DNA, Genes, and Chromosomes
... 2. Show students the spool of thread and ask them to describe what substances (wood and cotton) and structures (spool and thread) they see. As students describe the thread being wound around the spools, ask them to make an analogy between the thread and spool and what they did yesterday. What is the ...
... 2. Show students the spool of thread and ask them to describe what substances (wood and cotton) and structures (spool and thread) they see. As students describe the thread being wound around the spools, ask them to make an analogy between the thread and spool and what they did yesterday. What is the ...
Slide 1
... 23 pairs of chromosomes (2 of each chromosome). This is referred to as the diploid number for humans (2n). Gametes, sex cells, only have one set of chromosomes (23). This is referred to as the haploid number for humans (n). In diploid cells, each pair of chromosomes have the same genes, arra ...
... 23 pairs of chromosomes (2 of each chromosome). This is referred to as the diploid number for humans (2n). Gametes, sex cells, only have one set of chromosomes (23). This is referred to as the haploid number for humans (n). In diploid cells, each pair of chromosomes have the same genes, arra ...
Sex-omics - Florida State University College of Medicine
... We identified 12 core DEGs that have sex-specific differential gene expression in the hippocampus of males and females. A) Venn diagram of the sex-specific DEGs that overlap between the different strains. The genes that overlap in all strains make up a sub-set of the core DEGs (PWD is not shown due ...
... We identified 12 core DEGs that have sex-specific differential gene expression in the hippocampus of males and females. A) Venn diagram of the sex-specific DEGs that overlap between the different strains. The genes that overlap in all strains make up a sub-set of the core DEGs (PWD is not shown due ...
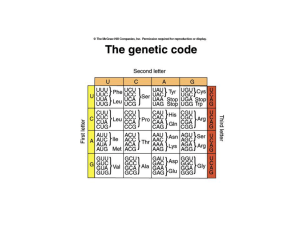
Features of the genetic code
... • Mutations that modify the genetic code are of 3 types: frameshift (include deletions and insertions), missense (lead to an amino acid replacement) and nonsense (mutation that generates any of the three stop codons leading a a premature truncation of the polypeptide. ...
... • Mutations that modify the genetic code are of 3 types: frameshift (include deletions and insertions), missense (lead to an amino acid replacement) and nonsense (mutation that generates any of the three stop codons leading a a premature truncation of the polypeptide. ...
Honors Biology - Genetics Study Guide
... during anaphase I of meiosis (or in other words, a gamete loses half its DNA to become haploid). This is why when we draw a Punnett square, if someone is heterozygous (Aa) they can give either the dominant or recessive allele. Law of independent assortment says that homologous chromosome pairs line ...
... during anaphase I of meiosis (or in other words, a gamete loses half its DNA to become haploid). This is why when we draw a Punnett square, if someone is heterozygous (Aa) they can give either the dominant or recessive allele. Law of independent assortment says that homologous chromosome pairs line ...
Interplay of Nature versus nurture
... fertilization. The new cell that is created is called a zygote. The zygote gets 23 pairs of chromosomes from the dad and 23 from the mom. ...
... fertilization. The new cell that is created is called a zygote. The zygote gets 23 pairs of chromosomes from the dad and 23 from the mom. ...
supplementary materials
... requires that two conditions be met. First, it is necessary to select an A-A translocation wherein one of the chromosome arms involved in the interchange is the same arm as that borne on the simple B-A chromosome and that the breakpoint in the arm of shared homology of the A-A translocation be dista ...
... requires that two conditions be met. First, it is necessary to select an A-A translocation wherein one of the chromosome arms involved in the interchange is the same arm as that borne on the simple B-A chromosome and that the breakpoint in the arm of shared homology of the A-A translocation be dista ...
Basic Equine Genetics.indd
... action. That is, many genes have an effect on the same trait. The effects of many of these genes are added together to produce the trait in the horse. Therefore, each gene has only a small effect on the trait. An example of this is racing speed. Racing speed is affected by such factors as size; leng ...
... action. That is, many genes have an effect on the same trait. The effects of many of these genes are added together to produce the trait in the horse. Therefore, each gene has only a small effect on the trait. An example of this is racing speed. Racing speed is affected by such factors as size; leng ...
