BIO.6
... of DNA is first copied and then the cell divides. New membrane forms between the two DNA copies and the cell pinches and constricts in the middle. A new cell wall then forms around the new membrane and the cell pinches into two identical daughter cells. Eukaryotic cells go through a cell cycle, cons ...
... of DNA is first copied and then the cell divides. New membrane forms between the two DNA copies and the cell pinches and constricts in the middle. A new cell wall then forms around the new membrane and the cell pinches into two identical daughter cells. Eukaryotic cells go through a cell cycle, cons ...
Name - Humble ISD
... is enlarged. The chromosomes are cut out and arranged in __homologous______ pairs in size order, with the sex chromosomes making up the 23rd pair. Karyotypes can only be used to detect __number ______ disorders and to determine _gender_____________ of an unborn child. They do not detect any other ty ...
... is enlarged. The chromosomes are cut out and arranged in __homologous______ pairs in size order, with the sex chromosomes making up the 23rd pair. Karyotypes can only be used to detect __number ______ disorders and to determine _gender_____________ of an unborn child. They do not detect any other ty ...
EXAM Banswers2 - HonorsBiologyWiki
... 21. A cross of a red cow with a white bull produces all roan (a combination of both red and white hair) offspring. This type of inheritance is known as A.incomplete dominance. B.polygenic inheritance. C.codominance. D.multiple alleles. ...
... 21. A cross of a red cow with a white bull produces all roan (a combination of both red and white hair) offspring. This type of inheritance is known as A.incomplete dominance. B.polygenic inheritance. C.codominance. D.multiple alleles. ...
Class Presentation Questions 12
... 11. If non-disjunction occurs, abnormal numbers of chromosomes may find their way to __________, & a disorder of _______________________ numbers may result. 12. If two copies of an autosomal chromosome fail to separate during meiosis, an individual may be form with ____________ copies of a chromosom ...
... 11. If non-disjunction occurs, abnormal numbers of chromosomes may find their way to __________, & a disorder of _______________________ numbers may result. 12. If two copies of an autosomal chromosome fail to separate during meiosis, an individual may be form with ____________ copies of a chromosom ...
DNA WebQuest
... recommended that you copy and paste the link into chrome rather than clicking this link.) Go to: http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/basics/oldtour/ Click on “What is DNA?” at the top and go through the animation. Answer the questions. 1) What is DNA? 2) The complete set of instructions for makin ...
... recommended that you copy and paste the link into chrome rather than clicking this link.) Go to: http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/basics/oldtour/ Click on “What is DNA?” at the top and go through the animation. Answer the questions. 1) What is DNA? 2) The complete set of instructions for makin ...
Exam101ANS
... 1. the products of meiosis are usually haploid. 2. somatic cells enter into meiosis….(only germ line cells undergo meiosis) 3. during meiosis, crossing over may occur between homologous chromosomes. 4. all of the above. ...
... 1. the products of meiosis are usually haploid. 2. somatic cells enter into meiosis….(only germ line cells undergo meiosis) 3. during meiosis, crossing over may occur between homologous chromosomes. 4. all of the above. ...
SexChromosomes - life.illinois.edu
... • In many genera, different species will have different ploidy levels (multiples of a base number) representing a series of polyploids. In the genus Chrysanthemum, different species have chromosome numbers = 18, 36, 54, 72, 90, and 198 - all multiples of a base chromosome number of n=9. ...
... • In many genera, different species will have different ploidy levels (multiples of a base number) representing a series of polyploids. In the genus Chrysanthemum, different species have chromosome numbers = 18, 36, 54, 72, 90, and 198 - all multiples of a base chromosome number of n=9. ...
chapter 2 nature with nurture
... • Mitosis—the process through which cells (other than reproductive cells) divide • Each resulting cell gets a full copy of all 46 chromosomes • Every cell in your body except the sex cells (sperm and ova) has 23 pairs of chromosomes—46 in all • http://www.youtube.com/watch? v=Ba9LXKH2ztU&feature=rel ...
