SF130-L SF140-L SF145-L SF150-L
... Next Generation CIS Solar Frontier’s new SF130–150 module series offers the highest conversion efficiency of any mass-produced thin-film module, up to 12.2%. The modules feature the lightsoaking effect unique to Solar Frontier’s CIS technology, which provides higher output than initially specified. ...
... Next Generation CIS Solar Frontier’s new SF130–150 module series offers the highest conversion efficiency of any mass-produced thin-film module, up to 12.2%. The modules feature the lightsoaking effect unique to Solar Frontier’s CIS technology, which provides higher output than initially specified. ...
DSTATCOM supported induction generator for improving power
... the saturation in the generator. Other offered advantages are balanced generator currents under any loading condition, harmonic currents mitigation, stable DC link voltage and the reduced number of sensors. The SMC algorithm is successfully implemented on a DSTATCOM employed with a three-phase SEIG ...
... the saturation in the generator. Other offered advantages are balanced generator currents under any loading condition, harmonic currents mitigation, stable DC link voltage and the reduced number of sensors. The SMC algorithm is successfully implemented on a DSTATCOM employed with a three-phase SEIG ...
SuperCap Battery - digitalequilibrium.com
... provide approximately 9 V. Transistor T3 uses its reverse biased baseemitter junction to act as a zener diode, providing a voltage reference to regulate the output. The zener voltage of a small signal NPN transistor is around 8 V in this configuration (an 8 V zener diode could be substituted for T3) ...
... provide approximately 9 V. Transistor T3 uses its reverse biased baseemitter junction to act as a zener diode, providing a voltage reference to regulate the output. The zener voltage of a small signal NPN transistor is around 8 V in this configuration (an 8 V zener diode could be substituted for T3) ...
What does the “PASSIVE” device mean
... it can be just resistor, capacitor or inductor, no other devices, device, where output power (Pout) is lower (or equal) than the input power (Pin), device, where input power (Pin) is lower (or equal) than the output power (Pout), all the semiconductor devices, e.g. LED, thyristors etc. 2. Wh ...
... it can be just resistor, capacitor or inductor, no other devices, device, where output power (Pout) is lower (or equal) than the input power (Pin), device, where input power (Pin) is lower (or equal) than the output power (Pout), all the semiconductor devices, e.g. LED, thyristors etc. 2. Wh ...
Ch. 35 – Review Questions
... a. In which case will there be more current in each of the three lamps – if they are connected to the same battery in series or in parallel? There will be more current in the lamps if they are connected in parallel. b. In which case will there be more voltage across each lamp? There will be more vol ...
... a. In which case will there be more current in each of the three lamps – if they are connected to the same battery in series or in parallel? There will be more current in the lamps if they are connected in parallel. b. In which case will there be more voltage across each lamp? There will be more vol ...
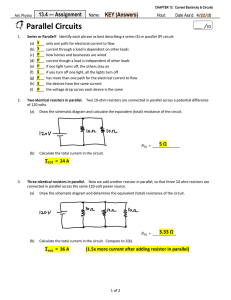
Parallel Circuits - Mr. Britton / FHS Physics
... if one light turns off, the others stay on if you turn off one light, all the lights turn off has more than one path for the electrical current to flow the devices have the same current the voltage drop across each device is the same ...
... if one light turns off, the others stay on if you turn off one light, all the lights turn off has more than one path for the electrical current to flow the devices have the same current the voltage drop across each device is the same ...
EXPERIMENT NO 4
... The aim of this part is to study the performance of a Difference amplifier by measuring its Commonmode and Differential gains. In an ideal difference amplifier, the Common-mode gain Ac is zero, thus giving an infinite Common-mode Rejection Ratio (CMRR = Ad/Ac). However, in a practical opamp circuit, ...
... The aim of this part is to study the performance of a Difference amplifier by measuring its Commonmode and Differential gains. In an ideal difference amplifier, the Common-mode gain Ac is zero, thus giving an infinite Common-mode Rejection Ratio (CMRR = Ad/Ac). However, in a practical opamp circuit, ...
TAP 318 - 3: Data transfer on an optical fibre
... cable, getting weaker but being detected at the other end by a photodiode. You can hear over a loudspeaker the amplified electrical signal from the photodiode. Remove the fibre-optic link and the signal disappears. Since the photodiode also responds to infrared, you can see the digital signals from ...
... cable, getting weaker but being detected at the other end by a photodiode. You can hear over a loudspeaker the amplified electrical signal from the photodiode. Remove the fibre-optic link and the signal disappears. Since the photodiode also responds to infrared, you can see the digital signals from ...
Series and Parallel Circuits
... be used in a circuit with a 6-volt battery. The bulb requires 1 amp of current. If the bulb were connected directly to the battery, it would draw 6 amps and burn out instantly. To limit the current, a resistor is added in series with the bulb. What size resistor is needed to make the current 1 amp? ...
... be used in a circuit with a 6-volt battery. The bulb requires 1 amp of current. If the bulb were connected directly to the battery, it would draw 6 amps and burn out instantly. To limit the current, a resistor is added in series with the bulb. What size resistor is needed to make the current 1 amp? ...
TF2 Smart Grid
... and power flow within a line are usually monitored at a substation or power plant on either end of the line. While it is critical to know the current flow, frequency, voltage, and overall power quality in a transmission line segment, it is typically done at the substation. However, some of the “smar ...
... and power flow within a line are usually monitored at a substation or power plant on either end of the line. While it is critical to know the current flow, frequency, voltage, and overall power quality in a transmission line segment, it is typically done at the substation. However, some of the “smar ...
