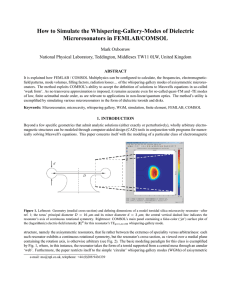
How to Simulate the Whispering-Gallery-Modes of Dielectric Microresonators in FEMLAB/COMSOL Mark Oxborrow
... With circular (or, more generally, planar) whispering-gallery modes, the configurational effort can be significantly relieved by invoking a so-called ‘transverse’ approximation, whereupon only a single (scalar) partial-differential equation needs to be solved –in 2D; here, either the magnetic or ele ...
... With circular (or, more generally, planar) whispering-gallery modes, the configurational effort can be significantly relieved by invoking a so-called ‘transverse’ approximation, whereupon only a single (scalar) partial-differential equation needs to be solved –in 2D; here, either the magnetic or ele ...
Lecture 5 : Potential
... The work done by a conservative force, in moving and object between two points A and B, is independent of the path taken is a function of A and B only – it is NOT a function of the path selected. We can define a potential energy difference as UAB=-W. W=AB F·dr ...
... The work done by a conservative force, in moving and object between two points A and B, is independent of the path taken is a function of A and B only – it is NOT a function of the path selected. We can define a potential energy difference as UAB=-W. W=AB F·dr ...
Atom Light Interactions
... The chief technical legacy of the early work on resonance spectroscopy is the family of lasers which have sprung up like the brooms of the sorcerer’s apprentice. The scientific applications of these devices have been prodigious. They caused the resurrection of physical optics- now freshly christened ...
... The chief technical legacy of the early work on resonance spectroscopy is the family of lasers which have sprung up like the brooms of the sorcerer’s apprentice. The scientific applications of these devices have been prodigious. They caused the resurrection of physical optics- now freshly christened ...
It is sometimes difficult to find the polarity of an
... to oppose the change in flux by adding to or subtracting from the original field. ...
... to oppose the change in flux by adding to or subtracting from the original field. ...
I. Analogy to electric field: Wind - UMD Physics
... 3. Here’s the punch line. Each of the three kites from question (1) and (2) feels a different wind force at point A. But they should each feel the same wind field because the wind itself is the same at point A no matter which kite you hold there. Is there some number having to do with wind force and ...
... 3. Here’s the punch line. Each of the three kites from question (1) and (2) feels a different wind force at point A. But they should each feel the same wind field because the wind itself is the same at point A no matter which kite you hold there. Is there some number having to do with wind force and ...
Charges and Electric Fields - University of Colorado Boulder
... E-field points away from positive charges, points toward negative charges. ...
... E-field points away from positive charges, points toward negative charges. ...
Casimir forces in the time domain: Theory Alejandro W. Rodriguez,
... thereof, with some exceptions 关26兴. A particular topic of interest is the geometry and material dependence of the force, a subject that has only recently begun to be addressed in experiments 关26兴 and by promising new theoretical methods 关27–38兴. For example, recent works have shown that it is possib ...
... thereof, with some exceptions 关26兴. A particular topic of interest is the geometry and material dependence of the force, a subject that has only recently begun to be addressed in experiments 关26兴 and by promising new theoretical methods 关27–38兴. For example, recent works have shown that it is possib ...
IB - MAGNETISM MCQ and SMALL PROBLEMS
... 38. Figure shows two parallel plates with a potential difference of 120 V a distance 5.0 cm apart. The top plate is at the higher potential and the shaded region is a region of magnetic field normal to the page. (a) What should the magnetic field magnitude and direction be such that an electron expe ...
... 38. Figure shows two parallel plates with a potential difference of 120 V a distance 5.0 cm apart. The top plate is at the higher potential and the shaded region is a region of magnetic field normal to the page. (a) What should the magnetic field magnitude and direction be such that an electron expe ...
Magnetic Fields and Forces
... Van Allen radiation belts act like a magnetic bottle, and produce aurora. These belts are due to the earth’s non-uniform field. ...
... Van Allen radiation belts act like a magnetic bottle, and produce aurora. These belts are due to the earth’s non-uniform field. ...
SPH4U Sample Test - Electric & Magnetic Fields
... 25. A ping-pong ball of mass 3.0 × 10–4 kg is hanging from a light thread 1.0 m long, between two vertical parallel plates 10 cm apart, as shown. When the potential difference across the plates is 420 V, the ball comes to equilibrium 1.0 cm to one side of its original position. (a) What is the elect ...
... 25. A ping-pong ball of mass 3.0 × 10–4 kg is hanging from a light thread 1.0 m long, between two vertical parallel plates 10 cm apart, as shown. When the potential difference across the plates is 420 V, the ball comes to equilibrium 1.0 cm to one side of its original position. (a) What is the elect ...
Magnetism and Electromagnetism - CSE
... through a variety of math-based activities. This guide contains problems focusing on Earth’s changing magnetic field in time and space. Students use compasses to discover how these changes can impact navigation on Earth’s surface. They use basic math skills to interpret graphical information showing ...
... through a variety of math-based activities. This guide contains problems focusing on Earth’s changing magnetic field in time and space. Students use compasses to discover how these changes can impact navigation on Earth’s surface. They use basic math skills to interpret graphical information showing ...