Elucidating the essentiality of essential genes in E. coli K-12
... metabolic networks. We have performed a comparison between essential and non-essential genes within an interaction network of E. coli and found that essential genes have significantly more links than the non-essential genes, validating earlier findings in budding yeast [3]. Furthermore, other topolo ...
... metabolic networks. We have performed a comparison between essential and non-essential genes within an interaction network of E. coli and found that essential genes have significantly more links than the non-essential genes, validating earlier findings in budding yeast [3]. Furthermore, other topolo ...
Prenatal Genetic Diagnosis
... DNA; mitochondria come only from the egg; more than 20 hereditary disorders maternal inheritance; fathers do not pass on the disease ...
... DNA; mitochondria come only from the egg; more than 20 hereditary disorders maternal inheritance; fathers do not pass on the disease ...
b) Inheritance - iGCSE Science Courses
... b) Inheritance 3.13 understand that the nucleus of a cell contains chromosomes on which genes are located 3.14 understand that a gene is a section of a molecule of DNA and that a gene codes for a specific protein 3.15 describe a DNA molecule as two strands coiled to form a double helix, the strands ...
... b) Inheritance 3.13 understand that the nucleus of a cell contains chromosomes on which genes are located 3.14 understand that a gene is a section of a molecule of DNA and that a gene codes for a specific protein 3.15 describe a DNA molecule as two strands coiled to form a double helix, the strands ...
An organism containing a normal chromosome complement and
... Other aneuploids (i.e. primary trisomics, tetrasomics, multiple trisomics, secondary trisomics, tertiary trisomics, compensating trisomics) ...
... Other aneuploids (i.e. primary trisomics, tetrasomics, multiple trisomics, secondary trisomics, tertiary trisomics, compensating trisomics) ...
Cell Free Fetal DNA Insurance Information for Patients
... If your doctor has ordered cell free fetal DNA testing in maternal blood, also called noninvasive prenatal testing (NIPT), there are four labs to choose from for your test. We suggest that you call your insurance company prior to your visit to ask: • Is this genetic test a covered benefit? • Is it c ...
... If your doctor has ordered cell free fetal DNA testing in maternal blood, also called noninvasive prenatal testing (NIPT), there are four labs to choose from for your test. We suggest that you call your insurance company prior to your visit to ask: • Is this genetic test a covered benefit? • Is it c ...
Dragon Traits
... –Lower case for the recessive trait •Example – for tall or short we might use T for Tall and t for short •How would you indicate each of the 4 traits we’ve looked at: ...
... –Lower case for the recessive trait •Example – for tall or short we might use T for Tall and t for short •How would you indicate each of the 4 traits we’ve looked at: ...
ALK Gene Rearrangement: the Evaluation of a New Strategy
... throughput than RACE alone. This novel detection method which combined RACE and SAGE will be designated as SAAT (serial analysis of amplified transcripts). We performed ALK (anaplastic lymphoma kinase) fusion gene analysis to evaluate the feasibility of SAAT. ALK is a receptor tyrosine kinase and fi ...
... throughput than RACE alone. This novel detection method which combined RACE and SAGE will be designated as SAAT (serial analysis of amplified transcripts). We performed ALK (anaplastic lymphoma kinase) fusion gene analysis to evaluate the feasibility of SAAT. ALK is a receptor tyrosine kinase and fi ...
Figure 1
... of the Cd9 (Cd 9 antigen) is visible in the prospective sensory region (Sr) of the utricule as well as the non-sensory region (Nsr), (large arrow). The two horizontal arrows points toward the separation between the sensory region and the non-sensory region. Mprs18c is strongly expressed in the senso ...
... of the Cd9 (Cd 9 antigen) is visible in the prospective sensory region (Sr) of the utricule as well as the non-sensory region (Nsr), (large arrow). The two horizontal arrows points toward the separation between the sensory region and the non-sensory region. Mprs18c is strongly expressed in the senso ...
BWS - Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome support
... • A growth promoting gene Insulin-like Growth Factor II (IGF2 which is active from the paternal chromosome). It can be predicted that genetic changes that result in reduced activity of CDKN1C or increased activity of IGF2 (or both!) would cause overgrowth. The activity of both of CDKN1C and IGF2 is ...