2013 Test 2 Solutions - Physics@Brock
... resistor is the same as the voltage of the battery. Solution: FALSE. The current through each resistor is the same as the current from the battery in a series circuit. The sum of the voltage drops across each resistor is equal to the battery voltage in a series circuit. (b) For several resistors con ...
... resistor is the same as the voltage of the battery. Solution: FALSE. The current through each resistor is the same as the current from the battery in a series circuit. The sum of the voltage drops across each resistor is equal to the battery voltage in a series circuit. (b) For several resistors con ...
Lab5
... Figure 1 Basic feedback topologies using BJT Figure 1 shows the basic feedback topologies for the BJT amplifier circuits. Please Note that the coupling capacitors have been replaced by short circuits in all of the above feedback topologies. The effect of the feedback topology on the amplifier input- ...
... Figure 1 Basic feedback topologies using BJT Figure 1 shows the basic feedback topologies for the BJT amplifier circuits. Please Note that the coupling capacitors have been replaced by short circuits in all of the above feedback topologies. The effect of the feedback topology on the amplifier input- ...
LX8580A_tk
... Sales Strategy Identifying the Application • Power supplies: isolated (AC:DC or DC:DC) with regulated 3.3V (or lower) output. • Power for sub-2.5V integrated circuits (e.g., microprocessors). • Step-down power conversion (step down) when minimal periphery components, cost, and size are the focus. ...
... Sales Strategy Identifying the Application • Power supplies: isolated (AC:DC or DC:DC) with regulated 3.3V (or lower) output. • Power for sub-2.5V integrated circuits (e.g., microprocessors). • Step-down power conversion (step down) when minimal periphery components, cost, and size are the focus. ...
What do all these have in common? What are they - Physics-S3
... • To reduce these losses, the National Grid transmits electricity at a low current. This needs a high voltage. • Power = voltage x current • Power stays the same so.... • Power = voltage x current ...
... • To reduce these losses, the National Grid transmits electricity at a low current. This needs a high voltage. • Power = voltage x current • Power stays the same so.... • Power = voltage x current ...
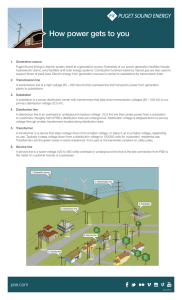
Fact Sheet: How Power Gets to You
... 4. Distribution line A distribution line is an overhead or underground medium-voltage (12.5 kV) line that carries power from a substation to customers. Roughly half of PSE’s distribution lines are underground. Distribution voltage is stepped down to service voltage through smaller transformers loca ...
... 4. Distribution line A distribution line is an overhead or underground medium-voltage (12.5 kV) line that carries power from a substation to customers. Roughly half of PSE’s distribution lines are underground. Distribution voltage is stepped down to service voltage through smaller transformers loca ...
Electricity Review
... a.Series circuits are battery circuits and parallel circuits are generator circuits. b.Series circuits have a single path and parallel circuits have two or more paths. c.Series circuits are used in computers and parallel circuits are used in homes. ...
... a.Series circuits are battery circuits and parallel circuits are generator circuits. b.Series circuits have a single path and parallel circuits have two or more paths. c.Series circuits are used in computers and parallel circuits are used in homes. ...
Today`s Objectives - RanelaghALevelPhysics
... Why does the resistance of metals increase with temperature? Positive temperature coefficient. Thermistor Temperature sensors Negative temperature coefficient. % change of resistance. Why? number of charge carriers. ...
... Why does the resistance of metals increase with temperature? Positive temperature coefficient. Thermistor Temperature sensors Negative temperature coefficient. % change of resistance. Why? number of charge carriers. ...
Lecture 1 - University of Minnesota Duluth
... – Voltage: Sum the voltages around a loop to Zero – Current: Sum the currents around a node to Zero ...
... – Voltage: Sum the voltages around a loop to Zero – Current: Sum the currents around a node to Zero ...
Resistive opto-isolator
Resistive opto-isolator (RO), also called photoresistive opto-isolator, vactrol (after a genericized trademark introduced by Vactec, Inc. in the 1960s), analog opto-isolator or lamp-coupled photocell, is an optoelectronic device consisting of a source and detector of light, which are optically coupled and electrically isolated from each other. The light source is usually a light-emitting diode (LED), a miniature incandescent lamp, or sometimes a neon lamp, whereas the detector is a semiconductor-based photoresistor made of cadmium selenide (CdSe) or cadmium sulfide (CdS). The source and detector are coupled through a transparent glue or through the air.Electrically, RO is a resistance controlled by the current flowing through the light source. In the dark state, the resistance typically exceeds a few MOhm; when illuminated, it decreases as the inverse of the light intensity. In contrast to the photodiode and phototransistor, the photoresistor can operate in both the AC and DC circuits and have a voltage of several hundred volts across it. The harmonic distortions of the output current by the RO are typically within 0.1% at voltages below 0.5 V.RO is the first and the slowest opto-isolator: its switching time exceeds 1 ms, and for the lamp-based models can reach hundreds of milliseconds. Parasitic capacitance limits the frequency range of the photoresistor by ultrasonic frequencies. Cadmium-based photoresistors exhibit a ""memory effect"": their resistance depends on the illumination history; it also drifts during the illumination and stabilizes within hours, or even weeks for high-sensitivity models. Heating induces irreversible degradation of ROs, whereas cooling to below −25 °C dramatically increases the response time. Therefore, ROs were mostly replaced in the 1970s by the faster and more stable photodiodes and photoresistors. ROs are still used in some sound equipment, guitar amplifiers and analog synthesizers owing to their good electrical isolation, low signal distortion and ease of circuit design.