Pedigree Practice: Pre Test
... 1. A "family tree" diagram showing the heritable traits of parents to offspring through a number of generations is called a - - - - - - - - - A. "probability tree" B. genotype C. pedigree D. phenotype ...
... 1. A "family tree" diagram showing the heritable traits of parents to offspring through a number of generations is called a - - - - - - - - - A. "probability tree" B. genotype C. pedigree D. phenotype ...
Does the Gene Affect Our Actions or Feelings?
... Is Violence In Your Genes? Scientists have discovered a gene in our body nicknamed the warrior gene. Is it harmful? ...
... Is Violence In Your Genes? Scientists have discovered a gene in our body nicknamed the warrior gene. Is it harmful? ...
Gene Set Testing - USU Math/Stat
... X = (xij) = matrix of “normalized” expression values (n rows, p columns) Y = vector of “clinical outcome” (usually 0/1) ...
... X = (xij) = matrix of “normalized” expression values (n rows, p columns) Y = vector of “clinical outcome” (usually 0/1) ...
Chapter 21 (part 1) - Nevada Agricultural Experiment
... enzyme is a multimeric protein a2,b, b’, w • The b’ subunit is involved in DNA binding • The b subunit contains the polymerase active site • The a subunit acts as scaffold on which the other subunits assemble. • Also requires s-factor for initiation –forms holo enzyme complex ...
... enzyme is a multimeric protein a2,b, b’, w • The b’ subunit is involved in DNA binding • The b subunit contains the polymerase active site • The a subunit acts as scaffold on which the other subunits assemble. • Also requires s-factor for initiation –forms holo enzyme complex ...
Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction
... Genes are regions in an organism’s DNA that encode information about heritable traits Alleles are different forms of the same gene • Offspring of sexual reproducers inherit new combinations of alleles, the basis of traits ...
... Genes are regions in an organism’s DNA that encode information about heritable traits Alleles are different forms of the same gene • Offspring of sexual reproducers inherit new combinations of alleles, the basis of traits ...
Autosomal dominant medullary cystic kidney disease: evidence of
... at the corticomedullary junction. While in NPH endstage renal disease ( ESRD) occurs in adolescence, ADMCKD leads to ESRD in adulthood. Recently a gene locus for ADMCKD has been localized to chromosome 1q21 in two large Cypriot families. This prompted us to examine linkage in three ADMCKDfamilies, u ...
... at the corticomedullary junction. While in NPH endstage renal disease ( ESRD) occurs in adolescence, ADMCKD leads to ESRD in adulthood. Recently a gene locus for ADMCKD has been localized to chromosome 1q21 in two large Cypriot families. This prompted us to examine linkage in three ADMCKDfamilies, u ...
Lesson 3- monohybrid crosses
... • An organism is said to be TRUE BREEDING if, when crossed with another organism of the same strain, it always produces offspring of exactly the same kind ...
... • An organism is said to be TRUE BREEDING if, when crossed with another organism of the same strain, it always produces offspring of exactly the same kind ...
Document
... presence of the allele as Xb. The “normal” vision allele is represented as XB. Females heterozygous for this trait (XB Xb) have normal vision, but are considered “carriers” of the allele because they can still pass the trait on to their children. The color perception defect manifests itself in femal ...
... presence of the allele as Xb. The “normal” vision allele is represented as XB. Females heterozygous for this trait (XB Xb) have normal vision, but are considered “carriers” of the allele because they can still pass the trait on to their children. The color perception defect manifests itself in femal ...
A Statistical Approach to Literature
... Ideas for the Statistical Model • Observation: typically, some genes in the list are related to a given word, but the other genes are not (Few gene clusters are perfect!) • Assumption: the count of a term in a document follows Poisson distribution • Idea: the count of a term in one gene is either f ...
... Ideas for the Statistical Model • Observation: typically, some genes in the list are related to a given word, but the other genes are not (Few gene clusters are perfect!) • Assumption: the count of a term in a document follows Poisson distribution • Idea: the count of a term in one gene is either f ...
File
... Match the word with the correct definition. Write the letter in the blank provided. ____ 1. Allele that is seen even if present with the recessive form. ____ 2. Another word for egg and sperm cells. ____ 3. Units of hereditary information (codes for one protein). ____ 4. Two identical alleles for a ...
