A non-zero variance of Tajima`s estimator for two
... In the first configuration, the loci are located effectively infinitely far apart on the same chromosome in both individuals. This means that these loci will be coupled for the first few generations, until separated by a recombination event. Once separated, they may later back-coalesce onto the same ...
... In the first configuration, the loci are located effectively infinitely far apart on the same chromosome in both individuals. This means that these loci will be coupled for the first few generations, until separated by a recombination event. Once separated, they may later back-coalesce onto the same ...
a complex voyage to the X chromosome
... larvae, labeled with an antibody specific for male-specific lethal (MSL) 2 (red) and with Hoechst to stain DNA (blue). (A) The MSL complex component MSL2 localizes specifically to the X chromosome (X) in wild-type males. (B) Ectopically expressed MSL2 recognizes a subset of sites in msl3 mutant fema ...
... larvae, labeled with an antibody specific for male-specific lethal (MSL) 2 (red) and with Hoechst to stain DNA (blue). (A) The MSL complex component MSL2 localizes specifically to the X chromosome (X) in wild-type males. (B) Ectopically expressed MSL2 recognizes a subset of sites in msl3 mutant fema ...
Barbara McClintock (1902-1992) - The Embryo Project Encyclopedia
... until 1936. Then she returned again to the University of Missouri where she worked as an assistant professor until 1941. During her time at the University of Missouri, McClintock studied the effects on maize of radiation [13], which could cause the chromosomes to break apart during cell division. Wh ...
... until 1936. Then she returned again to the University of Missouri where she worked as an assistant professor until 1941. During her time at the University of Missouri, McClintock studied the effects on maize of radiation [13], which could cause the chromosomes to break apart during cell division. Wh ...
Haploids and Doubled Haploids in Plant Breeding
... Media components, mainly the type and concentration of carbohydrates and plant growth regulators, play an important role in reprogramming haploid cells from gametophytic to the sporophytic pathway. The requirements are species and genotype dependent and no universal protocol for in vitro gynogenesis ...
... Media components, mainly the type and concentration of carbohydrates and plant growth regulators, play an important role in reprogramming haploid cells from gametophytic to the sporophytic pathway. The requirements are species and genotype dependent and no universal protocol for in vitro gynogenesis ...
Ectocarpus
... and develop as gametophytes (each containing either a U or a V sex chromosome), which then produce gametes in plurilocular gametangia (multiple-chambered, gamete-bearing structures; Plr). Fusion of male and female gametes produces a zygote (containing both the U and the V sex chromosomes), which dev ...
... and develop as gametophytes (each containing either a U or a V sex chromosome), which then produce gametes in plurilocular gametangia (multiple-chambered, gamete-bearing structures; Plr). Fusion of male and female gametes produces a zygote (containing both the U and the V sex chromosomes), which dev ...
A Haploid System of Sex Determination in the Brown Alga - Hal-CEA
... it from the XY and ZW systems described above [10], exhibits specific evolutionary and genetic properties that have no exact equivalent in diploid systems. In UV systems, the female and male SDR haplotypes function in independent, haploid, male and female, individuals and consequently there is no he ...
... it from the XY and ZW systems described above [10], exhibits specific evolutionary and genetic properties that have no exact equivalent in diploid systems. In UV systems, the female and male SDR haplotypes function in independent, haploid, male and female, individuals and consequently there is no he ...
Iterative Techniques for Maximizing Stochastic Robustness of a
... Thus, the allocation of compute nodes to applications in this environment can be considered to be static, i.e., all of the applications that are to be executed are known in advance and are immediately available for execution. Because this is a heterogeneous computing system, the execution times for ...
... Thus, the allocation of compute nodes to applications in this environment can be considered to be static, i.e., all of the applications that are to be executed are known in advance and are immediately available for execution. Because this is a heterogeneous computing system, the execution times for ...
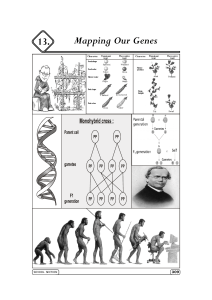
Mapping Our Genes 13. - mt
... Q.III (C) Write short notes for the following : *1. Darwin’s theory of evolution. Ans. 1. Darwin’s theory of evolution is based on natural selection. 2. On the basis of observations, Darwin suggested that only the fittest survive. All those plants and animals which are not fit, die. 3. These fit spe ...
... Q.III (C) Write short notes for the following : *1. Darwin’s theory of evolution. Ans. 1. Darwin’s theory of evolution is based on natural selection. 2. On the basis of observations, Darwin suggested that only the fittest survive. All those plants and animals which are not fit, die. 3. These fit spe ...