... • A growth promoting gene Insulin-like Growth Factor II (IGF2 which is active from the paternal chromosome). It can be predicted that genetic changes that result in reduced activity of CDKN1C or increased activity of IGF2 (or both!) would cause overgrowth. The activity of both of CDKN1C and IGF2 is ...
Complex Patterns of Inheritance
... Law of Independent Assortment: the alleles of different genes separate independently of one another during gamete formation ...
... Law of Independent Assortment: the alleles of different genes separate independently of one another during gamete formation ...
Chapter 9 Study Guide
... 32. In 4 o’clock flowers the dominant trait for flower color is Red (R), the recessive is white(r). In a codominance a heterozygous offspring would have what color petals? ...
... 32. In 4 o’clock flowers the dominant trait for flower color is Red (R), the recessive is white(r). In a codominance a heterozygous offspring would have what color petals? ...
chromatin fiber
... components called nucleosomes. Histones are the chief protein components of chromatin. It is the “spool” which DNA or “thread” is wrapped around. DNA wraps around 8 histone molecules approximately twice. ...
... components called nucleosomes. Histones are the chief protein components of chromatin. It is the “spool” which DNA or “thread” is wrapped around. DNA wraps around 8 histone molecules approximately twice. ...
introduction to drosophila genetics
... Drosophila of typical appearance are said to show the “wild-type” forms (phenotypes) of genetically-controlled traits for body colour, eye colour, wing shape, etc. Naturally-occurring or artificially-induced genetic variants (mutations) of the alleles that control these traits produce flies with dif ...
... Drosophila of typical appearance are said to show the “wild-type” forms (phenotypes) of genetically-controlled traits for body colour, eye colour, wing shape, etc. Naturally-occurring or artificially-induced genetic variants (mutations) of the alleles that control these traits produce flies with dif ...
You Light Up My Life - Lakefield District Secondary School
... another protein marker on red blood cells independent of type of blood inheritance works according to complete dominance either Rh+ or Rh- ; Rh+ is dominant special problem during pregnancy of second child if mom is Rh- and first was baby Rh+ ...
... another protein marker on red blood cells independent of type of blood inheritance works according to complete dominance either Rh+ or Rh- ; Rh+ is dominant special problem during pregnancy of second child if mom is Rh- and first was baby Rh+ ...
Mendelian Genetics
... predicted, and Mendel’s experimental results closely matched this It should be noted that genes for different traits can segregate independently, but isn’t guaranteed to (some are linked) ...
... predicted, and Mendel’s experimental results closely matched this It should be noted that genes for different traits can segregate independently, but isn’t guaranteed to (some are linked) ...
2.5.15 Summary - Intermediate School Biology
... When a cell replicates it makes copies of the mitochondria including the DNA contained inside them. This results in some parts of the offspring cells getting all of their genetic information from the maternal parent only. This is described as non nuclear inheritance. Mitochondrial and chloroplast DN ...
... When a cell replicates it makes copies of the mitochondria including the DNA contained inside them. This results in some parts of the offspring cells getting all of their genetic information from the maternal parent only. This is described as non nuclear inheritance. Mitochondrial and chloroplast DN ...
Mendelian genetics At the beginning of the last section, we
... One of the parent flowers (P plants) has two purple alleles, The other has two white alleles Thus, the gametes from the P generation are either P (purple) or p (white). (Note that unfortunately your text uses P for both the “P” generation and the P (purple) allele - they mean two different things). ...
... One of the parent flowers (P plants) has two purple alleles, The other has two white alleles Thus, the gametes from the P generation are either P (purple) or p (white). (Note that unfortunately your text uses P for both the “P” generation and the P (purple) allele - they mean two different things). ...
X-inactivation

X-inactivation (also called lyonization) is a process by which one of the two copies of the X chromosome present in female mammals is inactivated. The inactive X chromosome is silenced by its being packaged in such a way that it has a transcriptionally inactive structure called heterochromatin. As nearly all female mammals have two X chromosomes, X-inactivation prevents them from having twice as many X chromosome gene products as males, who only possess a single copy of the X chromosome (see dosage compensation). The choice of which X chromosome will be inactivated is random in placental mammals such as humans, but once an X chromosome is inactivated it will remain inactive throughout the lifetime of the cell and its descendants in the organism. Unlike the random X-inactivation in placental mammals, inactivation in marsupials applies exclusively to the paternally derived X chromosome.