MJ2A - Ch 8.9 System of Equations
... In a system of equations where the graph of each line is the same you will have an infinite number of solutions. Because the graphs of each line overlap, all points on each line will make the system of equations true, therefore you will have an infinite number of solutions Let’s look at an example… ...
... In a system of equations where the graph of each line is the same you will have an infinite number of solutions. Because the graphs of each line overlap, all points on each line will make the system of equations true, therefore you will have an infinite number of solutions Let’s look at an example… ...
Electromagnetic Unification
... scientists, who were able to work with permanent sources of «electrical fluid». Oersted started making experiments with a voltaic battery and proved, in April 1820, that an electrical current altered a nearby magnetised needle. He discovered that an electrical current produced magnetic effects and t ...
... scientists, who were able to work with permanent sources of «electrical fluid». Oersted started making experiments with a voltaic battery and proved, in April 1820, that an electrical current altered a nearby magnetised needle. He discovered that an electrical current produced magnetic effects and t ...
Electric Fields - Al
... Capacitance and Dielectrics, Current and Resistance, Direct Current Circuits, RC Circuit. * Objectives: ...
... Capacitance and Dielectrics, Current and Resistance, Direct Current Circuits, RC Circuit. * Objectives: ...
Electrostatic fields • Why study electrostatics? • Many applications in
... •Permeability quantifies how a material responds to magnetic fields in a manner analogous to how permittivity quantifies the material response to an electric field. •Permeability is a measure of the magnetic energy storage capabilities of a material. A material with a relative permeability of 1 is ...
... •Permeability quantifies how a material responds to magnetic fields in a manner analogous to how permittivity quantifies the material response to an electric field. •Permeability is a measure of the magnetic energy storage capabilities of a material. A material with a relative permeability of 1 is ...
Electromagnetism and Magnetic Induction
... 3) One of the four fundamental interactions of nature, along with strong interaction, weak interaction and gravitation is 4) A method you can use to determine the direction of conventional current is called the 5) Represents the direction of the thrust or resultant motion is the ...
... 3) One of the four fundamental interactions of nature, along with strong interaction, weak interaction and gravitation is 4) A method you can use to determine the direction of conventional current is called the 5) Represents the direction of the thrust or resultant motion is the ...
Lesson Outcome-Chap18
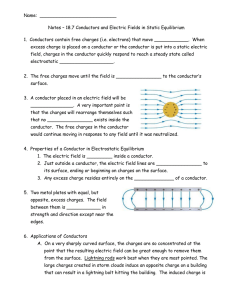
... charges and a pair of positive- negative charge. e) Explain the effect of the electric field on a positive Numerically determine the test charge placed at midpoint between a pair of field intensity on the right, positive or charges and a pair of positive-negative on the left and at charge. midpoin ...
... charges and a pair of positive- negative charge. e) Explain the effect of the electric field on a positive Numerically determine the test charge placed at midpoint between a pair of field intensity on the right, positive or charges and a pair of positive-negative on the left and at charge. midpoin ...
A electric generator is a electrical machine that converts mechanical
... electric charges through a material. A electric _________ is a complete path through Which electric charges can flow. ...
... electric charges through a material. A electric _________ is a complete path through Which electric charges can flow. ...