Review of dielectric and magnetic materials
... ~ where α is the electric polarizability. Molecules may have permanent dipoles, for example water has a that p~ = αE, permanent dipole. Permanent dipoles are in random directions at high temperature and low electric fields however they align at low temperatures and high electric fields. The degree o ...
... ~ where α is the electric polarizability. Molecules may have permanent dipoles, for example water has a that p~ = αE, permanent dipole. Permanent dipoles are in random directions at high temperature and low electric fields however they align at low temperatures and high electric fields. The degree o ...
Charges and Fields - Part I
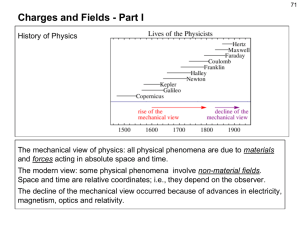
... The mechanical view of physics: all physical phenomena are due to materials and forces acting in absolute space and time. The modern view: some physical phenomena involve non-material fields. Space and time are relative coordinates; i.e., they depend on the observer. The decline of the mechanical vi ...
... The mechanical view of physics: all physical phenomena are due to materials and forces acting in absolute space and time. The modern view: some physical phenomena involve non-material fields. Space and time are relative coordinates; i.e., they depend on the observer. The decline of the mechanical vi ...
Problem set 2
... Consider a linear, isotropic, and homogeneous medium without sources (i.e., ρ = 0 and J = 0). a) State the Maxwell equations in this medium, expressed with E and H. State the equations twice: (i) For the physical, time-varying fields (time domaim), and (ii) for the corresponding phasors (frequency d ...
... Consider a linear, isotropic, and homogeneous medium without sources (i.e., ρ = 0 and J = 0). a) State the Maxwell equations in this medium, expressed with E and H. State the equations twice: (i) For the physical, time-varying fields (time domaim), and (ii) for the corresponding phasors (frequency d ...
Basics of electrodynamics
... is the retarded time taking into account the finite speed of the electromagnetic wave traveling from the source point r 0 to the observation point r. We assumed above that the material is like vacuum. It is straightforward to show that in a uniform medium obeying Ohm’s law the wave equations are ...
... is the retarded time taking into account the finite speed of the electromagnetic wave traveling from the source point r 0 to the observation point r. We assumed above that the material is like vacuum. It is straightforward to show that in a uniform medium obeying Ohm’s law the wave equations are ...
PHYS 431: Electricity and Magnetism
... Target audience The course is designed for senior level physics majors; however other engineering and science majors with the correct preparation are very welcome. Nb: this is a course that is mandatory for all Physics Majors. Therefore, this is a course whose audience is composed by students ...
... Target audience The course is designed for senior level physics majors; however other engineering and science majors with the correct preparation are very welcome. Nb: this is a course that is mandatory for all Physics Majors. Therefore, this is a course whose audience is composed by students ...
國立彰化師範大學八十八學年度碩士班招生考試試題
... 1. Explain the following terminologies: (1) Gauss’s Law, (2) Electric Dipole and Electric Dipole Moment, (3) Equation of Continuity, (4) Vector Magnetic Potential, (5) Plasma and Plasma Frequency. 2. a) Write the differential form of Maxwell’s equations. b) Derive the integral form of Maxwell’s equa ...
... 1. Explain the following terminologies: (1) Gauss’s Law, (2) Electric Dipole and Electric Dipole Moment, (3) Equation of Continuity, (4) Vector Magnetic Potential, (5) Plasma and Plasma Frequency. 2. a) Write the differential form of Maxwell’s equations. b) Derive the integral form of Maxwell’s equa ...