Topological Optimization Design of a Multilevel Star Network
... entering into next generation and diversity of population. It accepts optimal solution, accepts poor quality solutions conditionally at the same time. This way can avoid local optimum solutions. 3.9 Convergence criterion of algorithm The hybrid genetic simulated annealing algorithm is a repeatedly i ...
... entering into next generation and diversity of population. It accepts optimal solution, accepts poor quality solutions conditionally at the same time. This way can avoid local optimum solutions. 3.9 Convergence criterion of algorithm The hybrid genetic simulated annealing algorithm is a repeatedly i ...
Relationship between chromosome fragility, aneuploidy and
... monosomy was again very similar in FA patients and controls (P > 0.05). A tendency towards higher frequencies of monosomy 7 in FA patients was observed, but it did not reach statistical significance (P = 0.07). Similar non-significant results were obtained for other chromosome numerical abnormalitie ...
... monosomy was again very similar in FA patients and controls (P > 0.05). A tendency towards higher frequencies of monosomy 7 in FA patients was observed, but it did not reach statistical significance (P = 0.07). Similar non-significant results were obtained for other chromosome numerical abnormalitie ...
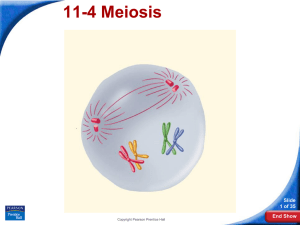
11-4 Meiosis - Midland Park School District
... Comparing Mitosis and Meiosis In mitosis, when the two sets of genetic material separate, each daughter cell receives one complete set of chromosomes. In meiosis, homologous chromosomes line up and then move to separate daughter cells. Mitosis does not normally change the chromosome number of the or ...
... Comparing Mitosis and Meiosis In mitosis, when the two sets of genetic material separate, each daughter cell receives one complete set of chromosomes. In meiosis, homologous chromosomes line up and then move to separate daughter cells. Mitosis does not normally change the chromosome number of the or ...
Genetics Lab: Monohybrid Crosses in Yeast
... In yeast, gametes contain eight chromosomes and diploid cells contain sixteen chromosomes. Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Baker’s yeast is an ideal organism for studying a complete life cycle because it can be maintained in either the haploid or diploid stages of development, thus making the concept of g ...
... In yeast, gametes contain eight chromosomes and diploid cells contain sixteen chromosomes. Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Baker’s yeast is an ideal organism for studying a complete life cycle because it can be maintained in either the haploid or diploid stages of development, thus making the concept of g ...
DNA - Lyndhurst Schools
... parent shows physically? Explain. A child can show the trait that neither parent shows physically if both parents are heterozygous for the trait and pass on the recessive trait to their offspring. 6. Colorblindness is a sex-linked trait that affects males more often than it does females. It requires ...
... parent shows physically? Explain. A child can show the trait that neither parent shows physically if both parents are heterozygous for the trait and pass on the recessive trait to their offspring. 6. Colorblindness is a sex-linked trait that affects males more often than it does females. It requires ...
The Snake in the Box Problem
... use the energy definition inductively, i.e., we begin with a known longest snake in the 3-dimensional hypercube and from there we begin to conjecture as to the number of points for the longest snake in the 4-dimensional hypercube, and so forth. Table 1 compares our conjectures with theoretical resul ...
... use the energy definition inductively, i.e., we begin with a known longest snake in the 3-dimensional hypercube and from there we begin to conjecture as to the number of points for the longest snake in the 4-dimensional hypercube, and so forth. Table 1 compares our conjectures with theoretical resul ...
Plant speciation through chromosome instability and ploidy change
... In plants, like in other species, polyploid genomes are typically associated with major changes in genomic structure and phenotypic outcome, providing a broader basis for adaptivity and evolvability compared to their diploid counterparts. Studies using neo- and synthetic polyploids have revealed tha ...
... In plants, like in other species, polyploid genomes are typically associated with major changes in genomic structure and phenotypic outcome, providing a broader basis for adaptivity and evolvability compared to their diploid counterparts. Studies using neo- and synthetic polyploids have revealed tha ...
Nematode genome evolution
... Most nematodes have haploid chromosome numbers of n=4–12 (Walton, 1959). The karyotypes of just ~300 species have been studied, but nematodes display a lot of karyotypic variation (Špakulová and Casanova, 2004). The lowest haploid number is n=1 in Parascaris univalens, but very high counts are seen ...
... Most nematodes have haploid chromosome numbers of n=4–12 (Walton, 1959). The karyotypes of just ~300 species have been studied, but nematodes display a lot of karyotypic variation (Špakulová and Casanova, 2004). The lowest haploid number is n=1 in Parascaris univalens, but very high counts are seen ...
Characterisation of interstitial duplications and triplications of
... showed that, in all cases, the duplications and triplications involved the PWACR and were not pseudogene expansions. Retrospective cytogenetic analysis in families 7 and 13 did not identify these duplications clearly. The size of the pericentromeric area of 15q varies greatly within the normal popul ...
