F 1 Generation
... X Inactivation in Female Mammals • In mammalian females, one of the two X chromosomes in each cell is randomly inactivated during embryonic development • The inactive X condenses into a Barr body • If a female is heterozygous for a particular gene located on the X chromosome, she will be a mosaic f ...
... X Inactivation in Female Mammals • In mammalian females, one of the two X chromosomes in each cell is randomly inactivated during embryonic development • The inactive X condenses into a Barr body • If a female is heterozygous for a particular gene located on the X chromosome, she will be a mosaic f ...
Did sex chromosome turnover promote divergence of the major
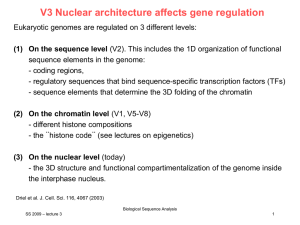
... is not a serious barrier to gene flow. Indeed, the importance of chromosome rearrangements has been suggested to be more in the isolation of regions of low recombination which might harbour packages of genes that work in one environment but not another [9, 10]. The role of chromosome change in speci ...
... is not a serious barrier to gene flow. Indeed, the importance of chromosome rearrangements has been suggested to be more in the isolation of regions of low recombination which might harbour packages of genes that work in one environment but not another [9, 10]. The role of chromosome change in speci ...
Gregor Mendel - HCC Learning Web
... Loci may have only one allele - fingernail growth rate Loci may have two alleles - boys and girls Loci may have multiple alleles - A,B,O blood types (but any individual organism can only have two) ...
... Loci may have only one allele - fingernail growth rate Loci may have two alleles - boys and girls Loci may have multiple alleles - A,B,O blood types (but any individual organism can only have two) ...
telomeres - Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and
... unprotected chromosome end are genetically unstable until telomere integrity has been restored. During this period of genetic instability, breakage-fusion-breakage (BFB) cycles occur, often culminating in chromosomal aneuploidies VI.3.2. BFB cycles and chromosomal instability also promote sister chr ...
... unprotected chromosome end are genetically unstable until telomere integrity has been restored. During this period of genetic instability, breakage-fusion-breakage (BFB) cycles occur, often culminating in chromosomal aneuploidies VI.3.2. BFB cycles and chromosomal instability also promote sister chr ...
5 BLY 122 Lecture Notes (O`Brien) 2009 II. Protists
... (1) Physical similarities exist between mitochondria, chloroplasts, and prokaryotes. (2) In addition, mitochondria . . . (a) are similar in size to most bacteria. (b) divide independently of the host cell. (c) divide by fission, as bacteria do. (d) have ribosomes and synthesize proteins. (e) have ri ...
... (1) Physical similarities exist between mitochondria, chloroplasts, and prokaryotes. (2) In addition, mitochondria . . . (a) are similar in size to most bacteria. (b) divide independently of the host cell. (c) divide by fission, as bacteria do. (d) have ribosomes and synthesize proteins. (e) have ri ...
Worksheet Packet
... 4. Next& move& the& chromosomes& into& Metaphase& I,& lining& up& the& homologous& chromosomes.& Remember,& homologous& chromosomes&are&the&same&length&and&have&the&same&genes,&although¬&always&the&same&alleles.&Using&your&colored& pencils,&recorded&what&your&cell&looks&like&below.& ...
... 4. Next& move& the& chromosomes& into& Metaphase& I,& lining& up& the& homologous& chromosomes.& Remember,& homologous& chromosomes&are&the&same&length&and&have&the&same&genes,&although¬&always&the&same&alleles.&Using&your&colored& pencils,&recorded&what&your&cell&looks&like&below.& ...
Genetics - Semantic Scholar
... Observing the pea plants’ Phenotypes, or observable inherited characteristics, led to the deduction of their Genotypes, or inherited genetic material. Genes are the modern name for the discrete units that Mendel observed to be inherited. Many individual varieties, or Alleles of each gene exist. For ...
... Observing the pea plants’ Phenotypes, or observable inherited characteristics, led to the deduction of their Genotypes, or inherited genetic material. Genes are the modern name for the discrete units that Mendel observed to be inherited. Many individual varieties, or Alleles of each gene exist. For ...
Summarizer PowerPoint - Butler Biology
... • Females need TWO recessive alleles to express the trait • Females can “carry” the trait • Trait skips a generation • Trait is expressed more often in males and is inherited from mother to son ...
