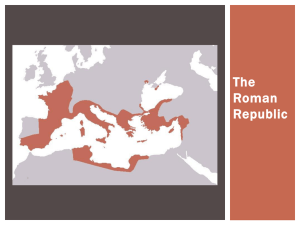
Gr. 7 CS: 17. Greek democracy and the Roman Republic were
... Gr. 7 CS: 17.Greek democracy and the Roman Republic were radical departures from monarchy and theocracy, influencing the structure and function of modern democratic governments. ...
... Gr. 7 CS: 17.Greek democracy and the Roman Republic were radical departures from monarchy and theocracy, influencing the structure and function of modern democratic governments. ...
Plebeians win victory for the rule of law in Ancient Rome, 449 BCE
... prevalent legal system is civil law, with 4.5 billion people, nearly two-thirds of the world’s population, living under this model, as nearly two-thirds of world’s countries and territories have adopted either a civil law system or a mixed system with significant civil law influence. Modern civil la ...
... prevalent legal system is civil law, with 4.5 billion people, nearly two-thirds of the world’s population, living under this model, as nearly two-thirds of world’s countries and territories have adopted either a civil law system or a mixed system with significant civil law influence. Modern civil la ...
Aulus Gellius Noctes Atticae 20.1.12
... used to protect the wives, children and slaves of Roman citizens. An injury to a dependent was an injury to the head of a household and so could be pursued by both the one injured and the head of a household, as is explained in the last sentence of III.221. The Gellius passage also demonstrates how ...
... used to protect the wives, children and slaves of Roman citizens. An injury to a dependent was an injury to the head of a household and so could be pursued by both the one injured and the head of a household, as is explained in the last sentence of III.221. The Gellius passage also demonstrates how ...
View/Open
... introduction of eras related to a city‘s incorporation by Rome; the more common use of Latin names; and new means of self-expression, both individually and for communities as a whole. The latter trend is primarily visible through the ―epigraphic habit‖, or the use of inscriptions in public and priva ...
... introduction of eras related to a city‘s incorporation by Rome; the more common use of Latin names; and new means of self-expression, both individually and for communities as a whole. The latter trend is primarily visible through the ―epigraphic habit‖, or the use of inscriptions in public and priva ...
introduction sovereignty, territoriality and universalism in the
... the emperor’s jurisdiction, and of a subject’s identity and allegiance, were to a point dependent on one’s legal place of origin.9 This was consequent upon the empire’s status as an empire – in the lifetime of Paul, the metropole and the provinces were powerfully discrepant at law – and resulted lik ...
... the emperor’s jurisdiction, and of a subject’s identity and allegiance, were to a point dependent on one’s legal place of origin.9 This was consequent upon the empire’s status as an empire – in the lifetime of Paul, the metropole and the provinces were powerfully discrepant at law – and resulted lik ...
Who did what in the Roman Republic - World History CP2
... organizers of public games, treasurers, and censors. Censors served a term of 18 months. Their primary responsibilities were to remove any unworthy senators and to enroll the new ones. They were also in charge of assessing property tax, granting contracts for public works, and conducting census of c ...
... organizers of public games, treasurers, and censors. Censors served a term of 18 months. Their primary responsibilities were to remove any unworthy senators and to enroll the new ones. They were also in charge of assessing property tax, granting contracts for public works, and conducting census of c ...
GREEK AND ROMAN POLITICAL INSTITUTIONS
... Rome. The constitution of the Roman republic, until the final decades of dissension in the first century B.C.E., which led to the establishment of the empire, tried to reconcile the various elements suggested by the Greek political experience, with primary reliance on the principle of aristocracy. A ...
... Rome. The constitution of the Roman republic, until the final decades of dissension in the first century B.C.E., which led to the establishment of the empire, tried to reconcile the various elements suggested by the Greek political experience, with primary reliance on the principle of aristocracy. A ...
Latin Project-Frank Kachmar-Government Under
... during their term as Praetor o If there were less than 6, Senate members based on seniority filled the position for the 1 year term o These special 6 Praetors were known as the “High Judges” of all of Rome and served 2 year terms o These high judges determined whether or not a law was fair, but they ...