... showed that, in all cases, the duplications and triplications involved the PWACR and were not pseudogene expansions. Retrospective cytogenetic analysis in families 7 and 13 did not identify these duplications clearly. The size of the pericentromeric area of 15q varies greatly within the normal popul ...
Prof. Kamakaka`s Lecture 7 Notes
... Are sc and vg linked/not linked??? To map them, we simply examine the pair-wise combinations and identify the parental and recombinant classes: To determine the distance between sc vg we remove ec sc ec vg Sc+ Ec+ Vg+ sc ec Vg+ Sc+ Ec+ vg sc Ec+ vg Sc+ ec Vg+ sc Ec+ Vg+ Sc+ ec vg ...
... Are sc and vg linked/not linked??? To map them, we simply examine the pair-wise combinations and identify the parental and recombinant classes: To determine the distance between sc vg we remove ec sc ec vg Sc+ Ec+ Vg+ sc ec Vg+ Sc+ Ec+ vg sc Ec+ vg Sc+ ec Vg+ sc Ec+ Vg+ Sc+ ec vg ...
ADVANTAGES OF FETAL CELLS IN NON
... trisomy 18. Arrow marks the additional chromosome 18. B, FISH analysis on uncultured amniocytes with probes to the centromeres of chromosomes X and 18 showed 3 copies of the chromosome 18 centromere (arrows) and 2 copies of the chromosome X centromere (unmarked signals) suggesting a female fetus wit ...
... trisomy 18. Arrow marks the additional chromosome 18. B, FISH analysis on uncultured amniocytes with probes to the centromeres of chromosomes X and 18 showed 3 copies of the chromosome 18 centromere (arrows) and 2 copies of the chromosome X centromere (unmarked signals) suggesting a female fetus wit ...
Chapter 10.2 ppt
... • ALL structures must be labeled in each slide • Bulleted list of steps taking place in each • Ability for EVERY member of the group to discuss any of the stages in depth • Extra credit if you include a video tutorial of mitosis using your beads at the end of your presentation ...
... • ALL structures must be labeled in each slide • Bulleted list of steps taking place in each • Ability for EVERY member of the group to discuss any of the stages in depth • Extra credit if you include a video tutorial of mitosis using your beads at the end of your presentation ...
concepts-of-biology
... chromosomes. A somatic cell contains two matched sets of chromosomes, a configuration known as diploid. The letter n is used to represent a single set of chromosomes; therefore a diploid organism is designated 2n. Human cells that contain one set of 23 chromosomes are called gametes, or sex cells; t ...
... chromosomes. A somatic cell contains two matched sets of chromosomes, a configuration known as diploid. The letter n is used to represent a single set of chromosomes; therefore a diploid organism is designated 2n. Human cells that contain one set of 23 chromosomes are called gametes, or sex cells; t ...
1030examII
... The products of fertilization would have the same number of chromosomes as their parents The products of fertilization would have more chromosomes than their parents The products of fertilization would have fewer chromosomes than their parents Fertilization could not occur None of the above are corr ...
... The products of fertilization would have the same number of chromosomes as their parents The products of fertilization would have more chromosomes than their parents The products of fertilization would have fewer chromosomes than their parents Fertilization could not occur None of the above are corr ...
Animal Science 434 Reproductive Physiology
... B. Human (mammals) • XY or XXY or XXYY or XXXY = Male (testis) • XX or XXX = Female (ovary) • XO = Female with incomplete ovarian development • XXY or XXYY or XXXY or XXXXY = testis but impaired sperm production C. Conclusion • The gene that controls testicular differentiation is on the Y chromosome ...
... B. Human (mammals) • XY or XXY or XXYY or XXXY = Male (testis) • XX or XXX = Female (ovary) • XO = Female with incomplete ovarian development • XXY or XXYY or XXXY or XXXXY = testis but impaired sperm production C. Conclusion • The gene that controls testicular differentiation is on the Y chromosome ...
secondary school improvement programme - Sci
... Karyotype: this is the number and appearance of the chromosomes arranged in homologous pairs, in the nucleus of an individual belonging to a specific species. In humans, we have 46 chromosomes = 23 pairs (22 pairs are autosomes and 1 pairs are sex chromosomes). The karyotype is used to study chromos ...
... Karyotype: this is the number and appearance of the chromosomes arranged in homologous pairs, in the nucleus of an individual belonging to a specific species. In humans, we have 46 chromosomes = 23 pairs (22 pairs are autosomes and 1 pairs are sex chromosomes). The karyotype is used to study chromos ...
Speciation
... of speciation in animals. • How can reproductive isolation be achieved in the absence of barriers to gene flow? • Again, there must be selection for assortative mating - i.e., like genotypes mate with like • Many entomologists argue that sympatric speciation is common in phytophagous insects via hos ...
... of speciation in animals. • How can reproductive isolation be achieved in the absence of barriers to gene flow? • Again, there must be selection for assortative mating - i.e., like genotypes mate with like • Many entomologists argue that sympatric speciation is common in phytophagous insects via hos ...
