click here
... 1. Independent assortment is based on the fact that the genes are NOT linked. In a dihybrid cross, you would expect a 9:3:3:1 ratio if genes are not linked. The three ratios shown are all expected results of a dihybrid (AaBb x AaBb) cross- all show a 9:3:3:1 ratio, or a variant of it. Ans: all of th ...
... 1. Independent assortment is based on the fact that the genes are NOT linked. In a dihybrid cross, you would expect a 9:3:3:1 ratio if genes are not linked. The three ratios shown are all expected results of a dihybrid (AaBb x AaBb) cross- all show a 9:3:3:1 ratio, or a variant of it. Ans: all of th ...
Genetics L311 exam 2
... transmissible disease. Examples produce scrapie in sheep or Creuzfeldt-Jakob disease in humans. C. Densely staining, compact and relatively transcriptionally inactive regions of chromosomes are referred to as heterochromatin . D. Based on the position of its centromere, this chromosome is said to be ...
... transmissible disease. Examples produce scrapie in sheep or Creuzfeldt-Jakob disease in humans. C. Densely staining, compact and relatively transcriptionally inactive regions of chromosomes are referred to as heterochromatin . D. Based on the position of its centromere, this chromosome is said to be ...
Update on genetics research on stuttering
... – 270 unrelated North American affected individuals – 96 unrelated normally fluent Pakistanis – 265 unrelated normally fluent North Americans – All have a family history of stuttering • Found several other mutations in this gene that occur in individuals who stutter but do not occur in normally flue ...
... – 270 unrelated North American affected individuals – 96 unrelated normally fluent Pakistanis – 265 unrelated normally fluent North Americans – All have a family history of stuttering • Found several other mutations in this gene that occur in individuals who stutter but do not occur in normally flue ...
Genetics
... • The genes are symbolized by the first letter of the dominant gene. • The letter for the dominant gene is always capitalized. • The letter for the recessive trait is always lower case (make sure you can tell the difference between the two) • Wild Type is the typical form of the organism, strain, or ...
... • The genes are symbolized by the first letter of the dominant gene. • The letter for the dominant gene is always capitalized. • The letter for the recessive trait is always lower case (make sure you can tell the difference between the two) • Wild Type is the typical form of the organism, strain, or ...
Linkage Analysis and Mapping
... • Recombination is caused by formation of chiasmata along the chromosome at multiple points. • If the distance between two genes is large enough, there can potentially be multiple chiasmata formation between them; – so there could be multiple crossovers. • What would happen if there were two crossov ...
... • Recombination is caused by formation of chiasmata along the chromosome at multiple points. • If the distance between two genes is large enough, there can potentially be multiple chiasmata formation between them; – so there could be multiple crossovers. • What would happen if there were two crossov ...
Dihybrid Crosses Involve 2 traits Eg. Crossing tall
... Predict the phenotypic outcome if a hetero tall, homozygous yellow pea plant is crossed with TTYY ...
... Predict the phenotypic outcome if a hetero tall, homozygous yellow pea plant is crossed with TTYY ...
Stage and developmental specific gene expression during
... mice. Therefore, it can be concluded that the DNA sequences located between the 400 bp and 900 bp upstream of ATG can function as enhancer elements. For further characterization of DNA cis-acting elements we sequenced about 1 kb of the 5' flanking region of the proaccrosin gene of different mammals. ...
... mice. Therefore, it can be concluded that the DNA sequences located between the 400 bp and 900 bp upstream of ATG can function as enhancer elements. For further characterization of DNA cis-acting elements we sequenced about 1 kb of the 5' flanking region of the proaccrosin gene of different mammals. ...
one
... dominant allele and one recessive, disorder-causing allele, do not have the disorder, but can pass it on because they are carriers of the disorder. • Sex-linked genes: Genes on the sex-chromosomes (the X and Y chromosomes in many species) are sex-linked genes. In mammals, including humans, and some ...
... dominant allele and one recessive, disorder-causing allele, do not have the disorder, but can pass it on because they are carriers of the disorder. • Sex-linked genes: Genes on the sex-chromosomes (the X and Y chromosomes in many species) are sex-linked genes. In mammals, including humans, and some ...
14-2
... dominant allele for a protein found in brain cells. The allele for this disease contains a long string of bases in which the codon CAG—coding for the amino acid glutamine—repeats over and over again, more than 40 times. Despite intensive study, the reason why these long strings of glutamine cause di ...
... dominant allele for a protein found in brain cells. The allele for this disease contains a long string of bases in which the codon CAG—coding for the amino acid glutamine—repeats over and over again, more than 40 times. Despite intensive study, the reason why these long strings of glutamine cause di ...
Mutations - Fulton County Schools
... …ALSO AN EFFECT…BUT WANTED TO PUT AFTER frameshift – changes the “reading frame” caused by insertion/deletion ...
... …ALSO AN EFFECT…BUT WANTED TO PUT AFTER frameshift – changes the “reading frame” caused by insertion/deletion ...
Meiosis - DigitalWebb.com
... 3. RNA pol III cytoplasmic and small nuclear RNA Eukaryotes also have more than 4 subunits in the core enzyme. Transcription takes place in the nucleus. Because DNA in eukaryotes is bound around protein histones (DNA + histone = nucleosomes), for transcription to take place, the protein histones mus ...
