Lecture_11
... spectrometer with fixed B′, the carbon traverses a path of radius 22.4 cm and the unknown’s path has a 26.2-cm radius. What is the unknown element? Assume the ions of both elements have the same ...
... spectrometer with fixed B′, the carbon traverses a path of radius 22.4 cm and the unknown’s path has a 26.2-cm radius. What is the unknown element? Assume the ions of both elements have the same ...
Physics Week 2(Sem. 2)
... Electric potential energy is analogous to gravitational potential energy. If a point charge, +qo, were placed between two oppositely charged plates. The force experienced by the point charge, F=qoE, would be directed toward the negative plate. Therefore the ...
... Electric potential energy is analogous to gravitational potential energy. If a point charge, +qo, were placed between two oppositely charged plates. The force experienced by the point charge, F=qoE, would be directed toward the negative plate. Therefore the ...
Swarm SCARF equatorial electric field inversion chain Patrick Alken , Stefan Maus
... The Swarm scalar magnetic measurements will contain contributions from the Earth’s core, lithospheric, ionospheric, and magnetospheric fields. An important step in the processing is to compute scalar magnetic residuals which represent the ionospheric equatorial electrojet, eliminating as many other ...
... The Swarm scalar magnetic measurements will contain contributions from the Earth’s core, lithospheric, ionospheric, and magnetospheric fields. An important step in the processing is to compute scalar magnetic residuals which represent the ionospheric equatorial electrojet, eliminating as many other ...
[SSM] True or false: (a) Maxwell`s equations apply only to electric
... Maxwell’s equations apply only to electric and magnetic fields that are constant over time. The electromagnetic wave equation can be derived from Maxwell’s equations. Electromagnetic waves are transverse waves. The electric and magnetic fields of an electromagnetic wave in free space are in phase. ...
... Maxwell’s equations apply only to electric and magnetic fields that are constant over time. The electromagnetic wave equation can be derived from Maxwell’s equations. Electromagnetic waves are transverse waves. The electric and magnetic fields of an electromagnetic wave in free space are in phase. ...
chapter24
... The net flux through any closed surface surrounding a point charge, q, is given by q/εo and is independent of the shape of that surface The net electric flux through a closed surface that surrounds no charge is zero Since the electric field due to many charges is the vector sum of the electric field ...
... The net flux through any closed surface surrounding a point charge, q, is given by q/εo and is independent of the shape of that surface The net electric flux through a closed surface that surrounds no charge is zero Since the electric field due to many charges is the vector sum of the electric field ...
Document
... so Ampere’s circuital law follows from Ampere’s force law. Just as Gauss’s law can be used to derive the electrostatic field from symmetric charge distributions, so Ampere’s law can be used to derive the magnetostatic field from symmetric current distributions. ...
... so Ampere’s circuital law follows from Ampere’s force law. Just as Gauss’s law can be used to derive the electrostatic field from symmetric charge distributions, so Ampere’s law can be used to derive the magnetostatic field from symmetric current distributions. ...
SEE 2053 Teknologi Elektrik
... through the coil is changed. This phenomenon is known as electromagnetic induction. d • The induced emf is given by e N ...
... through the coil is changed. This phenomenon is known as electromagnetic induction. d • The induced emf is given by e N ...
PowerPoint
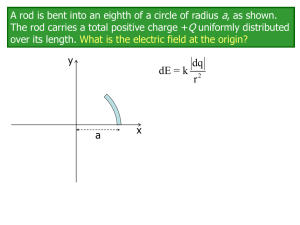
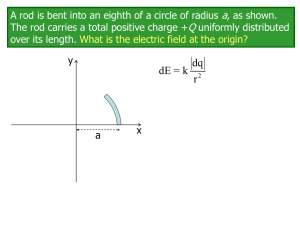
... The rod carries a total positive charge +Q uniformly distributed over its length. A negative point charge -q is placed at the origin. What is the electric force on the point charge? Express your answer in unit vector notation. You could start with Coulomb’s Law, rewrite it to calculate the dF on q1= ...
... The rod carries a total positive charge +Q uniformly distributed over its length. A negative point charge -q is placed at the origin. What is the electric force on the point charge? Express your answer in unit vector notation. You could start with Coulomb’s Law, rewrite it to calculate the dF on q1= ...







![[SSM] True or false: (a) Maxwell`s equations apply only to electric](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009585648_1-6e1ce010e283e25854fc5472a07dfa21-300x300.png)