EMT MODEL SET 2
... carrying current with loop radius ‘a’m and extend the same for finding the magnetic field intensity at the centre of a long solenoid. (OR) b) Derive expressions for i) Lorentz force ii) Force on a current element and ii) Force between two current elements. ...
... carrying current with loop radius ‘a’m and extend the same for finding the magnetic field intensity at the centre of a long solenoid. (OR) b) Derive expressions for i) Lorentz force ii) Force on a current element and ii) Force between two current elements. ...
Lecture Notes: Y F Chapter 28
... Be able to calculate the magnetic field from simple geometries by integrating the law of B & S ...
... Be able to calculate the magnetic field from simple geometries by integrating the law of B & S ...
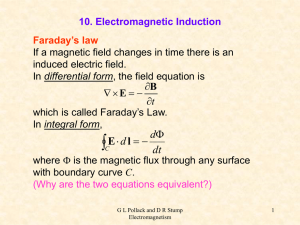
Maxwell`s Equations (4)
... The simplest magnetic structure that can exist is a magnetic dipole. Magnetic monopoles do not exist (as far as we know). ...
... The simplest magnetic structure that can exist is a magnetic dipole. Magnetic monopoles do not exist (as far as we know). ...
Lecture Notes Y F Chapter 29
... Direction of the Induced EMF’s and Currents In the previous problem, we found the direction of the induced current by noting that the force resulting from the induced current had to oppose the applied force. This observation can be generalized into: ...
... Direction of the Induced EMF’s and Currents In the previous problem, we found the direction of the induced current by noting that the force resulting from the induced current had to oppose the applied force. This observation can be generalized into: ...
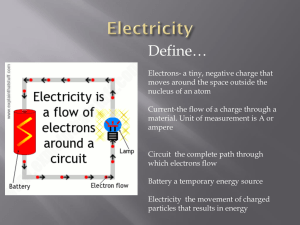
Electricity 2015
... Circuit the complete path through which electrons flow Battery a temporary energy source Electricity the movement of charged particles that results in energy ...
... Circuit the complete path through which electrons flow Battery a temporary energy source Electricity the movement of charged particles that results in energy ...
EE4302 Fl04 Class Sy..
... Homework 20% (Due each Thursday) Final 20% 11:00 AM Wednesday, Nov 30th. *Homework and notes handed in after the due date will not be counted! (This means that the homework can be slid under my door that night. I usually arrive at ~8 AM.) ...
... Homework 20% (Due each Thursday) Final 20% 11:00 AM Wednesday, Nov 30th. *Homework and notes handed in after the due date will not be counted! (This means that the homework can be slid under my door that night. I usually arrive at ~8 AM.) ...
Document
... A current I in a conducting loop creates a magnetic field. The flux through the loop is proportional to the current, = LI . The constant of proportionality L is the selfinductance, which depends on the geometry of the loop. If I changes in time there is an induced emf around the loop, which is by ...
... A current I in a conducting loop creates a magnetic field. The flux through the loop is proportional to the current, = LI . The constant of proportionality L is the selfinductance, which depends on the geometry of the loop. If I changes in time there is an induced emf around the loop, which is by ...
On the Magnet - Colorado Mesa University
... A Brief History of the Magnetic Monopole…. “On the Possible Existence of Magnetic Conductivity and Free Magnetism”, P. Curie, Seances Soc. Phys. (Paris, 1894) pp. 76-77 1st post-Amperian proposal of isolated poles ...
... A Brief History of the Magnetic Monopole…. “On the Possible Existence of Magnetic Conductivity and Free Magnetism”, P. Curie, Seances Soc. Phys. (Paris, 1894) pp. 76-77 1st post-Amperian proposal of isolated poles ...
∇ Homework Assignment #9 due Halloween
... Zangwill shows how to construct spherical waves in general. Today we’ll consider one special case, which is particularly important. ...
... Zangwill shows how to construct spherical waves in general. Today we’ll consider one special case, which is particularly important. ...
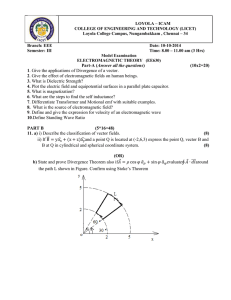
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 4. State Kirchoff’s laws of current electricity. 5. State Biot –Savart’s law. 6. Determine the magnetic intensity at a distance of 10 cm due to a long straight conductor carrying a current of 75A. 7. Calculate the time of leakage if the charge on a capacitor of capacitance 4 microfarad in leaking th ...
... 4. State Kirchoff’s laws of current electricity. 5. State Biot –Savart’s law. 6. Determine the magnetic intensity at a distance of 10 cm due to a long straight conductor carrying a current of 75A. 7. Calculate the time of leakage if the charge on a capacitor of capacitance 4 microfarad in leaking th ...