... during their term as Praetor o If there were less than 6, Senate members based on seniority filled the position for the 1 year term o These special 6 Praetors were known as the “High Judges” of all of Rome and served 2 year terms o These high judges determined whether or not a law was fair, but they ...
File
... "If a father surrender his son for sale three times, the son shall be free.“ Marriage by usage: If a man and woman live together continuously for a year, they are considered to be married; the woman legally is treated as the man's daughter. "If any person has sung or composed against another p ...
... "If a father surrender his son for sale three times, the son shall be free.“ Marriage by usage: If a man and woman live together continuously for a year, they are considered to be married; the woman legally is treated as the man's daughter. "If any person has sung or composed against another p ...
Unit VI: Ancient Rome
... anything the Senate did which would be bad for the poor people. Veto means "I forbid it" in Latin, and it meant that the tribunes could forbid any law that was bad for the poor. The poor people also made the aristocrats write down the laws and put them in a public square where anyone could read them ...
... anything the Senate did which would be bad for the poor people. Veto means "I forbid it" in Latin, and it meant that the tribunes could forbid any law that was bad for the poor. The poor people also made the aristocrats write down the laws and put them in a public square where anyone could read them ...
Roman Achievements
... beliefs – some became martyrs who sacrificed themselves for their beliefs. ...
... beliefs – some became martyrs who sacrificed themselves for their beliefs. ...
The Rise and Fall of the Roman Republic (circa. 800
... III. Roman Conquest of Italy (cont) • Growth of the city of Rome • Evolution of Roman nobility • Conquest of the Greek colonies in southern Italy (275 BCE) --leadership of Pyrrhus --predicts Sicily as future battleground with the Carthaginians ...
... III. Roman Conquest of Italy (cont) • Growth of the city of Rome • Evolution of Roman nobility • Conquest of the Greek colonies in southern Italy (275 BCE) --leadership of Pyrrhus --predicts Sicily as future battleground with the Carthaginians ...
Roman Government - Mr. Huff`s Class
... Key Ideas In the Roman republic, power was divided among many different people so that no one person could become too powerful. The government of the Roman republic was made up of three separate branches that held different powers. The Roman republic influenced later republics, including the United ...
... Key Ideas In the Roman republic, power was divided among many different people so that no one person could become too powerful. The government of the Roman republic was made up of three separate branches that held different powers. The Roman republic influenced later republics, including the United ...
(신) Mid Term Exam Study Outline with Timeline
... III) Axial Age is only partially successful . A. Where axial age is implemented, states/societies of great complexity and size develop – 1. China Empires, straight through to the present: 2. India (Asoka) (great empires off and on) 3. Iran – Persian Achaemenid, then Parthian, then Sassanian, then Sa ...
... III) Axial Age is only partially successful . A. Where axial age is implemented, states/societies of great complexity and size develop – 1. China Empires, straight through to the present: 2. India (Asoka) (great empires off and on) 3. Iran – Persian Achaemenid, then Parthian, then Sassanian, then Sa ...
Roman AchievementsCJ
... Definition of “INNOVATION”: something new or original (such as an idea, an invention, a device, a method) ...
... Definition of “INNOVATION”: something new or original (such as an idea, an invention, a device, a method) ...
The Rise and Fall of the Roman Republic (circa. 800
... III. Roman Conquest of Italy (cont) • Growth of the city of Rome • Evolution of Roman nobility • Conquest of the Greek colonies in southern Italy (275 BCE) --leadership of Pyrrhus --predicts Sicily as future battleground with the Carthaginians ...
... III. Roman Conquest of Italy (cont) • Growth of the city of Rome • Evolution of Roman nobility • Conquest of the Greek colonies in southern Italy (275 BCE) --leadership of Pyrrhus --predicts Sicily as future battleground with the Carthaginians ...
Domestic Crisis and the `Struggle of the Orders`
... “The following year [455 BCE]…was not of an even tenor but was varied and fraught with great events. For the internal struggles, which seemed to be already extinguished, were again stirred up by the tribunes; and some foreign wars sprang up, which, without being able to harm the commonwealth at all, ...
