Chapter 8 Introduction to Magnetic Fields
... The above expression can be taken as the working definition of the magnetic field at a G point in space. The magnitude of FB is given by FB = | q | vB sin θ ...
... The above expression can be taken as the working definition of the magnetic field at a G point in space. The magnitude of FB is given by FB = | q | vB sin θ ...
What are electric and magnetic fields?
... Do they present health risks? Most research into this question has concentrated on finding out whether the magnetic fields can cause cancer or could assist the development of a cancerous condition. Other effects investigated include miscarriages, Alzheimer’s disease and depression. In spite of all t ...
... Do they present health risks? Most research into this question has concentrated on finding out whether the magnetic fields can cause cancer or could assist the development of a cancerous condition. Other effects investigated include miscarriages, Alzheimer’s disease and depression. In spite of all t ...
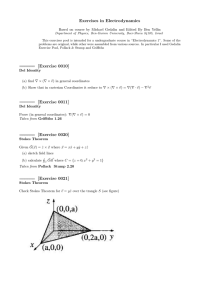
Exercises in Electrodynamics
... region on your graph corresponds to points and times (x, t) from which the particle cannot be seen? At what time does someone at point x first see the particle? (Prior to this the potential at x is evidently zero.) Is it possible for a particle, once seen, to disappear from view? (b) Determine the L ...
... region on your graph corresponds to points and times (x, t) from which the particle cannot be seen? At what time does someone at point x first see the particle? (Prior to this the potential at x is evidently zero.) Is it possible for a particle, once seen, to disappear from view? (b) Determine the L ...
Counter equatorial electrojet and overshielding after substorm onset
... These studies are mainly categorized into two ...
... These studies are mainly categorized into two ...
vcvc2
... We consider two charges q1 and q 2 with position vectors r1 and r2 respectively in a given field. In this situation, the total potential energy of the system is the algebraic sum of three parts : a. PE of q1 due to its interaction with the source, b. PE of q 2 due to its interaction with the source ...
... We consider two charges q1 and q 2 with position vectors r1 and r2 respectively in a given field. In this situation, the total potential energy of the system is the algebraic sum of three parts : a. PE of q1 due to its interaction with the source, b. PE of q 2 due to its interaction with the source ...
The origins of electrical resistivity in magnetic reconnection:
... and ions is 64 per cell for each species with the particle splitting technique to reduce discreteness noise. It is remarked that particle simulation has a reasonable resolution even with fewer grid points than MHD (fluid) simulations because the plasma current and charge are carried by Lagrangean pa ...
... and ions is 64 per cell for each species with the particle splitting technique to reduce discreteness noise. It is remarked that particle simulation has a reasonable resolution even with fewer grid points than MHD (fluid) simulations because the plasma current and charge are carried by Lagrangean pa ...