Pengaturan Ekspresi gen 1. Struktur gen prokaryot dan eukaryot
... alone (sometimes referred to as the primary transcript) would contain both coding (exon) and noncoding (intron) sequences. Before it can be translated into protein, the two ends of the RNA are modified, the introns are removed by an enzymatically catalyzed RNA splicing reaction, and the resulting mR ...
... alone (sometimes referred to as the primary transcript) would contain both coding (exon) and noncoding (intron) sequences. Before it can be translated into protein, the two ends of the RNA are modified, the introns are removed by an enzymatically catalyzed RNA splicing reaction, and the resulting mR ...
Document
... GgLl and ggll 1GgLl:1Ggll:1ggLl:1ggll = equal numbers of each type. Is that what was observed? No - most were like either parent What is the chance that crossing over will happen? ...
... GgLl and ggll 1GgLl:1Ggll:1ggLl:1ggll = equal numbers of each type. Is that what was observed? No - most were like either parent What is the chance that crossing over will happen? ...
Molecular-3
... silencing, has also been observed in some cancer cells. In the sporadic form of retinoblastoma, both alleles are also inactivated, but in this case, the inactivation results from two somatic events occurring in the same cell. ...
... silencing, has also been observed in some cancer cells. In the sporadic form of retinoblastoma, both alleles are also inactivated, but in this case, the inactivation results from two somatic events occurring in the same cell. ...
The diagrams below show two different scenarios for a pair of
... (C) The data indicate that the allele is most likely sex-linked because, in the F1 generation, female offspring express different phenotypes than male offspring, which occurs when genes are found on the X chromosome. Distractor Rationale: This answer suggests the student may understand that phenotyp ...
... (C) The data indicate that the allele is most likely sex-linked because, in the F1 generation, female offspring express different phenotypes than male offspring, which occurs when genes are found on the X chromosome. Distractor Rationale: This answer suggests the student may understand that phenotyp ...
The role of sex chromosomes in mammalian germ cell differentiation
... meiosis,47 and ultimately, the production of offspring is the only reliable evidence for functional gametes. The first success in obtaining the birth of live offspring from ESC‑derived male haploid cells was reported in 2006.42 The key to this success may be the selection of ESCs expressing STRA8, w ...
... meiosis,47 and ultimately, the production of offspring is the only reliable evidence for functional gametes. The first success in obtaining the birth of live offspring from ESC‑derived male haploid cells was reported in 2006.42 The key to this success may be the selection of ESCs expressing STRA8, w ...
DNA is - Mount Carmel Academy
... that _________ had to be the molecules that made up genes. There were so many different kinds proteins and DNA seemed to be too monotonous . . . repeating the same ...
... that _________ had to be the molecules that made up genes. There were so many different kinds proteins and DNA seemed to be too monotonous . . . repeating the same ...
Take Home Quiz- Genetics 1. A partial Punnett square is shown
... D. One parent is homozygous dominant and the other parent is heterozygous. 2. In fruit flies, the gene for eye color is located on the X chromosome, and the red eye allele (R) is dominant to the white eye allele (r). A female fly with genotype XRXr is mated with a male fly with genotype XrY. Which o ...
... D. One parent is homozygous dominant and the other parent is heterozygous. 2. In fruit flies, the gene for eye color is located on the X chromosome, and the red eye allele (R) is dominant to the white eye allele (r). A female fly with genotype XRXr is mated with a male fly with genotype XrY. Which o ...
17 Cell Differentiation and Gene Expression
... stored in DNA is used to produce a functional gene product. Gene products are either proteins or noncoding RNAs, such as tRNA and rRNA, which play essential roles in protein synthesis, but do not code for proteins. Gene expression is regulated throughout the lifespan of an individual cell to control ...
... stored in DNA is used to produce a functional gene product. Gene products are either proteins or noncoding RNAs, such as tRNA and rRNA, which play essential roles in protein synthesis, but do not code for proteins. Gene expression is regulated throughout the lifespan of an individual cell to control ...
Cancer Prone Disease Section Simpson-Golabi-Behmel Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... Wilms tumor, neuroblastoma during early childhood; one case of hepatocellular carcinoma reported. ...
... Wilms tumor, neuroblastoma during early childhood; one case of hepatocellular carcinoma reported. ...