... • Mitosis—the process through which cells (other than reproductive cells) divide • Each resulting cell gets a full copy of all 46 chromosomes • Every cell in your body except the sex cells (sperm and ova) has 23 pairs of chromosomes—46 in all • http://www.youtube.com/watch? v=Ba9LXKH2ztU&feature=rel ...
1 BI 112 Instructor: Waite Final Unit Practice Exam 1) Which of the
... 11) Different forms of the same gene present in the population are known as… a) Heterozygotes b) Alleles c) Mutations d) Recessive 12) A form of a given gene that is expressed when only one copy is present, regardless of other forms of the gene that may be present, is known as… a) Recessive b) Heter ...
... 11) Different forms of the same gene present in the population are known as… a) Heterozygotes b) Alleles c) Mutations d) Recessive 12) A form of a given gene that is expressed when only one copy is present, regardless of other forms of the gene that may be present, is known as… a) Recessive b) Heter ...
Document
... division. Results in 4 haploid daughter cells (gametes) that possess 1/2 the amount of DNA of the parent cell. Mutations also arise during meiosis. ...
... division. Results in 4 haploid daughter cells (gametes) that possess 1/2 the amount of DNA of the parent cell. Mutations also arise during meiosis. ...
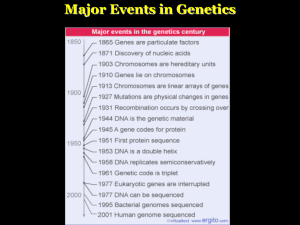
Major Events in Genetics
... -The information can be translated in a phenotype. -The information can be copied in a faithfull manner ...
... -The information can be translated in a phenotype. -The information can be copied in a faithfull manner ...
Unit 3
... existing cells. It ends with two diploid daughter cells. Meiosis, however, produces gametes for sexual reproduction, fertilization gives rise to a diploid cell (zygote). It ends with four haploid daughter cells. 11. Explain how independent assortment, crossing over, and random fertilization contribu ...
... existing cells. It ends with two diploid daughter cells. Meiosis, however, produces gametes for sexual reproduction, fertilization gives rise to a diploid cell (zygote). It ends with four haploid daughter cells. 11. Explain how independent assortment, crossing over, and random fertilization contribu ...
2.5.4. DNA Revision Qs
... (b) the production of an enzyme _____________________________________ (c) the ability to play a musical instrument _____________________________________ (d) the ability to form a blood clot _____________________________________ (e) the ability to read _____________________________________ ...
... (b) the production of an enzyme _____________________________________ (c) the ability to play a musical instrument _____________________________________ (d) the ability to form a blood clot _____________________________________ (e) the ability to read _____________________________________ ...
Part I: Multiple Choice ______1. A haploid cell is a cell a. in which
... ______2. The members of a homologous pair of chromosomes a. are identical in size and appearance. b. contain identical genetic information. c. separate to opposite poles of the cell during mitosis. d. are found only in haploid cells. ______3. For a prokaryote cell to divide, which of the following m ...
... ______2. The members of a homologous pair of chromosomes a. are identical in size and appearance. b. contain identical genetic information. c. separate to opposite poles of the cell during mitosis. d. are found only in haploid cells. ______3. For a prokaryote cell to divide, which of the following m ...
Meiosis Notes - Roslyn Public Schools
... During anaphase I, spindle fibers pull each ___________________ chromosome pair toward opposite ends of the cell. ...
... During anaphase I, spindle fibers pull each ___________________ chromosome pair toward opposite ends of the cell. ...
Biology Chapter 14 TEST (2010)
... ____ 35. If nondisjunction occurs during meiosis, a. only two gametes may form instead of four. b. some gametes may have an extra copy of some genes. c. the chromatids do not separate. d. it occurs during prophase. ____ 36. Nondisjunction can involve a. autosomes. b. sex chromosomes. c. homologous ...