Rather than test an unmapped gene successively for linkage to... groups, it is advantageous to test all linkage groups in... alcoy David Perkins
... temperature sensitive-1, yellow-1, and conidial separation-2 (which marks linkage group VII). All four are readily scored by eye. The strains grow on minimal medium. No transfer to test-media is necessary. Crosses heterozygous for alcoy .have proved useful in cytological studies of the synaptonemal ...
... temperature sensitive-1, yellow-1, and conidial separation-2 (which marks linkage group VII). All four are readily scored by eye. The strains grow on minimal medium. No transfer to test-media is necessary. Crosses heterozygous for alcoy .have proved useful in cytological studies of the synaptonemal ...
Families of SMA - Children with Spinal Muscular Atrophy
... development, and determines physical characteristics Every cell in the human body has the same genetic information Each cell uses a different part of the genetic information to perform that cell’s function, e.g. skin, blood, muscle, nerve, etc. ...
... development, and determines physical characteristics Every cell in the human body has the same genetic information Each cell uses a different part of the genetic information to perform that cell’s function, e.g. skin, blood, muscle, nerve, etc. ...
Correct!
... How many chromosomes are present in a normal human sex cell? Click on the letter of the correct answer ...
... How many chromosomes are present in a normal human sex cell? Click on the letter of the correct answer ...
Transvection and pairing of a Drosophila Hox long noncoding RNA
... 1995). This region is also associated with numerous mutations resulting in a dominant gain of function (GOF) Scr homeotic transformation, whereby sex combs (normally specific to the male T1 leg) are ectopically formed on legs of the T2 and T3 segments (Pattatucci et al. 1991). Strikingly, five diffe ...
... 1995). This region is also associated with numerous mutations resulting in a dominant gain of function (GOF) Scr homeotic transformation, whereby sex combs (normally specific to the male T1 leg) are ectopically formed on legs of the T2 and T3 segments (Pattatucci et al. 1991). Strikingly, five diffe ...
Leukaemia Section del (13q) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... in chronic idiopathic myelofibrosis and polycythaemia vera patients without 13q abnormality on conventional cytogenetics. These show that 13q deletions may occur as a sub-microscopic lesion only detectable with molecular techniques such as LOH study and FISH. Molecular Cytogenetics: In a series 20 p ...
... in chronic idiopathic myelofibrosis and polycythaemia vera patients without 13q abnormality on conventional cytogenetics. These show that 13q deletions may occur as a sub-microscopic lesion only detectable with molecular techniques such as LOH study and FISH. Molecular Cytogenetics: In a series 20 p ...
View - OhioLINK Electronic Theses and Dissertations Center
... During animal spermatogenesis, early spermatids have a typical centrosome with a pair of centrioles surrounded by PCM that can nucleate astral microtubules (Manandhar and Schatten, 2000). As spermatids mature (spermiogenesis), the centrosome loses many of its characteristics via a process called cen ...
... During animal spermatogenesis, early spermatids have a typical centrosome with a pair of centrioles surrounded by PCM that can nucleate astral microtubules (Manandhar and Schatten, 2000). As spermatids mature (spermiogenesis), the centrosome loses many of its characteristics via a process called cen ...
Variable Autosomal and X Divergence Near and Far from Genes
... distance from genes increased on both the X and the autosomes (fig. 1). We observed that divergence estimates exhibit a similar pattern along the genome for all great ape subspecies (fig. 1). This was expected because divergence estimates were computed from the MRCA of great apes (approximately 10.5 ...
... distance from genes increased on both the X and the autosomes (fig. 1). We observed that divergence estimates exhibit a similar pattern along the genome for all great ape subspecies (fig. 1). This was expected because divergence estimates were computed from the MRCA of great apes (approximately 10.5 ...
genetics and cytogenetics
... treated, in this manner is readily stained by certain dyes, some of which stain one part of the cell and not others. The parts so stained stand o.l.lt in marked contrast to the rest of the cell, and their structure is much more easily observed than it is in the living condition. In the resting nucle ...
... treated, in this manner is readily stained by certain dyes, some of which stain one part of the cell and not others. The parts so stained stand o.l.lt in marked contrast to the rest of the cell, and their structure is much more easily observed than it is in the living condition. In the resting nucle ...
Leukaemia Section Classification of acute myeloid leukemias Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... occur mainly in the elderly population and are rare in childhood. They are characterized by multilineage involvement of bone marrow cells suggesting an early commitment precursor (stem cell). Cytogenetic studies usually show complex chromosome aberrations, mainly loss of genetic material. These dise ...
... occur mainly in the elderly population and are rare in childhood. They are characterized by multilineage involvement of bone marrow cells suggesting an early commitment precursor (stem cell). Cytogenetic studies usually show complex chromosome aberrations, mainly loss of genetic material. These dise ...
Postzygotic isolation in Drosophila simulans and D. mauritiana
... would cause a pronounced decrease in gene flow in the wild when females have the opportunity to mate with more than one male. One component of variation of the song produced by males of different Drosophila species is caused by a gene called period (Kyriacou and Hall 1980). One subclass of pre-zygot ...
