Vibrations of an elastic structure with shunted piezoelectric
... global unknowns: on the one hand, the free electric charges contained in the electrodes of the piezoelectric patches and on the other hand the associated terminal potential differences. This formulation enables to take into account both the direct and indirect piezoelectric effects, separately or at ...
... global unknowns: on the one hand, the free electric charges contained in the electrodes of the piezoelectric patches and on the other hand the associated terminal potential differences. This formulation enables to take into account both the direct and indirect piezoelectric effects, separately or at ...
Chapter 21: ELECTRIC CHARGE
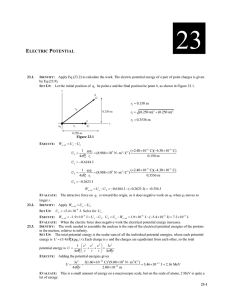
... A. midway between Q and −Q B. on the perpendicular bisector of the line joining Q and −Q, but not on that line itself C. on the line joining Q and −Q, to the side of Q opposite −Q D. on the line joining Q and −Q, to the side of −Q opposite Q E. at none of these places (there is no place) ans: E 36. ...
... A. midway between Q and −Q B. on the perpendicular bisector of the line joining Q and −Q, but not on that line itself C. on the line joining Q and −Q, to the side of Q opposite −Q D. on the line joining Q and −Q, to the side of −Q opposite Q E. at none of these places (there is no place) ans: E 36. ...
Semiclassical model of stimulated Raman scattering in photonic crystals * Lucia Florescu
... Eq. 共2.1兲 has a much smaller contribution than the remaining terms describing the free evolution of the electromagnetic field. This fact is taken into account in our formalism by introducing a small perturbation parameter ⬇ ⬇ 10−8 into the wave Eq. 共2.1兲, and rewriting it as ⵜ2Es共x,t兲 − ...
... Eq. 共2.1兲 has a much smaller contribution than the remaining terms describing the free evolution of the electromagnetic field. This fact is taken into account in our formalism by introducing a small perturbation parameter ⬇ ⬇ 10−8 into the wave Eq. 共2.1兲, and rewriting it as ⵜ2Es共x,t兲 − ...
Ch27 Homework Solutions
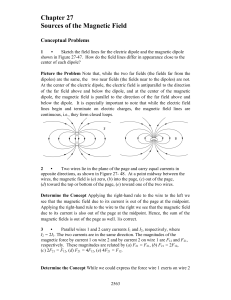
... Sketch the field lines for the electric dipole and the magnetic dipole shown in Figure 27-47. How do the field lines differ in appearance close to the center of each dipole? Picture the Problem Note that, while the two far fields (the fields far from the dipoles) are the same, the two near fields (t ...
... Sketch the field lines for the electric dipole and the magnetic dipole shown in Figure 27-47. How do the field lines differ in appearance close to the center of each dipole? Picture the Problem Note that, while the two far fields (the fields far from the dipoles) are the same, the two near fields (t ...
Electricity Notes (2015/16) - The Dublin School of Grinds
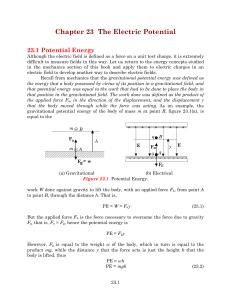
... When charge is placed on the metal cap the leaves diverge due to the repulsion of like charges. The earthed metal case makes the instrument more sensitive due to the opposite charge induced on the inside of the case. The GLE measures the potential difference between the leaves and the case. The bigg ...
... When charge is placed on the metal cap the leaves diverge due to the repulsion of like charges. The earthed metal case makes the instrument more sensitive due to the opposite charge induced on the inside of the case. The GLE measures the potential difference between the leaves and the case. The bigg ...
E - Northern Highlands
... actions will increase the electric field strength at the position of the dot? A. Make the rod longer without changing the charge. B. Make the rod fatter without changing the charge. C. Make the rod shorter without changing the charge. D. Remove charge from the rod. E. Make the rod narrower without c ...
... actions will increase the electric field strength at the position of the dot? A. Make the rod longer without changing the charge. B. Make the rod fatter without changing the charge. C. Make the rod shorter without changing the charge. D. Remove charge from the rod. E. Make the rod narrower without c ...