... “The following year [455 BCE]…was not of an even tenor but was varied and fraught with great events. For the internal struggles, which seemed to be already extinguished, were again stirred up by the tribunes; and some foreign wars sprang up, which, without being able to harm the commonwealth at all, ...
Law and Justice in Ancient Times
... In time, history’s first legal profession developed in Rome, and law books began to appear. The crowning achievement of Roman law was the code drawn up between AD 529 and 565 by Emperor Justinian of the eastern part of the empire. (The western part had collapsed a little earlier.) The Justinian Cod ...
... In time, history’s first legal profession developed in Rome, and law books began to appear. The crowning achievement of Roman law was the code drawn up between AD 529 and 565 by Emperor Justinian of the eastern part of the empire. (The western part had collapsed a little earlier.) The Justinian Cod ...
Roman Government
... Read the following paragraph and use what you have learned about the Roman Republic to answer these questions. ...
... Read the following paragraph and use what you have learned about the Roman Republic to answer these questions. ...
Formation of Roman Law in Monarchy
... (it is a separate group of people having their own separate patrons or benefactors). Slaves have been considered capture of war. Thus, slaves mainly were people of different nations, though there were cases when the one who had a debt and have not returned it, had been judged for slavery at the cred ...
... (it is a separate group of people having their own separate patrons or benefactors). Slaves have been considered capture of war. Thus, slaves mainly were people of different nations, though there were cases when the one who had a debt and have not returned it, had been judged for slavery at the cred ...
Roman Law and Its Influence on Western Civilization
... to the story incompletely revealed by these problematical sources. They do not go back to the beginnings; the Roman people enter upon the scene of history relatively advanced in culture and with remarkably few vestiges of more primitive antecedents. For practical purposes, the known history of Roman ...
... to the story incompletely revealed by these problematical sources. They do not go back to the beginnings; the Roman people enter upon the scene of history relatively advanced in culture and with remarkably few vestiges of more primitive antecedents. For practical purposes, the known history of Roman ...
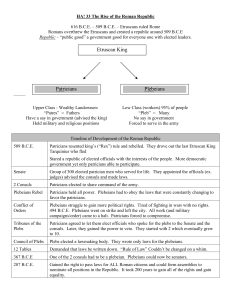
Patricians Plebeians Etruscan King
... 2 *consuls—chief magistrates who presided over the Senate and assemblies, administered legislation, served as generals in military campaigns, and represented Rome in foreign affairs. Consuls could appoint and/or serve as *dictator for up to 6 months in times of emergency. When their term of office w ...
... 2 *consuls—chief magistrates who presided over the Senate and assemblies, administered legislation, served as generals in military campaigns, and represented Rome in foreign affairs. Consuls could appoint and/or serve as *dictator for up to 6 months in times of emergency. When their term of office w ...
Excerpt, Roman Legal and Constitutional History, Kunkel, 1966 A.D.
... capital city, which already in the third century B.C. had been more and more drawn into the trade of the Hellenistic world, soon became a commercial centre of the first rank and, above all, the dominant moneymarket of the whole ancient world. The immense fortunes which flowed to Rome through wars an ...
... capital city, which already in the third century B.C. had been more and more drawn into the trade of the Hellenistic world, soon became a commercial centre of the first rank and, above all, the dominant moneymarket of the whole ancient world. The immense fortunes which flowed to Rome through wars an ...
The Roman Republic Worksheet
... The Roman Senate Consuls ‐ At the top of the Roman Republic was the consul. The consul was a very powerful position. In order to keep the consul from becoming a king or dictator, there were always two consuls elected and they only served for one year. Also, the consuls could veto each other if th ...
... The Roman Senate Consuls ‐ At the top of the Roman Republic was the consul. The consul was a very powerful position. In order to keep the consul from becoming a king or dictator, there were always two consuls elected and they only served for one year. Also, the consuls could veto each other if th ...
Roman Achievements
... Definition of “INNOVATION”: something new or original (such as an idea, an invention, a device, a method) ...
... Definition of “INNOVATION”: something new or original (such as an idea, an invention, a device, a method) ...