Week3-Week4. - WordPress.com
... • When the flux changes—because B changes, or because the wire loop is moved or deformed, or both—Faraday's law of induction says that the wire loop acquires an EMF, defined as the energy available from a unit charge that has travelled once around the ...
... • When the flux changes—because B changes, or because the wire loop is moved or deformed, or both—Faraday's law of induction says that the wire loop acquires an EMF, defined as the energy available from a unit charge that has travelled once around the ...
PHYS4210 Electromagnetic Theory Quiz 26 Jan 2009
... 1. A wave component moving in the z-direction is written as the complex function E(z, t) = E0 e−i(kz−ωt) Which of the following represents the physical wave corresponding to this function? A. E0 sin(kz − ωt) B. E0 cos(kz − ωt) C. E0 sin[i(kz − ωt)] D. E0 cos[i(kz − ωt)] E. E0 cos(kz − ωt) + E0 sin(k ...
... 1. A wave component moving in the z-direction is written as the complex function E(z, t) = E0 e−i(kz−ωt) Which of the following represents the physical wave corresponding to this function? A. E0 sin(kz − ωt) B. E0 cos(kz − ωt) C. E0 sin[i(kz − ωt)] D. E0 cos[i(kz − ωt)] E. E0 cos(kz − ωt) + E0 sin(k ...
Electric currents Review: Charge and Field The development of electric power
... Joule’s law James Joule showed that the power released as heat when a wire is connected to a battery is Power = U / t = I2 R; or, equivalently, P = I V. (1840) The electric light bulb (Direct Current) ...
... Joule’s law James Joule showed that the power released as heat when a wire is connected to a battery is Power = U / t = I2 R; or, equivalently, P = I V. (1840) The electric light bulb (Direct Current) ...
Course Syllabus E M
... hands on lab assignments. We also use Pasco equipment and wireless laptop computers. Most labs begin as a problem for which the students must propose and develop their own solution. They then conduct an experiment to test their predictions, make observations and take measurements. Finally, they form ...
... hands on lab assignments. We also use Pasco equipment and wireless laptop computers. Most labs begin as a problem for which the students must propose and develop their own solution. They then conduct an experiment to test their predictions, make observations and take measurements. Finally, they form ...
Final Exam (Fall 2014) PHYS 320: Electricity and Magnetism I
... (c) Plot the magnitude of the electric field with respect to r. 4. (20 points.) Consider a right circular cone with uniform polarization P0 , of infinite height, apex at the origin, aperture angle 2θ0 , described by P(r) = P0 θfun (θ0 − θ), ...
... (c) Plot the magnitude of the electric field with respect to r. 4. (20 points.) Consider a right circular cone with uniform polarization P0 , of infinite height, apex at the origin, aperture angle 2θ0 , described by P(r) = P0 θfun (θ0 − θ), ...
Electric field
... For the charge distributions shown on the spherical conductors below, which field lines are most reasonable? ...
... For the charge distributions shown on the spherical conductors below, which field lines are most reasonable? ...
The homopolar generator: an analytical example
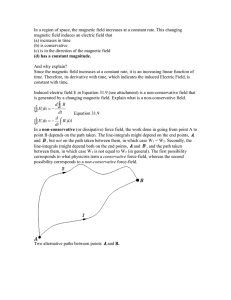
... this law is read as if a time-varying magnetic field is the source of a solenoidal electric field. As the study of the complete Maxwell equations shows, this is not correct in the literal sense, because the solutions of the Maxwell equations show that the causal sources of the electromagnetic field, ...
... this law is read as if a time-varying magnetic field is the source of a solenoidal electric field. As the study of the complete Maxwell equations shows, this is not correct in the literal sense, because the solutions of the Maxwell equations show that the causal sources of the electromagnetic field, ...