conduction current
... The x-direction is the direction of propagation Waves in which the electric and magnetic fields are restricted to being parallel to a pair of perpendicular axes are said to be linearly polarized waves We assume that at any point in space, the magnitudes E and B of the fields depend upon x and t only ...
... The x-direction is the direction of propagation Waves in which the electric and magnetic fields are restricted to being parallel to a pair of perpendicular axes are said to be linearly polarized waves We assume that at any point in space, the magnitudes E and B of the fields depend upon x and t only ...
Chapter 9 The Nature of Electromagnetic Waves Electromagnetic Radiation
... • EMR requires no medium to travel- can travel thru a vacuum • Speed • 300,000 kilometers /sec • 186,000 miles /sec ...
... • EMR requires no medium to travel- can travel thru a vacuum • Speed • 300,000 kilometers /sec • 186,000 miles /sec ...
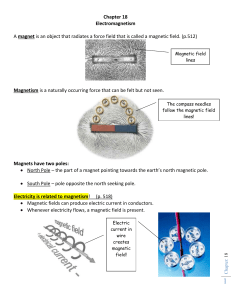
Chapter 18
... Magnetism is a naturally occurring force that can be felt but not seen. The compass needles follow the magnetic field lines! ...
... Magnetism is a naturally occurring force that can be felt but not seen. The compass needles follow the magnetic field lines! ...
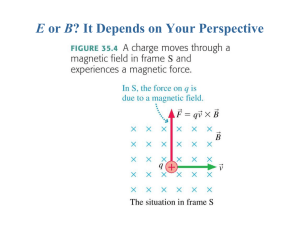
E or B? It Depends on Your Perspective
... where V is the velocity of frame S' relative to frame S and where the fields are measured at the same point in space by experimenters at rest in each reference frame. NOTE: These equations are only valid if V << c. ...
... where V is the velocity of frame S' relative to frame S and where the fields are measured at the same point in space by experimenters at rest in each reference frame. NOTE: These equations are only valid if V << c. ...
Atomic and Molecular Physics for Physicists Ben-Gurion University of the Negev
... In non-dispersive, isotropic media, ε and µ are time-independent scalars, and Maxwell's equations reduce to ...
... In non-dispersive, isotropic media, ε and µ are time-independent scalars, and Maxwell's equations reduce to ...
MATHEMATICS
... Fluids: pressure, hydrostatics, Euler and Lagrange variables of a continuum, continuity equation, Euler equation of motion. Thermodynamics: first law, internal energy, work, heat. Reversible and irreversible processes, second law, Carnot cycles. Equations of state, change of phase, ideal gases, chem ...
... Fluids: pressure, hydrostatics, Euler and Lagrange variables of a continuum, continuity equation, Euler equation of motion. Thermodynamics: first law, internal energy, work, heat. Reversible and irreversible processes, second law, Carnot cycles. Equations of state, change of phase, ideal gases, chem ...
Electromagnetic Field Energy - Physics Department, Princeton
... 8π in Gaussian units. Here, D is the electric displacement vector, E is the electric field, B is the magnetic induction, and H is the magnetic field. In static situations the electromagnetic energy can also be expressed in terms of sources and potentials as à ...
... 8π in Gaussian units. Here, D is the electric displacement vector, E is the electric field, B is the magnetic induction, and H is the magnetic field. In static situations the electromagnetic energy can also be expressed in terms of sources and potentials as à ...
Please review my solution to the problem and explain in
... Please review my solution to the problem and explain in detail what I may be doing wrong and what concepts I may not be applying correctly. I am not sure if I am apply the crossed fields concept correct in presuming that B is perpendicular. ...
... Please review my solution to the problem and explain in detail what I may be doing wrong and what concepts I may not be applying correctly. I am not sure if I am apply the crossed fields concept correct in presuming that B is perpendicular. ...
Answers to The Electric field Homework
... 32.For the net field to be zero at point P, the magnitudes of the fields created by Q1 and Q2 must be equal. Also, the distance x will be taken as positive to the left of Q1. That is the only region where the total field due to the two charges can be zero. Let the variable Q Q2 E1 = E2 ® k 21 = k x ...
... 32.For the net field to be zero at point P, the magnitudes of the fields created by Q1 and Q2 must be equal. Also, the distance x will be taken as positive to the left of Q1. That is the only region where the total field due to the two charges can be zero. Let the variable Q Q2 E1 = E2 ® k 21 = k x ...