... 3. RNA pol III cytoplasmic and small nuclear RNA Eukaryotes also have more than 4 subunits in the core enzyme. Transcription takes place in the nucleus. Because DNA in eukaryotes is bound around protein histones (DNA + histone = nucleosomes), for transcription to take place, the protein histones mus ...
Chapter 15
... • Genomic imprinting is thought to affect only a small fraction of mammalian genes • Most imprinted genes are critical for embryonic development Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
... • Genomic imprinting is thought to affect only a small fraction of mammalian genes • Most imprinted genes are critical for embryonic development Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
Fund of Genetics Gallery Walk
... C. The cells of the offspring undergo mitosis many times as the offspring grow and develop. D. The offspring have a period of embryonic development, rather than being ...
... C. The cells of the offspring undergo mitosis many times as the offspring grow and develop. D. The offspring have a period of embryonic development, rather than being ...
Gallery Walk - Katy Independent School District
... C. The cells of the offspring undergo mitosis many times as the offspring grow and develop. D. The offspring have a period of embryonic development, rather than being ...
... C. The cells of the offspring undergo mitosis many times as the offspring grow and develop. D. The offspring have a period of embryonic development, rather than being ...
File
... cycle that regularly alternates between a haploid phase and a diploid phase. As shown in Figure 8, in plants, the diploid phase in the life cycle that produces spores is called Sporophyte. Sporeforming cells in the Sporophyte undergo meiosis to produce spores. A spore is a haploid reproductive cell ...
... cycle that regularly alternates between a haploid phase and a diploid phase. As shown in Figure 8, in plants, the diploid phase in the life cycle that produces spores is called Sporophyte. Sporeforming cells in the Sporophyte undergo meiosis to produce spores. A spore is a haploid reproductive cell ...
article - British Academy
... level hand preference among gorillas preparing vegetable matter for consumption, with about two-thirds showing a right-hand preference for the more intricate components. McGrew & Marchant (1997: 201) have expressed some scepticism as to the generality of this work; in a review of handedness in prima ...
... level hand preference among gorillas preparing vegetable matter for consumption, with about two-thirds showing a right-hand preference for the more intricate components. McGrew & Marchant (1997: 201) have expressed some scepticism as to the generality of this work; in a review of handedness in prima ...
Fetal Hemoglobin Levels in Sickle Cell Disease and
... and L alleles from females who were homozygous for the H allele. We can only deduce from this analysis that nonanemic individuals with greater than 3.3% F cells have at least one H allele. Phenotypes and genotypes of SS subjects. Due to preferential survival of F cells in the circulation of SS subje ...
... and L alleles from females who were homozygous for the H allele. We can only deduce from this analysis that nonanemic individuals with greater than 3.3% F cells have at least one H allele. Phenotypes and genotypes of SS subjects. Due to preferential survival of F cells in the circulation of SS subje ...
Prenatal Care… - Coudersport Area School District / Overview
... - Tiny structures w/in the nuclei of cells that carry information about hereditary traits (genes/ DNA…) DNA: Is the portion of a chromosome that makes each of us unique to others… - The shape that DNA is arranged in is called a double helix… ...
... - Tiny structures w/in the nuclei of cells that carry information about hereditary traits (genes/ DNA…) DNA: Is the portion of a chromosome that makes each of us unique to others… - The shape that DNA is arranged in is called a double helix… ...
... for the previou g cells. or terminal that such a microfluid morphologic ns have been s issues of The results show screening on circulating criteria of malign [2] used for deletions KREATECH reported. early-stage cancer You can also occur in equal NEWS ancy 8p23 applica other cancer types possibilitie ...
18. GENETIC REGULATION OF DEVELOPMENT.
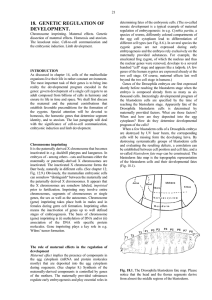
... will leak out. The head and the thorax segments are missing from the embryo that develops inside the egg (Fig. 18.2). Results of the pricking experiments show (i) the presence of a maternally derived factor in the anterior tip of the eggs. (ii) The factor must have a long range effect since it organ ...
... will leak out. The head and the thorax segments are missing from the embryo that develops inside the egg (Fig. 18.2). Results of the pricking experiments show (i) the presence of a maternally derived factor in the anterior tip of the eggs. (ii) The factor must have a long range effect since it organ ...
Eukaryotic Chromosome Mapping
... Double recombinants have two crossovers: one between the first and middle gene and one between the middle and third gene These will be the two smallest classes. Double Recombinants: red, tall, normal green, dwarf, ragged ...
... Double recombinants have two crossovers: one between the first and middle gene and one between the middle and third gene These will be the two smallest classes. Double Recombinants: red, tall, normal green, dwarf, ragged ...
X-inactivation

X-inactivation (also called lyonization) is a process by which one of the two copies of the X chromosome present in female mammals is inactivated. The inactive X chromosome is silenced by its being packaged in such a way that it has a transcriptionally inactive structure called heterochromatin. As nearly all female mammals have two X chromosomes, X-inactivation prevents them from having twice as many X chromosome gene products as males, who only possess a single copy of the X chromosome (see dosage compensation). The choice of which X chromosome will be inactivated is random in placental mammals such as humans, but once an X chromosome is inactivated it will remain inactive throughout the lifetime of the cell and its descendants in the organism. Unlike the random X-inactivation in placental mammals, inactivation in marsupials applies exclusively to the paternally derived X chromosome.