Name, Date
... Determine the characteristics of a strong electromagnet and explore how an electric current produces a magnetic field Define and explore how electromagnetic induction interacts with a magnetic field to generate electricity Pickup Coil Tab – General Electromagnetic Induction 1. Set the number of ...
... Determine the characteristics of a strong electromagnet and explore how an electric current produces a magnetic field Define and explore how electromagnetic induction interacts with a magnetic field to generate electricity Pickup Coil Tab – General Electromagnetic Induction 1. Set the number of ...
16 Part 2
... 1. Field lines indicate the direction of the field; the field is tangent to the line. 2. The magnitude of the field is proportional to the density of the lines. 3. Field lines start on positive charges and end on negative charges; the number is proportional to the magnitude of the charge. ...
... 1. Field lines indicate the direction of the field; the field is tangent to the line. 2. The magnitude of the field is proportional to the density of the lines. 3. Field lines start on positive charges and end on negative charges; the number is proportional to the magnitude of the charge. ...
Coulomb`s Law of Magnetism
... Magnetic Fields of Force • Magnetic fields can be represented by lines of flux • A line of flux is drawn so that a tangent to it at any point indicates the direction of the magnetic field • The unit of magnetic flux () is the weber (Wb) ...
... Magnetic Fields of Force • Magnetic fields can be represented by lines of flux • A line of flux is drawn so that a tangent to it at any point indicates the direction of the magnetic field • The unit of magnetic flux () is the weber (Wb) ...
Study Guide for Part Three
... 28) A long wire runs carries a current of 300 amps from the North to the South. a) What is the magnetic field due to the current at a location 2 cm East of the wire? b) What is the magnetic field due to the current at a location 12 meters below the wire? c) What is the acceleration of an electron mo ...
... 28) A long wire runs carries a current of 300 amps from the North to the South. a) What is the magnetic field due to the current at a location 2 cm East of the wire? b) What is the magnetic field due to the current at a location 12 meters below the wire? c) What is the acceleration of an electron mo ...
L29
... electric currents produce magnetic fields (Ampere) magnetic field lines are always closed loops – no isolated magnetic poles • permanent magnets: the currents are atomic currents – due to electrons spinning in atomsthese currents are always there • electromagnets: the currents flow through wires a ...
... electric currents produce magnetic fields (Ampere) magnetic field lines are always closed loops – no isolated magnetic poles • permanent magnets: the currents are atomic currents – due to electrons spinning in atomsthese currents are always there • electromagnets: the currents flow through wires a ...
Magnetism
... Electricity and magnetism are related. This is called electromagnetism An electric current flowing through a wire gives rise to a magnetic field whose direction depends upon the direction of the current. Coiling a conductor around a piece of soft iron will produce a powerful magnet. This is temporar ...
... Electricity and magnetism are related. This is called electromagnetism An electric current flowing through a wire gives rise to a magnetic field whose direction depends upon the direction of the current. Coiling a conductor around a piece of soft iron will produce a powerful magnet. This is temporar ...
magnetic field lines
... • Faraday thought that if currents could produce magnetic fields, magnetic fields should be able to produce currents • He was correct with one important requirement the magnetic field must be changing in some way to induce a current • the phenomenon that a changing magnetic field can induce a curr ...
... • Faraday thought that if currents could produce magnetic fields, magnetic fields should be able to produce currents • He was correct with one important requirement the magnetic field must be changing in some way to induce a current • the phenomenon that a changing magnetic field can induce a curr ...
Magnetism Webquest - Mrs. Blevins` Science
... *Read through the following website and answer the questions below. http://istp.gsfc.nasa.gov/earthmag/reversal.htm 1) What is basalt and how do scientists use it to determine the direction of Earth’s magnetic field over time? ...
... *Read through the following website and answer the questions below. http://istp.gsfc.nasa.gov/earthmag/reversal.htm 1) What is basalt and how do scientists use it to determine the direction of Earth’s magnetic field over time? ...
No Slide Title
... (3) Imaginary contour C versus loop of wire. There is an emf induced around C in either case by the setting up of an electric field. A loop of wire will result in a current flowing in the wire. (4) Lenz’s Law. States that the sense of the induced emf is such that any current it produces, if the clos ...
... (3) Imaginary contour C versus loop of wire. There is an emf induced around C in either case by the setting up of an electric field. A loop of wire will result in a current flowing in the wire. (4) Lenz’s Law. States that the sense of the induced emf is such that any current it produces, if the clos ...
Quantum electrodynamics: one- and two-photon processes Contents December 19, 2005
... The force on a particle moving in an electric and magnetic field is given by Lorentz law. According to Ampère’s law the force on a piece of the parallel wire of length l if F = BIl/α. If in a wire of length l a charge q is moving with a velocity v than the current I = qv/l, so Il = qv and ...
... The force on a particle moving in an electric and magnetic field is given by Lorentz law. According to Ampère’s law the force on a piece of the parallel wire of length l if F = BIl/α. If in a wire of length l a charge q is moving with a velocity v than the current I = qv/l, so Il = qv and ...
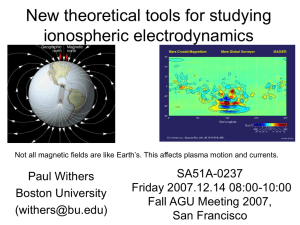
fallagu2007posterv02
... – Vertical transport important where transport timescales are shorter than photochemical timescales, F region and above – Freezing in of ions/electrons to magnetic fieldlines is controlled by ratio of gyrofrequency to collision frequency ...
... – Vertical transport important where transport timescales are shorter than photochemical timescales, F region and above – Freezing in of ions/electrons to magnetic fieldlines is controlled by ratio of gyrofrequency to collision frequency ...