... Match the word with the correct definition. Write the letter in the blank provided. ____ 1. Allele that is seen even if present with the recessive form. ____ 2. Another word for egg and sperm cells. ____ 3. Units of hereditary information (codes for one protein). ____ 4. Two identical alleles for a ...
Name
... Sex-linked traits are traits whose genes are found on the sex chromosomes (X or Y). Most sexlinked traits are found on the X chromosome; in fact, since they’re only found on the X chromosome we can guess that they are found on the fourth “leg” that the X has instead of 3 legs on the Y. Further, sex- ...
... Sex-linked traits are traits whose genes are found on the sex chromosomes (X or Y). Most sexlinked traits are found on the X chromosome; in fact, since they’re only found on the X chromosome we can guess that they are found on the fourth “leg” that the X has instead of 3 legs on the Y. Further, sex- ...
Introduction When we think of a disease, most of us imagine a nasty
... cancer is needed. Certain genes regulate cell growth and division, and if one of these genes is mutated, the cell will not be able to regulate its growth and division, leading to cancer. A gene mutation may be spontaneous, or caused by environmental influences such as, X-rays, viruses or chemical ca ...
... cancer is needed. Certain genes regulate cell growth and division, and if one of these genes is mutated, the cell will not be able to regulate its growth and division, leading to cancer. A gene mutation may be spontaneous, or caused by environmental influences such as, X-rays, viruses or chemical ca ...
What to know and be able to do
... 1. Which cell structures are involved in the processes of mitosis and meiosis 2. What are the purposes of mitosis and meiosis? 3. Be able to put unlabeled diagrams into the right order for meiosis. Be able to name the phase pictured in a diagram. 4. How do the cells that result from mitosis and meio ...
... 1. Which cell structures are involved in the processes of mitosis and meiosis 2. What are the purposes of mitosis and meiosis? 3. Be able to put unlabeled diagrams into the right order for meiosis. Be able to name the phase pictured in a diagram. 4. How do the cells that result from mitosis and meio ...
osb week06 geneticsproblems
... What are the potential types and proportions of offspring from this cross? What is the outcome if two plants from the F1 generation are crossed? 12) How would you determine the genotype of a tall, red-fruited tomato plant? What would be the results of the test-cross if the tall, red-fruited plant wa ...
... What are the potential types and proportions of offspring from this cross? What is the outcome if two plants from the F1 generation are crossed? 12) How would you determine the genotype of a tall, red-fruited tomato plant? What would be the results of the test-cross if the tall, red-fruited plant wa ...
PATTERNS OF HEREDITY AND HUMAN GENETICS CHapter 12
... potential to develop and function. • As the organism develops, many factors can influence how the gene is expressed, or even whether the gene is expressed at all. • Two such influences are the organism’s external and internal environments. ...
... potential to develop and function. • As the organism develops, many factors can influence how the gene is expressed, or even whether the gene is expressed at all. • Two such influences are the organism’s external and internal environments. ...
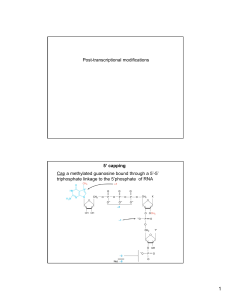
Post-transcriptional modifications Cap a
... Gene silencing is probably often the result of more than one mechanism. Transcriptional gene silencing (TGS) is often associated with methylation of the gene, which may inhibit transcription. In posttranscriptional gene silencing (PTGS), high levels of normal mRNA can cause activation of RNA-depende ...
... Gene silencing is probably often the result of more than one mechanism. Transcriptional gene silencing (TGS) is often associated with methylation of the gene, which may inhibit transcription. In posttranscriptional gene silencing (PTGS), high levels of normal mRNA can cause activation of RNA-depende ...
Measuring the Rates of Transcriptional Elongation in the Female
... Supporting the view that rasiRNAs act to silence repetitive sequence by reducing their rate of transcription, mutations in spn-E, aubergine, and piwi are reported to cause loss of lysine-9 methylation of histone H3 on silenced genes (Pal-Bhadra et al. 2004). Historically, heterochromatin has been re ...
