PDF
... Fig. 1. ACF1 expression is developmentally regulated. Wholemount immunofluorescence microscopy (IFM) was performed on different developmental stages of Drosophila. ACF1 is very abundant at early embryonic stages (A,B), but its expression is progressively restricted to subsets of cells (C) and genera ...
... Fig. 1. ACF1 expression is developmentally regulated. Wholemount immunofluorescence microscopy (IFM) was performed on different developmental stages of Drosophila. ACF1 is very abundant at early embryonic stages (A,B), but its expression is progressively restricted to subsets of cells (C) and genera ...
The Effect of a Coat Colour-Associated Genes Polymorphism on
... et al., 1999). Horses of roan phenotype are characterized by grey coat colour that results from blending the basic colour with white bristles in the thorax, neck, and partially limb areas. Roan coat colour in horses is a semi-dominant trait (Rnrn). The dominant homozygote (RnRn) is lethal in utero ( ...
... et al., 1999). Horses of roan phenotype are characterized by grey coat colour that results from blending the basic colour with white bristles in the thorax, neck, and partially limb areas. Roan coat colour in horses is a semi-dominant trait (Rnrn). The dominant homozygote (RnRn) is lethal in utero ( ...
Replication Protein A (RPA1a) Is Required for Meiotic and Somatic
... thaliana) and rice (Oryza sativa), however, possess multiple copies of an RPA gene. Rice has three paralogs each of RPA1 and RPA2, and one for RPA3. Previous studies have established their biochemical interactions in vitro and in vivo, but little is known about their exact function in rice. We exami ...
... thaliana) and rice (Oryza sativa), however, possess multiple copies of an RPA gene. Rice has three paralogs each of RPA1 and RPA2, and one for RPA3. Previous studies have established their biochemical interactions in vitro and in vivo, but little is known about their exact function in rice. We exami ...
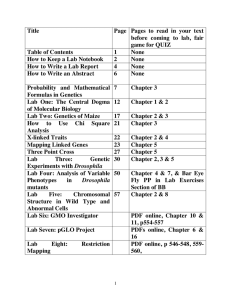
Title Page Pages to read in ... before coming to lab, fair
... We expect 1 TT: 2Tt: 1 tt, where T is tall and t is dwarf. 1. What is the probability of a dwarf plant? P = 1 dwarf/4 total = 1/4 dwarf or 25% 2. What is the probability of a tall plant? P = 3 tall/4 total = 3/4 or 75% 3. What is the probability of a heterozygous plant? P = 2 heterozygous/4 total = ...
... We expect 1 TT: 2Tt: 1 tt, where T is tall and t is dwarf. 1. What is the probability of a dwarf plant? P = 1 dwarf/4 total = 1/4 dwarf or 25% 2. What is the probability of a tall plant? P = 3 tall/4 total = 3/4 or 75% 3. What is the probability of a heterozygous plant? P = 2 heterozygous/4 total = ...
Meiosis Lecture - Mayfield City Schools
... Meiosis takes place in two sets of cell divisions, called meiosis I and meiosis II The two cell divisions result in four daughter cells, rather than the two daughter cells in mitosis Each daughter cell has only half as many chromosomes as the parent cell ...
... Meiosis takes place in two sets of cell divisions, called meiosis I and meiosis II The two cell divisions result in four daughter cells, rather than the two daughter cells in mitosis Each daughter cell has only half as many chromosomes as the parent cell ...
Direct Deletion Analysis in Two Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
... Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is the most common hereditary neuromuscular disease. It is inherited as an X-linked recessive trait in which males show clinical manifestations. In some rare cases, the disease can also be manifested in females. The aim of the present study was to determine the mole ...
... Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is the most common hereditary neuromuscular disease. It is inherited as an X-linked recessive trait in which males show clinical manifestations. In some rare cases, the disease can also be manifested in females. The aim of the present study was to determine the mole ...
The importance of chromosomes from the sixth homeologic group in
... timopheevii cytoplasm. The F2 population used in this study consisted of 414 individuals and was developed by the pollination of male sterile inbred line CMS-Salvo 15/1 by restorer line Stan I. The male sterile maternal component of the cross was kindly provided by H. Góral (The Agricultural Univers ...