... would cause a pronounced decrease in gene flow in the wild when females have the opportunity to mate with more than one male. One component of variation of the song produced by males of different Drosophila species is caused by a gene called period (Kyriacou and Hall 1980). One subclass of pre-zygot ...
"Hybrid Incompatibility in Drosophila: An Updated Genetic and
... fragment (QTL) larger than one that does produce HMS in combination with two other QTL failed to induce HMS. These authors claimed that this result supports that the size of the introgressed fragment is not responsible of HMS and discredits the extreme PT model. Even so, in that study it is possible ...
... fragment (QTL) larger than one that does produce HMS in combination with two other QTL failed to induce HMS. These authors claimed that this result supports that the size of the introgressed fragment is not responsible of HMS and discredits the extreme PT model. Even so, in that study it is possible ...
A Common Polygenic Basis for Quinine and
... confirmation of each QTL, and better position resolution for those confirmed, are needed before any of the linked genes are seriously considered as candidate genes. Nor are genes closest to the markers necessarily the most likely candidates. Point correlations do not distinguish between QTL with sma ...
... confirmation of each QTL, and better position resolution for those confirmed, are needed before any of the linked genes are seriously considered as candidate genes. Nor are genes closest to the markers necessarily the most likely candidates. Point correlations do not distinguish between QTL with sma ...
Studies on the Mechanisms of Homolog Pairing and Sister
... Meiosis, conserved in eukaryotes, is a special cell division which allows for the exchange of genetic material between parental chromosomes to maintain the genetic diversity of offspring. Meiosis comprises a round of DNA replication followed by two successive nuclear divisions, meiosis I and meiosis ...
... Meiosis, conserved in eukaryotes, is a special cell division which allows for the exchange of genetic material between parental chromosomes to maintain the genetic diversity of offspring. Meiosis comprises a round of DNA replication followed by two successive nuclear divisions, meiosis I and meiosis ...
Natural variation in nucleolar dominance reveals
... discovered as a change in chromosome structure (5). At nucleolus organizer regions (NORs), the loci where nucleoli form during interphase (6, 7), and where genes encoding the precursor transcript for 18S, 5.8S, and 25S rRNA are tandemly arrayed (8–10), NOR-bearing chromosomes in pure species (nonhyb ...
... discovered as a change in chromosome structure (5). At nucleolus organizer regions (NORs), the loci where nucleoli form during interphase (6, 7), and where genes encoding the precursor transcript for 18S, 5.8S, and 25S rRNA are tandemly arrayed (8–10), NOR-bearing chromosomes in pure species (nonhyb ...
Slayt Başlığı Yok
... When an ovum is fertilized, the pairs (chromosomes) are reconstituted in a single cell called a zygote, with one member of each new pair coming from each parent. ...
... When an ovum is fertilized, the pairs (chromosomes) are reconstituted in a single cell called a zygote, with one member of each new pair coming from each parent. ...
A selfish origin for recombination
... of recombination at the molecular level. Classical population genetics models have emphasized the role of modifier genes (for a review see Feldman et al., 1996) on the evolution of recombination, that is they have considered the evolution of recombination at a certain site as something imposed by ano ...
... of recombination at the molecular level. Classical population genetics models have emphasized the role of modifier genes (for a review see Feldman et al., 1996) on the evolution of recombination, that is they have considered the evolution of recombination at a certain site as something imposed by ano ...
Karyotype

A karyotype (from Greek κάρυον karyon, ""kernel"", ""seed"", or ""nucleus"", and τύπος typos, ""general form"") is the number and appearance of chromosomes in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell. The term is also used for the complete set of chromosomes in a species, or an individual organism.Karyotypes describe the chromosome count of an organism, and what these chromosomes look like under a light microscope. Attention is paid to their length, the position of the centromeres, banding pattern, any differences between the sex chromosomes, and any other physical characteristics. The preparation and study of karyotypes is part of cytogenetics. The study of whole sets of chromosomes is sometimes known as karyology. The chromosomes are depicted (by rearranging a photomicrograph) in a standard format known as a karyogram or idiogram: in pairs, ordered by size and position of centromere for chromosomes of the same size.The basic number of chromosomes in the somatic cells of an individual or a species is called the somatic number and is designated 2n. Thus, in humans 2n = 46. In the germ-line (the sex cells) the chromosome number is n (humans: n = 23).p28So, in normal diploid organisms, autosomal chromosomes are present in two copies. There may, or may not, be sex chromosomes. Polyploid cells have multiple copies of chromosomes and haploid cells have single copies.The study of karyotypes is important for cell biology and genetics, and the results may be used in evolutionary biology (karyosystematics) and medicine. Karyotypes can be used for many purposes; such as to study chromosomal aberrations, cellular function, taxonomic relationships, and to gather information about past evolutionary events.