spin_conference_xie
... When graphene is in the SSC the non-local resistance is very large, because that the spin current can dissipationlessly flow through the super-spin-fluid region. Here we emphasize that the changes of the normal resistance and non-local resistance are sharp, similar as the resistance change when a sa ...
... When graphene is in the SSC the non-local resistance is very large, because that the spin current can dissipationlessly flow through the super-spin-fluid region. Here we emphasize that the changes of the normal resistance and non-local resistance are sharp, similar as the resistance change when a sa ...
AP-C Electric Potential
... AP-C Objectives (from College Board Learning Objectives for AP Physics) 1. Electric potential due to point charges a. Determine the electric potential in the vicinity of one or more point charges. b. Calculate the electrical work done on a charge or use conservation of energy to determine the speed ...
... AP-C Objectives (from College Board Learning Objectives for AP Physics) 1. Electric potential due to point charges a. Determine the electric potential in the vicinity of one or more point charges. b. Calculate the electrical work done on a charge or use conservation of energy to determine the speed ...
Lecture 1210
... The circuit shown in the figure consists of a wire loop connected to a sensitive ammeter (known as a "galvanometer"). If we approach the loop with a permanent magnet we see a current being registered by the galvanometer. The results can be summarized as follows: 1. A current appears only if there is ...
... The circuit shown in the figure consists of a wire loop connected to a sensitive ammeter (known as a "galvanometer"). If we approach the loop with a permanent magnet we see a current being registered by the galvanometer. The results can be summarized as follows: 1. A current appears only if there is ...
Molecules in Electric and Magnetic Fields
... From equ. (3.05) we can see that the quadrupole tensor has no trace. Even though single magnetic charges do not exist, we can write a relationship for magnetic potential analogous to equ. (3.03). It is important that we treat the magnetic moment, which is also represented by μ, since, together with ...
... From equ. (3.05) we can see that the quadrupole tensor has no trace. Even though single magnetic charges do not exist, we can write a relationship for magnetic potential analogous to equ. (3.03). It is important that we treat the magnetic moment, which is also represented by μ, since, together with ...
Magnet
... the domains will still be aligned. ► No matter how many times a magnet is cut, each piece will have two different poles. ► A magnet can never have just a north pole or a south pole. ...
... the domains will still be aligned. ► No matter how many times a magnet is cut, each piece will have two different poles. ► A magnet can never have just a north pole or a south pole. ...
Welcome to Physics 220!
... terms of the charge in a very small volume at each point in space. The density then looks like a derivative: ...
... terms of the charge in a very small volume at each point in space. The density then looks like a derivative: ...
Gauss`s Law - Engineering Sciences
... The net flux through any closed surface surrounding a point charge, q, is given by q/εo and is independent of the shape of that surface The net electric flux through a closed surface that surrounds no charge is zero Since the electric field due to many charges is the vector sum of the electric field ...
... The net flux through any closed surface surrounding a point charge, q, is given by q/εo and is independent of the shape of that surface The net electric flux through a closed surface that surrounds no charge is zero Since the electric field due to many charges is the vector sum of the electric field ...
Chapter24
... The net flux through any closed surface surrounding a point charge, q, is given by q/εo and is independent of the shape of that surface The net electric flux through a closed surface that surrounds no charge is zero Since the electric field due to many charges is the vector sum of the electric field ...
... The net flux through any closed surface surrounding a point charge, q, is given by q/εo and is independent of the shape of that surface The net electric flux through a closed surface that surrounds no charge is zero Since the electric field due to many charges is the vector sum of the electric field ...
CHAPTER 24: CAPACITANCE AND DIELECTRICS • Suppose you
... Suppose you have two isolated conductors that are insulated from each other and initially they are both neutral Now imagine moving a small quantity of charge from one conductor to the other so that one has a net positive charge and the other a net negative charge This creates an electric field ...
... Suppose you have two isolated conductors that are insulated from each other and initially they are both neutral Now imagine moving a small quantity of charge from one conductor to the other so that one has a net positive charge and the other a net negative charge This creates an electric field ...
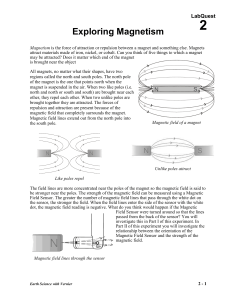
02 Expl Magnet LQ
... PROCESSING THE DATA 1. What happens when you bring two like poles together? What happens when you bring two unlike poles together? ...
... PROCESSING THE DATA 1. What happens when you bring two like poles together? What happens when you bring two unlike poles together? ...