22.2 Production of Electromagnetic Waves Oscillating charges will
... consisting of electric and magnetic fields. Furthermore the equation predicted the velocity of this “new” type of wave and it was the velocity of light. This suggested that light was an electromagnetic phenomena. ...
... consisting of electric and magnetic fields. Furthermore the equation predicted the velocity of this “new” type of wave and it was the velocity of light. This suggested that light was an electromagnetic phenomena. ...
Maxwell`s Equations
... ∂ B̄ ∂t ∂ D̄ ∇ × H̄ = ∂t ∇ · B̄ = 0 ∇ · D̄ = 0 E & H are coupled, they are not independent. This coupling generate the phenomenon of EM wave propagation ∇ × Ē = − ...
... ∂ B̄ ∂t ∂ D̄ ∇ × H̄ = ∂t ∇ · B̄ = 0 ∇ · D̄ = 0 E & H are coupled, they are not independent. This coupling generate the phenomenon of EM wave propagation ∇ × Ē = − ...
Lesson 1: 2 Equations 2 Unknowns
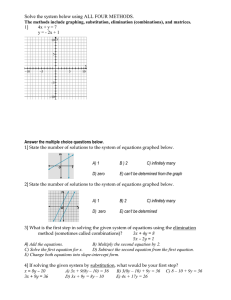
... Note 1: Systems of Equations Systems of equations involve two or more variables related to each other through a set of equations. The solution to the system is the set of values of the variables which satisfies all equations. Algebraic methods used to solve are: Elimination Substitution ...
... Note 1: Systems of Equations Systems of equations involve two or more variables related to each other through a set of equations. The solution to the system is the set of values of the variables which satisfies all equations. Algebraic methods used to solve are: Elimination Substitution ...
Electricity & Optics Physics 24100 Lecture 21 – Chapter 30 sec. 1-4
... In “free space” where there are no electric charges or sources of current, Maxwell’s equations are quite ...
... In “free space” where there are no electric charges or sources of current, Maxwell’s equations are quite ...
B/∂t - Harry Kroto
... k - Boltzmann's constant, q - charge, B - magnetic induction, Φ - magnetic flux, J - current density, i - electric current, c ≈ 299 792 458 m/s - the speed of light, µ0 = 4π×10-7 - magnetic permeability of free space, ∇ - del operator (for a vector function V: ∇. V - divergence of V, ∇×V - the curl ...
... k - Boltzmann's constant, q - charge, B - magnetic induction, Φ - magnetic flux, J - current density, i - electric current, c ≈ 299 792 458 m/s - the speed of light, µ0 = 4π×10-7 - magnetic permeability of free space, ∇ - del operator (for a vector function V: ∇. V - divergence of V, ∇×V - the curl ...
Columbs lov Elektrisk flux Transformers Resonans i krets
... LC-krets(fig(7) LRC-seriekrets(fig8) Faraday’s law(fig9) Lenz’s law statwes that an induced current or emf always tends to oppose or cancel out the change thet caused it.(fig10) Motional emf(fig11) Induced electric fields(fig12) Gauss’s law for ...
... LC-krets(fig(7) LRC-seriekrets(fig8) Faraday’s law(fig9) Lenz’s law statwes that an induced current or emf always tends to oppose or cancel out the change thet caused it.(fig10) Motional emf(fig11) Induced electric fields(fig12) Gauss’s law for ...
PHYS 520B - Electromagnetic Theory
... E cos α + cB sin α, cB cos α − E sin α, cqe cos α + qm sin α, qm cos α − cqe sin α, ...
... E cos α + cB sin α, cB cos α − E sin α, cqe cos α + qm sin α, qm cos α − cqe sin α, ...
Waves & Oscillations Physics 42200 Spring 2015 Semester
... • A unified picture was provided by Maxwell c. 1864 ...
... • A unified picture was provided by Maxwell c. 1864 ...
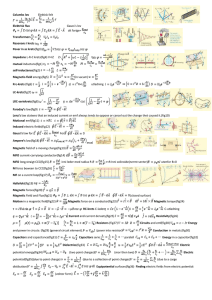
Name___________________________________________ Date_________________________ Algebra I – Pd ____ Complex Equations
... Name___________________________________________ Date_________________________ Algebra I – Pd ____ Complex Equations 2A ...
... Name___________________________________________ Date_________________________ Algebra I – Pd ____ Complex Equations 2A ...
Midterm Exam No. 02 (Spring 2014)
... 4. (20 points.) A charged particle with charge q moves on the z-axis with constant speed v, β = v/c. The electric and magnetic field generated by this charged particle is given by E(r, t) = (1 − β 2 ) ...
... 4. (20 points.) A charged particle with charge q moves on the z-axis with constant speed v, β = v/c. The electric and magnetic field generated by this charged particle is given by E(r, t) = (1 − β 2 ) ...