... timopheevii cytoplasm. The F2 population used in this study consisted of 414 individuals and was developed by the pollination of male sterile inbred line CMS-Salvo 15/1 by restorer line Stan I. The male sterile maternal component of the cross was kindly provided by H. Góral (The Agricultural Univers ...
Genetics then and now: breeding the best and
... specific diseases or disorders is also increased. These genetic defects, resulting from the concentration of ‘liability genes’ beyond the threshold that permits the birth of a ‘normal’ offspring, are referred to as ‘threshold traits’ (106, 107). The majority of the defects encountered in domestic an ...
... specific diseases or disorders is also increased. These genetic defects, resulting from the concentration of ‘liability genes’ beyond the threshold that permits the birth of a ‘normal’ offspring, are referred to as ‘threshold traits’ (106, 107). The majority of the defects encountered in domestic an ...
DNA Replication/Transcription/RNA Splicing
... Sites of Ongoing Transcription The intranuclear position of many genes has been correlated with their activity state, suggesting that migration to functional subcompartments may influence gene expression. Indeed, nascent RNA production and RNA polymerase II seem to be localized into discrete foci or ...
... Sites of Ongoing Transcription The intranuclear position of many genes has been correlated with their activity state, suggesting that migration to functional subcompartments may influence gene expression. Indeed, nascent RNA production and RNA polymerase II seem to be localized into discrete foci or ...
Chpt9_Transposition.doc
... instance, some retroviruses can integrate into a host genome to form endogenous retroviruses. Indeed, some viruses may be derived from natural transposable elements and vice versa. Since viruses move between individuals, at least some transposable elements can move between genomes (between individua ...
... instance, some retroviruses can integrate into a host genome to form endogenous retroviruses. Indeed, some viruses may be derived from natural transposable elements and vice versa. Since viruses move between individuals, at least some transposable elements can move between genomes (between individua ...
Analysis of Flanking Sequences from Dissociation
... NOR4. A general increase in insertion frequency with increasing proximity to the NOR2 and NOR4 further suggests a positive influence of NORs upon transposition frequency. A closer view of the region immediately adjacent to NOR4, covering z300 kb, is offered in Figure 3. There is no obvious specifici ...
... NOR4. A general increase in insertion frequency with increasing proximity to the NOR2 and NOR4 further suggests a positive influence of NORs upon transposition frequency. A closer view of the region immediately adjacent to NOR4, covering z300 kb, is offered in Figure 3. There is no obvious specifici ...
IGA 8/e Chapter 4
... or not they are linked, when all three genes have simple dominant-recessive relationships among their alleles. The general formula for the number of expected phenotypes is 2n , where n is the number of genes being studied. 11. If the three genes were on separate chromosomes, the expectation is a ...
... or not they are linked, when all three genes have simple dominant-recessive relationships among their alleles. The general formula for the number of expected phenotypes is 2n , where n is the number of genes being studied. 11. If the three genes were on separate chromosomes, the expectation is a ...
Rearrangements in the Human T-Cell-Receptor Â
... Particularly close association of HTLV-I infection with leukemogenesis of ATL has often been reported by a number of serological and epidemiológica! studies (1,2). However, lack of oncogenes in the HTLV-I genome (3) and the occurrence of disease in a very small proportion (0.01-0.02%) of HTLV-Iinfe ...
... Particularly close association of HTLV-I infection with leukemogenesis of ATL has often been reported by a number of serological and epidemiológica! studies (1,2). However, lack of oncogenes in the HTLV-I genome (3) and the occurrence of disease in a very small proportion (0.01-0.02%) of HTLV-Iinfe ...
How is the biological information arranged in genome?
... syndrome might be affected the conformation of the region derived on the environmental, or the entire chromosome 21 structure, and a series of their reports for Down syndrome genes in chromosome 21 using mice were suggestive for the future functional genome analysis [18,19]. It was not enough to ana ...
... syndrome might be affected the conformation of the region derived on the environmental, or the entire chromosome 21 structure, and a series of their reports for Down syndrome genes in chromosome 21 using mice were suggestive for the future functional genome analysis [18,19]. It was not enough to ana ...
Fact Sheet 61|TUBEROUS SCLEROSIS COMPLEX In summary
... numbered and are known as autosomal chromosomes. The 23rd pair is made up of the sex chromosomes called X and Y. Males have an X and a Y chromosome and females have two copies of the X chromosome. Since all our chromosomes come in pairs, all our genes also come in pairs. Sometimes, a gene may have a ...