Rapid generation of nested chromosomal
... largest extending six or seven centiMorgans. The cytology of the deletion chromosomes were determined by fluorescent in situ hybridization. Eight deletions were cytologically normal, but the two largest deletions had additional rearrangements. Three deletions, including the largest unrearranged dele ...
... largest extending six or seven centiMorgans. The cytology of the deletion chromosomes were determined by fluorescent in situ hybridization. Eight deletions were cytologically normal, but the two largest deletions had additional rearrangements. Three deletions, including the largest unrearranged dele ...
Page 1 - Mr Waring`s Biology Blog
... positive child was evidence that the allele for Rhesus positive is dominant. It should also be noted that many candidates suggested that 4 was the child of 1 and 2, indicating a lack of understanding of family trees. ...
... positive child was evidence that the allele for Rhesus positive is dominant. It should also be noted that many candidates suggested that 4 was the child of 1 and 2, indicating a lack of understanding of family trees. ...
Genomic patterns of species diversity and divergence in Eucalyptus
... (Euclid, 2006). Of the six species examined, only E. dunnii and E. grandis have some overlap in their native range. Despite this, no hybrids have been reported for this species pair or any of the six studied species in the wild (Griffin et al., 1988); suggesting the presence of strong reproductive b ...
... (Euclid, 2006). Of the six species examined, only E. dunnii and E. grandis have some overlap in their native range. Despite this, no hybrids have been reported for this species pair or any of the six studied species in the wild (Griffin et al., 1988); suggesting the presence of strong reproductive b ...
Unit 4 – Genetics – Chapter Objectives (13,14,15) from C
... 12. Describe how sex is genetically determined in humans and explain the significance of the SRY gene. 13. Distinguish between linked genes and sex-linked genes. 14. Explain why sex-linked diseases are more common in human males. 15. Describe the inheritance patterns and symptoms of color blindness, ...
... 12. Describe how sex is genetically determined in humans and explain the significance of the SRY gene. 13. Distinguish between linked genes and sex-linked genes. 14. Explain why sex-linked diseases are more common in human males. 15. Describe the inheritance patterns and symptoms of color blindness, ...
Lecture Notes in Population Genetics
... are located on the X-chromosome in humans. (The gene for the blue pigment is autosomal.) As expected, hemophilia and red/green color blindness are much more common in males than in females. One sex or two? In most higher animals and some plants, the population is split into two sexes and mating occu ...
... are located on the X-chromosome in humans. (The gene for the blue pigment is autosomal.) As expected, hemophilia and red/green color blindness are much more common in males than in females. One sex or two? In most higher animals and some plants, the population is split into two sexes and mating occu ...
Prentice Hall Biology
... •Mendel concluded that heredity is dictated by chemical factors called genes (it would be almost 100 years later before Watson & Crick and the whole DNA thing) •Genes have alternate forms depending on the plant – These alternate versions of the same gene are called alleles Plant height = gene Short ...
... •Mendel concluded that heredity is dictated by chemical factors called genes (it would be almost 100 years later before Watson & Crick and the whole DNA thing) •Genes have alternate forms depending on the plant – These alternate versions of the same gene are called alleles Plant height = gene Short ...
8. Principles of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... Gametogenesis and syngamy in plants. Mendelian genetics–Mendel’s principles of heredity, deviation from Mendelian inheritance, pleiotropy, threshold characters, co-dominance, penetrance and expressivity. Chromosome theory of inheritance, gene interaction. Modification of monohybrid and dihybrid rati ...
... Gametogenesis and syngamy in plants. Mendelian genetics–Mendel’s principles of heredity, deviation from Mendelian inheritance, pleiotropy, threshold characters, co-dominance, penetrance and expressivity. Chromosome theory of inheritance, gene interaction. Modification of monohybrid and dihybrid rati ...
Karyotype

A karyotype (from Greek κάρυον karyon, ""kernel"", ""seed"", or ""nucleus"", and τύπος typos, ""general form"") is the number and appearance of chromosomes in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell. The term is also used for the complete set of chromosomes in a species, or an individual organism.Karyotypes describe the chromosome count of an organism, and what these chromosomes look like under a light microscope. Attention is paid to their length, the position of the centromeres, banding pattern, any differences between the sex chromosomes, and any other physical characteristics. The preparation and study of karyotypes is part of cytogenetics. The study of whole sets of chromosomes is sometimes known as karyology. The chromosomes are depicted (by rearranging a photomicrograph) in a standard format known as a karyogram or idiogram: in pairs, ordered by size and position of centromere for chromosomes of the same size.The basic number of chromosomes in the somatic cells of an individual or a species is called the somatic number and is designated 2n. Thus, in humans 2n = 46. In the germ-line (the sex cells) the chromosome number is n (humans: n = 23).p28So, in normal diploid organisms, autosomal chromosomes are present in two copies. There may, or may not, be sex chromosomes. Polyploid cells have multiple copies of chromosomes and haploid cells have single copies.The study of karyotypes is important for cell biology and genetics, and the results may be used in evolutionary biology (karyosystematics) and medicine. Karyotypes can be used for many purposes; such as to study chromosomal aberrations, cellular function, taxonomic relationships, and to gather information about past evolutionary events.