Physics, Chapter 31: Forces on Moving Charges and Currents
... opposite forces. Since the forces on symmetrical elements of the wire are directed along the same straight line, the resultant force on the coil and the resultant torque on the coil due to these elements are zero. Similarly, the elements at c and d contribute a net force of zero and a net torque of ...
... opposite forces. Since the forces on symmetrical elements of the wire are directed along the same straight line, the resultant force on the coil and the resultant torque on the coil due to these elements are zero. Similarly, the elements at c and d contribute a net force of zero and a net torque of ...
Gauss` Law - University of Colorado Boulder
... poking out = number of lines poking in). Is that consistent with Gauss' law? Yes it is - the cube was empty! E field lines came in and went back out. (If there were any charges in there, E field lines would start or end on the charges: if they pass on through, there's no charge in there!) Suppose we ...
... poking out = number of lines poking in). Is that consistent with Gauss' law? Yes it is - the cube was empty! E field lines came in and went back out. (If there were any charges in there, E field lines would start or end on the charges: if they pass on through, there's no charge in there!) Suppose we ...
ON THE ELECTRODYNAMICS OF MOVING BODIES By A. Einstein June 30, 1905
... leads to asymmetries which do not appear to be inherent in the phenomena. Take, for example, the reciprocal electrodynamic action of a magnet and a conductor. The observable phenomenon here depends only on the relative motion of the conductor and the magnet, whereas the customary view draws a sharp ...
... leads to asymmetries which do not appear to be inherent in the phenomena. Take, for example, the reciprocal electrodynamic action of a magnet and a conductor. The observable phenomenon here depends only on the relative motion of the conductor and the magnet, whereas the customary view draws a sharp ...
magnetic_conceptual_2008
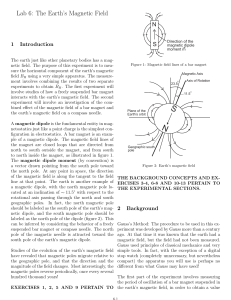
... The magnetic field of long straight conductor is in the circular magnetic lines of force. The center of these imaginary lines lies on the wire. The plane of magnetic lines of force is perpendicular to the length of the conductor and is given by right hand thumb rule. ...
... The magnetic field of long straight conductor is in the circular magnetic lines of force. The center of these imaginary lines lies on the wire. The plane of magnetic lines of force is perpendicular to the length of the conductor and is given by right hand thumb rule. ...
Chapter 1 ELECTROMAGNETICS OF METALS
... by integrating (1.17). At DC, relaxation effects of free charges are therefore conveniently described via the real DC-conductivity σ0 , whereas the response of bound charges is put into a dielectric constant εB , as discussed above in the examination of the interlinked nature between ε and σ . At hi ...
... by integrating (1.17). At DC, relaxation effects of free charges are therefore conveniently described via the real DC-conductivity σ0 , whereas the response of bound charges is put into a dielectric constant εB , as discussed above in the examination of the interlinked nature between ε and σ . At hi ...
Powerpoint
... causes static cling. You immediately take two empty soda cans, which each have a mass of 120 grams, from the recycling bin. You tie the cans to the two ends of a string (one to each end) and hang the center of the string over a nail sticking out of the wall. Each can now hangs straight down 30 cm fr ...
... causes static cling. You immediately take two empty soda cans, which each have a mass of 120 grams, from the recycling bin. You tie the cans to the two ends of a string (one to each end) and hang the center of the string over a nail sticking out of the wall. Each can now hangs straight down 30 cm fr ...