... numbered and are known as autosomal chromosomes. The 23rd pair is made up of the sex chromosomes called X and Y. Males have an X and a Y chromosome and females have two copies of the X chromosome. Since all our chromosomes come in pairs, all our genes also come in pairs. Sometimes, a gene may have a ...
on Mendel`s principles of heredity
... • Sickle cell anemia is a single gene, recessive disease that causes red blood cells to “sickle” (“C” shaped) as shown here. • The disease can be painful if one allele is inherited and even more serious if two alleles are inherited (one from each parent). ...
... • Sickle cell anemia is a single gene, recessive disease that causes red blood cells to “sickle” (“C” shaped) as shown here. • The disease can be painful if one allele is inherited and even more serious if two alleles are inherited (one from each parent). ...
Molecular Basis for the Recently Described Hereditary
... genetic disorder of the iron metabolism here described. Hereditary cataract is genotypically and phenotypically heterogeneous, and couldbe caused by either dysfunction of genes coding for lens-specific proteins or by alteration of the environment of the lens.I7 Recently, a membrane protein (MP19) of ...
... genetic disorder of the iron metabolism here described. Hereditary cataract is genotypically and phenotypically heterogeneous, and couldbe caused by either dysfunction of genes coding for lens-specific proteins or by alteration of the environment of the lens.I7 Recently, a membrane protein (MP19) of ...
Molecular basis for the recently described hereditary
... genetic disorder of the iron metabolism here described. Hereditary cataract is genotypically and phenotypically heterogeneous, and couldbe caused by either dysfunction of genes coding for lens-specific proteins or by alteration of the environment of the lens.I7 Recently, a membrane protein (MP19) of ...
... genetic disorder of the iron metabolism here described. Hereditary cataract is genotypically and phenotypically heterogeneous, and couldbe caused by either dysfunction of genes coding for lens-specific proteins or by alteration of the environment of the lens.I7 Recently, a membrane protein (MP19) of ...
Cytogenetics
... developing breast cancer doubles Several gene mutations are known in DNA repair e.g. BRCA1 at 17q21 and BRCA2 at 13q12 However, >90% breast cancers are not hereditary Environmental factors – nulliparity, high fat diet, alcohol, oestrogen replacement therapy Frequent screening by mammography ...
... developing breast cancer doubles Several gene mutations are known in DNA repair e.g. BRCA1 at 17q21 and BRCA2 at 13q12 However, >90% breast cancers are not hereditary Environmental factors – nulliparity, high fat diet, alcohol, oestrogen replacement therapy Frequent screening by mammography ...
Human Genes
... In the sickle cell allele, just one DNA base is changed. As a result, the abnormal hemoglobin is less soluble than normal hemoglobin. Low oxygen levels cause some red blood cells to become sickle shaped. Slide 33 of 43 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall ...
... In the sickle cell allele, just one DNA base is changed. As a result, the abnormal hemoglobin is less soluble than normal hemoglobin. Low oxygen levels cause some red blood cells to become sickle shaped. Slide 33 of 43 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall ...
Supplementary Information (doc 1084K)
... each family on chromosome 10q, in regions including the CDH23 locus. Haplotypes were not shared by deaf relatives from different families, and sequencing revealed three different missense mutations, each homozygous in the deaf individuals in one family: Pro346Ser in family G, Pro346Leu in family DA, ...
... each family on chromosome 10q, in regions including the CDH23 locus. Haplotypes were not shared by deaf relatives from different families, and sequencing revealed three different missense mutations, each homozygous in the deaf individuals in one family: Pro346Ser in family G, Pro346Leu in family DA, ...
X-inactivation

X-inactivation (also called lyonization) is a process by which one of the two copies of the X chromosome present in female mammals is inactivated. The inactive X chromosome is silenced by its being packaged in such a way that it has a transcriptionally inactive structure called heterochromatin. As nearly all female mammals have two X chromosomes, X-inactivation prevents them from having twice as many X chromosome gene products as males, who only possess a single copy of the X chromosome (see dosage compensation). The choice of which X chromosome will be inactivated is random in placental mammals such as humans, but once an X chromosome is inactivated it will remain inactive throughout the lifetime of the cell and its descendants in the organism. Unlike the random X-inactivation in placental mammals, inactivation in marsupials applies exclusively to the paternally derived X chromosome.