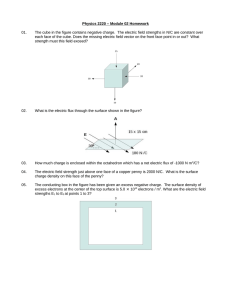
Test Review Jeopardy
... the left end of the conductor, but do not touch it. What charge will the right end of the conductor have? ...
... the left end of the conductor, but do not touch it. What charge will the right end of the conductor have? ...
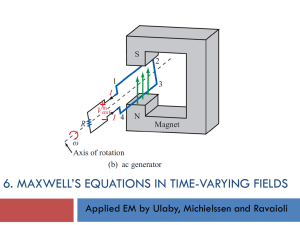
ECE 315 Lecture 8 – Gauss Law for Magnetism and Ampere`s Law
... (The 0s are on the RHS because there are no “magnetic charges”.) How do you use this? Unlike Gauss Law for E, Gauss Law for H is rarely used in practice, except to verify the form of a magnetic field. ...
... (The 0s are on the RHS because there are no “magnetic charges”.) How do you use this? Unlike Gauss Law for E, Gauss Law for H is rarely used in practice, except to verify the form of a magnetic field. ...
Unpacking Outcomes - NESD Curriculum Corner
... conduct experiments, observe occurrences and demonstrate/make conclusions ...
... conduct experiments, observe occurrences and demonstrate/make conclusions ...
Magnetism and spintransport in the heterostructure of Ferroelectric/ferromagnetic films
... The operation of the current generation magnetic memories is based on the control of magnetization by a magnetic field generated by a current through wires or a local magnetic field generated from current through the spin-torque transfer. These two approaches unfortunately suffer from significant en ...
... The operation of the current generation magnetic memories is based on the control of magnetization by a magnetic field generated by a current through wires or a local magnetic field generated from current through the spin-torque transfer. These two approaches unfortunately suffer from significant en ...
Main Y1 SemII Electr.. - UR-CST
... ii) Explain why electric field is zero inside the conductor? (3marks) e. Write the loop rule for loops abcda and befcb, and the junction rule at b in the network shown in the figure below. Assume the currents as shown in the figure below (4marks) ...
... ii) Explain why electric field is zero inside the conductor? (3marks) e. Write the loop rule for loops abcda and befcb, and the junction rule at b in the network shown in the figure below. Assume the currents as shown in the figure below (4marks) ...
Part V
... Sums of fields: Electromagnetism is linear, so the principle of Superposition holds. If E1(x,t) and E2(x,t) are solutions to the wave equation, then E1(x,t) + E2(x,t) is also a solution. ...
... Sums of fields: Electromagnetism is linear, so the principle of Superposition holds. If E1(x,t) and E2(x,t) are solutions to the wave equation, then E1(x,t) + E2(x,t) is also a solution. ...
Chapter S34
... Gauss’s law (electrical): The total electric flux through any closed surface equals the net charge inside that surface divided by o This relates an electric field to the charge distribution that creates it Gauss’s law (magnetism): The total magnetic flux through any closed surface is zero This says ...
... Gauss’s law (electrical): The total electric flux through any closed surface equals the net charge inside that surface divided by o This relates an electric field to the charge distribution that creates it Gauss’s law (magnetism): The total magnetic flux through any closed surface is zero This says ...
Electricity Magnetism
... 4. The Earth is sometimes modeled as an ideal spherical conductor, embedded in an infinte medium of a weak conductor (the air). The conductivity σ and permittivity ² of the air are known. Assume that at the time t = 0, the Earth is charged with a charge of Q0 Coulombs. The charge will leak into the ...
... 4. The Earth is sometimes modeled as an ideal spherical conductor, embedded in an infinte medium of a weak conductor (the air). The conductivity σ and permittivity ² of the air are known. Assume that at the time t = 0, the Earth is charged with a charge of Q0 Coulombs. The charge will leak into the ...