... • Females need TWO recessive alleles to express the trait • Females can “carry” the trait • Trait skips a generation • Trait is expressed more often in males and is inherited from mother to son ...
Chromosome mapping of the sweet potato little leaf
... with the same four enzymes revealed genome heterogeneity when compared to the closely related SPLL-V4, and a preliminary chromosome size for the TBB phytoplasma of 662 kb was estimated. This mapping information has revealed that significant genome diversity exists within the phytoplasmas. ...
... with the same four enzymes revealed genome heterogeneity when compared to the closely related SPLL-V4, and a preliminary chromosome size for the TBB phytoplasma of 662 kb was estimated. This mapping information has revealed that significant genome diversity exists within the phytoplasmas. ...
Leukaemia Section t(1;21)(p36;q22) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... Department of Human Genetics, Radboud University Nijmegen Medical Centre, Nijmegen, the Netherlands Published in Atlas Database: March 2006 Online updated version: http://AtlasGeneticsOncology.org/Anomalies/t0121ID1186.html ...
... Department of Human Genetics, Radboud University Nijmegen Medical Centre, Nijmegen, the Netherlands Published in Atlas Database: March 2006 Online updated version: http://AtlasGeneticsOncology.org/Anomalies/t0121ID1186.html ...
chromosomal
... ~ 92 % of cases are numerical: trisomy 21 KARYOTYPE: 47,XX,+21 or 47,XY,+21 In 90 % in trisomy 21 additional chromosome comes from the mother’s egg [error in oogenesis: maternal non-disjunction meiosis I ] ...
... ~ 92 % of cases are numerical: trisomy 21 KARYOTYPE: 47,XX,+21 or 47,XY,+21 In 90 % in trisomy 21 additional chromosome comes from the mother’s egg [error in oogenesis: maternal non-disjunction meiosis I ] ...
14–1 Human Heredity
... recessive allele will show the sex-linked recessive trait. • Females have 2 X chromosomes, so a female must inherit two recessive alleles for the recessive trait to be expressed. Slide 15 of 43 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall ...
... recessive allele will show the sex-linked recessive trait. • Females have 2 X chromosomes, so a female must inherit two recessive alleles for the recessive trait to be expressed. Slide 15 of 43 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall ...
Variations on a theme: Genomics of sex
... present at all, are often homomorphic and differentiation is not detectable by karyotyping [2]. Overall, fish show frequent turnover of sex-determining systems [5], which stands in sharp contrast to other vertebrate clades, especially to birds or mammals, where an entire class shares the same sex ch ...
... present at all, are often homomorphic and differentiation is not detectable by karyotyping [2]. Overall, fish show frequent turnover of sex-determining systems [5], which stands in sharp contrast to other vertebrate clades, especially to birds or mammals, where an entire class shares the same sex ch ...
DNA MUTATIONS - American Medical Technologists
... Sequences of DNA that can move or transpose themselves to new positions within the genome of a single cell The mechanism of transposition can be either "copy and paste" or "cut and paste“ Oncogenes (genes that cause tumors) may be activated by the random reshuffling of transposons to a positio ...
... Sequences of DNA that can move or transpose themselves to new positions within the genome of a single cell The mechanism of transposition can be either "copy and paste" or "cut and paste“ Oncogenes (genes that cause tumors) may be activated by the random reshuffling of transposons to a positio ...
Prentice Hall Biology - Mid
... If there is only a small sample of DNA available- more copies can be made by PCR -polymerase chain reaction (p371) ...
... If there is only a small sample of DNA available- more copies can be made by PCR -polymerase chain reaction (p371) ...
Recombination Chromosome Separations At Anaphase I And II
... No RN at kinetochore--(Fig 12) o Never in kinetochore, very rare close to kinetochore. o Probably protect repeat sequences important for normal spindle attachment. RN more common in euchromatin than heterochromatin --(Table 5) o 20-50 x more likely. o Low recombination in heterochromatic regions can ...
... No RN at kinetochore--(Fig 12) o Never in kinetochore, very rare close to kinetochore. o Probably protect repeat sequences important for normal spindle attachment. RN more common in euchromatin than heterochromatin --(Table 5) o 20-50 x more likely. o Low recombination in heterochromatic regions can ...
