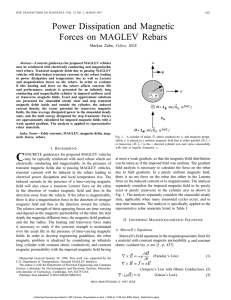
Zahn, M. Power Dissipation and Magnetic Forces on MAGLEV Rebars, IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, Vol. 33, No. 2, March 1997, pp. 1021-1036
... electrically conducting and magnetizable. In the presence of transient magnetic fields due to passing MAGLEV vehicles, transient currents will be induced in the rebars leading to electrical power dissipation and local temperature rise. The induced currents in the presence of a time-varying magnetic ...
... electrically conducting and magnetizable. In the presence of transient magnetic fields due to passing MAGLEV vehicles, transient currents will be induced in the rebars leading to electrical power dissipation and local temperature rise. The induced currents in the presence of a time-varying magnetic ...
Chapter 30
... stationary charged particles to exert a force of attraction on the other two? (b) Is it possible for each of three stationary charged particles to repel both of the other particles? (c) Is it possible for each of three current-carrying metal wires to attract the other two wires? (d) Is it possible f ...
... stationary charged particles to exert a force of attraction on the other two? (b) Is it possible for each of three stationary charged particles to repel both of the other particles? (c) Is it possible for each of three current-carrying metal wires to attract the other two wires? (d) Is it possible f ...
fi̇zi̇k 2 güz
... derivatives, directional derivatives, gradients. Differentials and the tangent plane: the Fundamental Lemma, approximations. The Mean Value, implicite and Inverse function theorems. Extreme values. Introduction to vector differential calculus: the gradient, divergence and curl. Double Integrals, pol ...
... derivatives, directional derivatives, gradients. Differentials and the tangent plane: the Fundamental Lemma, approximations. The Mean Value, implicite and Inverse function theorems. Extreme values. Introduction to vector differential calculus: the gradient, divergence and curl. Double Integrals, pol ...
11 - HCC Learning Web
... electric current (d) a difference in electric potential (e) a charged capacitor disconnected from a battery and at rest Note: In Chapter 34, we will see that a changing electric field also creates a magnetic field. 2. A long, vertical, metallic wire carries downward electric current. (i) What is the ...
... electric current (d) a difference in electric potential (e) a charged capacitor disconnected from a battery and at rest Note: In Chapter 34, we will see that a changing electric field also creates a magnetic field. 2. A long, vertical, metallic wire carries downward electric current. (i) What is the ...
ll ne - Arihant Book
... charge can neither be created nor be destroyed. In any physical process, the charge may get transferred from one part of the system to another, but the net charge will always remain the same. It is impossible to create or destroy net charge carried by an isolated system although charge carrying part ...
... charge can neither be created nor be destroyed. In any physical process, the charge may get transferred from one part of the system to another, but the net charge will always remain the same. It is impossible to create or destroy net charge carried by an isolated system although charge carrying part ...
N - Mr Bernabo at Affton High School
... 15 A of current flows through both wires below. If they are seperated by a distance of 30 cm. What will the magnetic field strength be midway between the? I ...
... 15 A of current flows through both wires below. If they are seperated by a distance of 30 cm. What will the magnetic field strength be midway between the? I ...
EXAM 1
... [10 pts.] Find the current through the 5.00-Ω resistor at the top, including its direction if non-zero (from c to d, or from d to c). [10 pts.] Find the current through the 3.00-Ω resistor, including its direction if non-zero (from c to f, or from f to c). [10 pts.] Find the voltage across the capac ...
... [10 pts.] Find the current through the 5.00-Ω resistor at the top, including its direction if non-zero (from c to d, or from d to c). [10 pts.] Find the current through the 3.00-Ω resistor, including its direction if non-zero (from c to f, or from f to c). [10 pts.] Find the voltage across the capac ...