Detection of unpaired DNA at meiosis results in RNA‐mediated
... tip forms a crozier, the terminal pair of nuclei undergo one synchronous mitotic division and the products are partitioned into different cells such that the penultimate cell contains one nucleus from each parent. These nuclei fuse (karyogamy) to form the diploid zygote (C), which immediately underg ...
... tip forms a crozier, the terminal pair of nuclei undergo one synchronous mitotic division and the products are partitioned into different cells such that the penultimate cell contains one nucleus from each parent. These nuclei fuse (karyogamy) to form the diploid zygote (C), which immediately underg ...
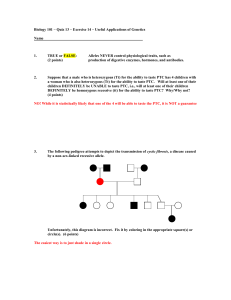
Biology 101 – Quiz 13 – Exercise 14 – Useful Applications of Genetics
... Billy Bob is NOT a hemophiliac (hemophilia is a X-linked recessive disorder). Billy Bob has a daughter, Edna, with Noreen, a carrier of the hemophilia trait. What are the chances that Edna will be a hemophiliac? What are the chances that Edna will be a carrier of the hemophilia trait? (5 points) Sin ...
... Billy Bob is NOT a hemophiliac (hemophilia is a X-linked recessive disorder). Billy Bob has a daughter, Edna, with Noreen, a carrier of the hemophilia trait. What are the chances that Edna will be a hemophiliac? What are the chances that Edna will be a carrier of the hemophilia trait? (5 points) Sin ...
Transcription and Translation
... a gene (called exons) are interrupted by introns. • The function of introns remains unclear. They may help is RNA transport or in control of gene expression in some cases, and they may make it easier for sections of genes to be shuffled in evolution. But , no generally accepted reason for the existe ...
... a gene (called exons) are interrupted by introns. • The function of introns remains unclear. They may help is RNA transport or in control of gene expression in some cases, and they may make it easier for sections of genes to be shuffled in evolution. But , no generally accepted reason for the existe ...
Principles & Patterns of inheritance ppt
... Recessive trait : Sugary kernels shown only when no dominant allele is present ...
... Recessive trait : Sugary kernels shown only when no dominant allele is present ...
Patterns of Inheritance Understanding the Chromosome A History of
... 2. Certain traits have dominance over others. - The purple flower color seemed to “hide” the white flower color during the first generation of offspring. - The purple color was the dominant allele. - It blocked expression of the white color gene. ...
... 2. Certain traits have dominance over others. - The purple flower color seemed to “hide” the white flower color during the first generation of offspring. - The purple color was the dominant allele. - It blocked expression of the white color gene. ...
ID_3183_Organism as a level of life or_English_sem_1
... Genetic variation State the way of combinatorial variation: Homologous chromosomes on the equatorial platter of the meiotic spindle in a random arrangement, thus facilitating genetic mixing; Homologous chromosomes pair making physical contact (synapsis) and forming a tetrad in the prophase of meiosi ...
... Genetic variation State the way of combinatorial variation: Homologous chromosomes on the equatorial platter of the meiotic spindle in a random arrangement, thus facilitating genetic mixing; Homologous chromosomes pair making physical contact (synapsis) and forming a tetrad in the prophase of meiosi ...
Inheritance and Adaptations
... birth alone in a tank. In 2008, her keepers noticed that a baby shark was lying at the bottom of the tank. DNA testing has not yet been done, but the keepers are sure that the female has never been in contact with another shark. Because of the chromosome arrangement of sharks, they can produce only ...
... birth alone in a tank. In 2008, her keepers noticed that a baby shark was lying at the bottom of the tank. DNA testing has not yet been done, but the keepers are sure that the female has never been in contact with another shark. Because of the chromosome arrangement of sharks, they can produce only ...
just disorders - local.brookings.k12.sd.us
... that appears during middle age resulting in nursing home care and early death Huntington’s ____________________ disease (HD) Progressive weakening of muscle proteins resulting in inability to walk Duchenne Muscular dystrophy and eventually death _________________________ Inability to distinguish bet ...
