 10µA and decreases with temperature at approximately 2.5mV/°C. Components R1, C1, and the UJT form a relaxation oscillator, ...
Early Born-Digital Audio Formats
... Other quantization methods • PWM: Pulse wide modulation • Delta-Sigma: sum of change • Delta-Modulation: change in value (used in SACD’s “direct stream digital”) ...
... Other quantization methods • PWM: Pulse wide modulation • Delta-Sigma: sum of change • Delta-Modulation: change in value (used in SACD’s “direct stream digital”) ...
This quiz will cover ONLY Section 2
... a circuit. SAME as voltage Electric Current: flow of electrons through a material Voltage: causes current to flow through an electric circuit Voltage source: creates a potential difference in electric circuit Ohm: units of resistance Voltmeter: measures voltage Ammeter: measures amps (or current) Co ...
... a circuit. SAME as voltage Electric Current: flow of electrons through a material Voltage: causes current to flow through an electric circuit Voltage source: creates a potential difference in electric circuit Ohm: units of resistance Voltmeter: measures voltage Ammeter: measures amps (or current) Co ...
Resistive opto-isolator
Resistive opto-isolator (RO), also called photoresistive opto-isolator, vactrol (after a genericized trademark introduced by Vactec, Inc. in the 1960s), analog opto-isolator or lamp-coupled photocell, is an optoelectronic device consisting of a source and detector of light, which are optically coupled and electrically isolated from each other. The light source is usually a light-emitting diode (LED), a miniature incandescent lamp, or sometimes a neon lamp, whereas the detector is a semiconductor-based photoresistor made of cadmium selenide (CdSe) or cadmium sulfide (CdS). The source and detector are coupled through a transparent glue or through the air.Electrically, RO is a resistance controlled by the current flowing through the light source. In the dark state, the resistance typically exceeds a few MOhm; when illuminated, it decreases as the inverse of the light intensity. In contrast to the photodiode and phototransistor, the photoresistor can operate in both the AC and DC circuits and have a voltage of several hundred volts across it. The harmonic distortions of the output current by the RO are typically within 0.1% at voltages below 0.5 V.RO is the first and the slowest opto-isolator: its switching time exceeds 1 ms, and for the lamp-based models can reach hundreds of milliseconds. Parasitic capacitance limits the frequency range of the photoresistor by ultrasonic frequencies. Cadmium-based photoresistors exhibit a ""memory effect"": their resistance depends on the illumination history; it also drifts during the illumination and stabilizes within hours, or even weeks for high-sensitivity models. Heating induces irreversible degradation of ROs, whereas cooling to below −25 °C dramatically increases the response time. Therefore, ROs were mostly replaced in the 1970s by the faster and more stable photodiodes and photoresistors. ROs are still used in some sound equipment, guitar amplifiers and analog synthesizers owing to their good electrical isolation, low signal distortion and ease of circuit design.