... ____ 35. If nondisjunction occurs during meiosis, a. only two gametes may form instead of four. b. some gametes may have an extra copy of some genes. c. the chromatids do not separate. d. it occurs during prophase. ____ 36. Nondisjunction can involve a. autosomes. b. sex chromosomes. c. homologous ...
0.-intro-to-biopsych..
... unexpressed genes Phenotype: only expressed genes ◦ EX: the violent gene may never evolve into a phenotype ◦ EX: you may be coded for freckles, but if you don’t go into the sun, you won’t develop them ...
... unexpressed genes Phenotype: only expressed genes ◦ EX: the violent gene may never evolve into a phenotype ◦ EX: you may be coded for freckles, but if you don’t go into the sun, you won’t develop them ...
Section11.4Meiosis
... consists of two identical sister chromatids held together by a centromere. ...
... consists of two identical sister chromatids held together by a centromere. ...
Review - UCR Class!
... • Name the process by which a parent cell splits into two daughter cells ...
... • Name the process by which a parent cell splits into two daughter cells ...
The modern synthesis
... One of the key assumptions of the theory of natural selection. How does that work? Genes! ...
... One of the key assumptions of the theory of natural selection. How does that work? Genes! ...
File - Down the Rabbit Hole
... itself. • The two copies move to opposite sides of the cell • Cell membrane forms between two new and identical cells. ...
... itself. • The two copies move to opposite sides of the cell • Cell membrane forms between two new and identical cells. ...
Chromosome
A chromosome (chromo- + -some) is a packaged and organized structure containing most of the DNA of a living organism. It is not usually found on its own, but rather is complexed with many structural proteins called histones as well as associated transcription (copying of genetic sequences) factors and several other macromolecules. Two ""sister"" chromatids (half a chromosome) join together at a protein junction called a centromere. Chromosomes are normally visible under a light microscope only when the cell is undergoing mitosis. Even then, the full chromosome containing both joined sister chromatids becomes visible only during a sequence of mitosis known as metaphase (when chromosomes align together, attached to the mitotic spindle and prepare to divide). This DNA and its associated proteins and macromolecules is collectively known as chromatin, which is further packaged along with its associated molecules into a discrete structure called a nucleosome. Chromatin is present in most cells, with a few exceptions - erythrocytes for example. Occurring only in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells, chromatin composes the vast majority of all DNA, except for a small amount inherited maternally which is found in mitochondria. In prokaryotic cells, chromatin occurs free-floating in cytoplasm, as these cells lack organelles and a defined nucleus. The main information-carrying macromolecule is a single piece of coiled double-stranded DNA, containing many genes, regulatory elements and other noncoding DNA. The DNA-bound macromolecules are proteins, which serve to package the DNA and control its functions. Chromosomes vary widely between different organisms. Some species such as certain bacteria also contain plasmids or other extrachromosomal DNA. These are circular structures in the cytoplasm which contain cellular DNA and play a role in horizontal gene transfer.Compaction of the duplicated chromosomes during cell division (mitosis or meiosis) results either in a four-arm structure (pictured to the right) if the centromere is located in the middle of the chromosome or a two-arm structure if the centromere is located near one of the ends. Chromosomal recombination during meiosis and subsequent sexual reproduction plays a vital role in genetic diversity. If these structures are manipulated incorrectly, through processes known as chromosomal instability and translocation, the cell may undergo mitotic catastrophe and die, or it may unexpectedly evade apoptosis leading to the progression of cancer.In prokaryotes (see nucleoids) and viruses, the DNA is often densely packed and organized. In the case of archaea by homologs to eukaryotic histones, in the case of bacteria by histone-like proteins. Small circular genomes called plasmids are often found in bacteria and also in mitochondria and chloroplasts, reflecting their bacterial origins.