Lecture11: Faraday`s Law of Induction
... If dI/dt is positive, B is growing, then Bind opposes change and I’ is counter-clockwise ...
... If dI/dt is positive, B is growing, then Bind opposes change and I’ is counter-clockwise ...
The Case for Using Blunt-Tipped Lightning Rods as Strike Receptors
... the tip of a positively charged electrode. From these studies, it appears that an electric field with a strength in excess of 6.8 MV m 21 under a pressure of one atmosphere is necessary to accelerate negative ions sufficiently to detach seed electrons. These liberated electrons, in turn, can be acce ...
... the tip of a positively charged electrode. From these studies, it appears that an electric field with a strength in excess of 6.8 MV m 21 under a pressure of one atmosphere is necessary to accelerate negative ions sufficiently to detach seed electrons. These liberated electrons, in turn, can be acce ...
Chapter 4 MHD Equilibrium and Stability
... Exercise: Consider one-dimensional solutions with ∂/∂x 6= 0. Obtain the first integral of the equation (4.13) by multiplying the equation with dAz /dx and integration. The resulting equation is the equation of total pressure balance. Interpret the term in the first integral in this manner. Exercise: ...
... Exercise: Consider one-dimensional solutions with ∂/∂x 6= 0. Obtain the first integral of the equation (4.13) by multiplying the equation with dAz /dx and integration. The resulting equation is the equation of total pressure balance. Interpret the term in the first integral in this manner. Exercise: ...
Conductivity and magnetoresistance of a periodic composite by network discretization
... treating such composites, which focuses attention on a single unit cell in real space. The scheme, a natural outgrowth of the method described in Ref. 15, is basically to represent a unit cell of the periodic conductor as a (d-dimensional! square or cubic impedance network. The network is easy to co ...
... treating such composites, which focuses attention on a single unit cell in real space. The scheme, a natural outgrowth of the method described in Ref. 15, is basically to represent a unit cell of the periodic conductor as a (d-dimensional! square or cubic impedance network. The network is easy to co ...
File
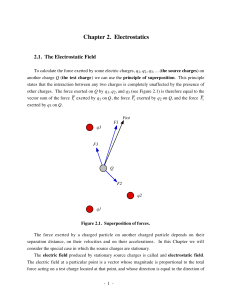
... • Suppose a small test charge of 0.200 C was placed at the point that is 0.100 m from the charged object. What force would be exerted on the test charge and on the object? – Answer: 1.19 N for both test charge and object ...
... • Suppose a small test charge of 0.200 C was placed at the point that is 0.100 m from the charged object. What force would be exerted on the test charge and on the object? – Answer: 1.19 N for both test charge and object ...
SC related electric and magnetic field phenomena observed by the... satellite inside the plasmasphere
... Electric and magnetic field variations inside the plasmasphere associated with SCs identified on the ground are analyzed based on the Akebono satellite observations which have been carried out more than 13 years since March 1989. 126 electric field observation data corresponding to SCs show abrupt c ...
... Electric and magnetic field variations inside the plasmasphere associated with SCs identified on the ground are analyzed based on the Akebono satellite observations which have been carried out more than 13 years since March 1989. 126 electric field observation data corresponding to SCs show abrupt c ...