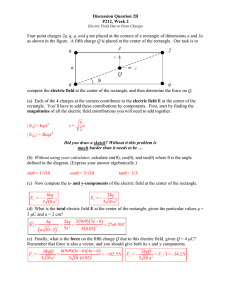
III
... 5. Field is strongest where the lines are close together. C. Electric Fields between parallel plates 1. Two oppositely charged plates create an Electric Field 2. The field in uniform (equal at all locations in the field) 3. Electrons and protons moving through the field get deflected (draw) D. Elect ...
... 5. Field is strongest where the lines are close together. C. Electric Fields between parallel plates 1. Two oppositely charged plates create an Electric Field 2. The field in uniform (equal at all locations in the field) 3. Electrons and protons moving through the field get deflected (draw) D. Elect ...
Phys202_Exam2_2007.doc
... You may not have a cell phone or any electronic device (other than a non-programmable calculator with one memory and two pencils at your desk during the exam. You may not have any paper even blank or notes at your seat. You are to take your test questions home with you and only submit your answer sh ...
... You may not have a cell phone or any electronic device (other than a non-programmable calculator with one memory and two pencils at your desk during the exam. You may not have any paper even blank or notes at your seat. You are to take your test questions home with you and only submit your answer sh ...
Chapter 4
... carpet and touching a doorknob; can be caused by contact, friction or INDUCTION where all cause movement of NEGATIVE CHARGES and the result is like a capacitor- storage of energy UNTIL something causes it to discharge – lightening is a prime example where the negative charges continue to mount in th ...
... carpet and touching a doorknob; can be caused by contact, friction or INDUCTION where all cause movement of NEGATIVE CHARGES and the result is like a capacitor- storage of energy UNTIL something causes it to discharge – lightening is a prime example where the negative charges continue to mount in th ...
Chapter 32Light: Reflection and Refraction
... Induced Electric Fields • Electric & Magnetic fields induce each other ...
... Induced Electric Fields • Electric & Magnetic fields induce each other ...
Al-Balqa Applied University
... report will be used as bonus points (added to the participation) to help the students with their grade and must and discuss their results with the instructor in order to better understand the course. One report at least will be handed to the students. The report will ask the students to solve, deriv ...
... report will be used as bonus points (added to the participation) to help the students with their grade and must and discuss their results with the instructor in order to better understand the course. One report at least will be handed to the students. The report will ask the students to solve, deriv ...
Answers 6
... If it were non-zero for some reason, charges would move within the conductor. The separation of positive and negative charge would set up an internal electric field which would oppose the original field. In equilibrium the two fields would be equal and opposite, making the total field zero. ...
... If it were non-zero for some reason, charges would move within the conductor. The separation of positive and negative charge would set up an internal electric field which would oppose the original field. In equilibrium the two fields would be equal and opposite, making the total field zero. ...
Electromagnetism - David Brotherton CCCMC
... twisted, the magnetic fields produced by each loop are added together. Solenoid: A long coil of wire with many loops that produce magnetic fields. The power can be increased by adding more coils and decreased by removing coils. Electromagnet: A solenoid with a magnetic material such as iron (Fe) ins ...
... twisted, the magnetic fields produced by each loop are added together. Solenoid: A long coil of wire with many loops that produce magnetic fields. The power can be increased by adding more coils and decreased by removing coils. Electromagnet: A solenoid with a magnetic material such as iron (Fe) ins ...