... that appears during middle age resulting in nursing home care and early death Huntington’s ____________________ disease (HD) Progressive weakening of muscle proteins resulting in inability to walk Duchenne Muscular dystrophy and eventually death _________________________ Inability to distinguish bet ...
Eukaryotic Gene Regulation
... condensed than that of mitotic chromosomes • Much of the interphase chromatin is present as a 10-nm fiber, and some is 30-nm fiber, which in some regions is folded into looped domains ...
... condensed than that of mitotic chromosomes • Much of the interphase chromatin is present as a 10-nm fiber, and some is 30-nm fiber, which in some regions is folded into looped domains ...
thalassemia occurs when one or more of the 4 alpha chain genes
... since one of the 2 beta genes functions normally. The red cells are small and a mild anemia may exist. People with the condition generally have no symptoms. The condition can be detected by a routine laboratory blood evaluation. (Note that in many ways, the one-gene beta thalassemia and the two-gene ...
... since one of the 2 beta genes functions normally. The red cells are small and a mild anemia may exist. People with the condition generally have no symptoms. The condition can be detected by a routine laboratory blood evaluation. (Note that in many ways, the one-gene beta thalassemia and the two-gene ...
Chapter Two Theories - Dimensions Family Therapy
... the traits that are most useful will become more frequent, thus making survival of ...
... the traits that are most useful will become more frequent, thus making survival of ...
plasmids - genemol de Jean
... Integrons are mobile DNA elements able to capture genes, notably those encoding antibiotic resistance, by site-specific recombination. Class 1 integrons have been examined the most extensively. They consist of a variable region bordered by 5' and 3' conserved regions. The 5' region is made up of th ...
... Integrons are mobile DNA elements able to capture genes, notably those encoding antibiotic resistance, by site-specific recombination. Class 1 integrons have been examined the most extensively. They consist of a variable region bordered by 5' and 3' conserved regions. The 5' region is made up of th ...
RNA interference was popularized by work in C
... in C.elegans. When long double-stranded RNAs were injected into a worm’s gonad, a standard way of introducing transgenes into worms, they blocked the expression of endogenous genes in the sequence specific manner. In eukaryotes, most protein coding genes are transcribed by RNA polymerase II, which g ...
... in C.elegans. When long double-stranded RNAs were injected into a worm’s gonad, a standard way of introducing transgenes into worms, they blocked the expression of endogenous genes in the sequence specific manner. In eukaryotes, most protein coding genes are transcribed by RNA polymerase II, which g ...
Putting it all Together
... Putting it all Together: Part A 1. For how many traits is the mother homozygous? _____ The father? ____ 2. For how many trait is the mother heterozygous? ______ The father? ____ 3. Complete the Punnett Squares below and figure out the genotypes and phenotypes that the offspring might have by fillin ...
... Putting it all Together: Part A 1. For how many traits is the mother homozygous? _____ The father? ____ 2. For how many trait is the mother heterozygous? ______ The father? ____ 3. Complete the Punnett Squares below and figure out the genotypes and phenotypes that the offspring might have by fillin ...
GENETIC DISORDER RESEARCH PACKET
... In order to summarize your knowledge of cells, cell division, genetics, DNA, and proteins, you are being assigned a genetic disorder to research. Genetic disorders are caused by changes to DNA. These changes are either really small and involve only one tiny piece of DNA or really large and result in ...
... In order to summarize your knowledge of cells, cell division, genetics, DNA, and proteins, you are being assigned a genetic disorder to research. Genetic disorders are caused by changes to DNA. These changes are either really small and involve only one tiny piece of DNA or really large and result in ...
X-inactivation

X-inactivation (also called lyonization) is a process by which one of the two copies of the X chromosome present in female mammals is inactivated. The inactive X chromosome is silenced by its being packaged in such a way that it has a transcriptionally inactive structure called heterochromatin. As nearly all female mammals have two X chromosomes, X-inactivation prevents them from having twice as many X chromosome gene products as males, who only possess a single copy of the X chromosome (see dosage compensation). The choice of which X chromosome will be inactivated is random in placental mammals such as humans, but once an X chromosome is inactivated it will remain inactive throughout the lifetime of the cell and its descendants in the organism. Unlike the random X-inactivation in placental mammals, inactivation in marsupials applies exclusively to the paternally derived X chromosome.