Bio2250 - Principles of Genetics
... are autosomes and one pair are sex chromosomes. Female Drosophila are XX, and males XY. A gene is a heritable factor that controls the expression of some trait, which may be morphological, behavioural, molecular, etc. Each such gene occupies a specific physical locus (pl. loci) on a particular chrom ...
... are autosomes and one pair are sex chromosomes. Female Drosophila are XX, and males XY. A gene is a heritable factor that controls the expression of some trait, which may be morphological, behavioural, molecular, etc. Each such gene occupies a specific physical locus (pl. loci) on a particular chrom ...
File
... • Color blindness is a recessive sex linked disorder. A color blind man and his wife have a son who is color blind. The wife is upset that her husband passed color blindness on to their son. Use a Punnett square to show her who she should be upset with. What percentage of their sons are predicted to ...
... • Color blindness is a recessive sex linked disorder. A color blind man and his wife have a son who is color blind. The wife is upset that her husband passed color blindness on to their son. Use a Punnett square to show her who she should be upset with. What percentage of their sons are predicted to ...
Grade 9 Final Exam review
... ____ 67. an organism is broken into parts with one or more parts developing into a new organism that is identical to the parent ____ 68. an organism produces a single cell capable of growing into a new individual by mitosis ____ 69. part of an organism pushes outward to form an outgrowth, which pinc ...
... ____ 67. an organism is broken into parts with one or more parts developing into a new organism that is identical to the parent ____ 68. an organism produces a single cell capable of growing into a new individual by mitosis ____ 69. part of an organism pushes outward to form an outgrowth, which pinc ...
Section 13-2
... Words to Know Transformation - a cell incorporates DNA from outside the cell into its own DNA Bacteria can be transformed simply by placing them in a solution containing DNA molecules (Recall Griffith’s experiments.) Plasmid – small circular DNA molecule One way to make recombinant DNA is to insert ...
... Words to Know Transformation - a cell incorporates DNA from outside the cell into its own DNA Bacteria can be transformed simply by placing them in a solution containing DNA molecules (Recall Griffith’s experiments.) Plasmid – small circular DNA molecule One way to make recombinant DNA is to insert ...
Chromosome
A chromosome (chromo- + -some) is a packaged and organized structure containing most of the DNA of a living organism. It is not usually found on its own, but rather is complexed with many structural proteins called histones as well as associated transcription (copying of genetic sequences) factors and several other macromolecules. Two ""sister"" chromatids (half a chromosome) join together at a protein junction called a centromere. Chromosomes are normally visible under a light microscope only when the cell is undergoing mitosis. Even then, the full chromosome containing both joined sister chromatids becomes visible only during a sequence of mitosis known as metaphase (when chromosomes align together, attached to the mitotic spindle and prepare to divide). This DNA and its associated proteins and macromolecules is collectively known as chromatin, which is further packaged along with its associated molecules into a discrete structure called a nucleosome. Chromatin is present in most cells, with a few exceptions - erythrocytes for example. Occurring only in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells, chromatin composes the vast majority of all DNA, except for a small amount inherited maternally which is found in mitochondria. In prokaryotic cells, chromatin occurs free-floating in cytoplasm, as these cells lack organelles and a defined nucleus. The main information-carrying macromolecule is a single piece of coiled double-stranded DNA, containing many genes, regulatory elements and other noncoding DNA. The DNA-bound macromolecules are proteins, which serve to package the DNA and control its functions. Chromosomes vary widely between different organisms. Some species such as certain bacteria also contain plasmids or other extrachromosomal DNA. These are circular structures in the cytoplasm which contain cellular DNA and play a role in horizontal gene transfer.Compaction of the duplicated chromosomes during cell division (mitosis or meiosis) results either in a four-arm structure (pictured to the right) if the centromere is located in the middle of the chromosome or a two-arm structure if the centromere is located near one of the ends. Chromosomal recombination during meiosis and subsequent sexual reproduction plays a vital role in genetic diversity. If these structures are manipulated incorrectly, through processes known as chromosomal instability and translocation, the cell may undergo mitotic catastrophe and die, or it may unexpectedly evade apoptosis leading to the progression of cancer.In prokaryotes (see nucleoids) and viruses, the DNA is often densely packed and organized. In the case of archaea by homologs to eukaryotic histones, in the case of bacteria by histone-like proteins. Small circular genomes called plasmids are often found in bacteria and also in mitochondria and chloroplasts, reflecting their bacterial origins.