... Supporting the view that rasiRNAs act to silence repetitive sequence by reducing their rate of transcription, mutations in spn-E, aubergine, and piwi are reported to cause loss of lysine-9 methylation of histone H3 on silenced genes (Pal-Bhadra et al. 2004). Historically, heterochromatin has been re ...
L 04 _transcription
... eukaryotes is complex, and involved many transcription factors. Termination depends on both proteins and DNA sequences, and perhaps DNA structures (the single-stranded DNA created to allow transcription may adopt secondary structure). Note that DNA replication begins at origins of replication scatte ...
... eukaryotes is complex, and involved many transcription factors. Termination depends on both proteins and DNA sequences, and perhaps DNA structures (the single-stranded DNA created to allow transcription may adopt secondary structure). Note that DNA replication begins at origins of replication scatte ...
Chapter 15 ppt
... X chromosome in humans: – Color blindness – Duchenne muscular dystrophy – progressive weakening of muscles and loss of coordination; affected individuals rarely live past early 20s – Hemophilia – having blood with an inability to clot normally, caused by the absence of proteins required for blood cl ...
... X chromosome in humans: – Color blindness – Duchenne muscular dystrophy – progressive weakening of muscles and loss of coordination; affected individuals rarely live past early 20s – Hemophilia – having blood with an inability to clot normally, caused by the absence of proteins required for blood cl ...
Gene Section NUP98 (nucleoporin 98 kDa) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... Huret JL. NUP98 (nucleoporin 98 kDa). Atlas Genet Cytogenet Oncol Haematol.1999;3(1):15-16. Huret JL. NUP98 (nucleoporin 98 kDa). Atlas Genet Cytogenet Oncol Haematol.1998;2(1):7. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 2.0 France Licence. © 2000 ...
... Huret JL. NUP98 (nucleoporin 98 kDa). Atlas Genet Cytogenet Oncol Haematol.1999;3(1):15-16. Huret JL. NUP98 (nucleoporin 98 kDa). Atlas Genet Cytogenet Oncol Haematol.1998;2(1):7. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 2.0 France Licence. © 2000 ...
Inferring Function From Known Genes
... There are several ways in which known genes can be used to infer the function of unknown genes in a microarray experiment. 3) Pathway analysis If the genes are sufficiently well understood, they may be assembled into networks showing which genes regulate other genes. Unknown genes that have expressi ...
... There are several ways in which known genes can be used to infer the function of unknown genes in a microarray experiment. 3) Pathway analysis If the genes are sufficiently well understood, they may be assembled into networks showing which genes regulate other genes. Unknown genes that have expressi ...
Inferring Function From Known Genes
... There are several ways in which known genes can be used to infer the function of unknown genes in a microarray experiment. 3) Pathway analysis If the genes are sufficiently well understood, they may be assembled into networks showing which genes regulate other genes. Unknown genes that have expressi ...
... There are several ways in which known genes can be used to infer the function of unknown genes in a microarray experiment. 3) Pathway analysis If the genes are sufficiently well understood, they may be assembled into networks showing which genes regulate other genes. Unknown genes that have expressi ...
Hox
... Codes for a DNA binding segment (aa sequence) in the transcription factor. The transcription factors activate structural genes. Structural genes produce structures appropriate for that location. Mutations in Hox genes result in inappropriate structures for that ...
... Codes for a DNA binding segment (aa sequence) in the transcription factor. The transcription factors activate structural genes. Structural genes produce structures appropriate for that location. Mutations in Hox genes result in inappropriate structures for that ...
X-inactivation

X-inactivation (also called lyonization) is a process by which one of the two copies of the X chromosome present in female mammals is inactivated. The inactive X chromosome is silenced by its being packaged in such a way that it has a transcriptionally inactive structure called heterochromatin. As nearly all female mammals have two X chromosomes, X-inactivation prevents them from having twice as many X chromosome gene products as males, who only possess a single copy of the X chromosome (see dosage compensation). The choice of which X chromosome will be inactivated is random in placental mammals such as humans, but once an X chromosome is inactivated it will remain inactive throughout the lifetime of the cell and its descendants in the organism. Unlike the random X-inactivation in placental mammals, inactivation in marsupials applies exclusively to the paternally derived X chromosome.